Nearly Neutral Theory in Genome Age
... – About equal in the brain, heart, kidney, liver but three fold higher in the testes Brain: Ratio of the change of the human lineage to that of chimpanzee is larger than the same ratio in the liver or heart Khaitovich et al. 2006 ...
... – About equal in the brain, heart, kidney, liver but three fold higher in the testes Brain: Ratio of the change of the human lineage to that of chimpanzee is larger than the same ratio in the liver or heart Khaitovich et al. 2006 ...
Mutations that happen during Transcription and
... pass to separate cells during the first meiotic division ...
... pass to separate cells during the first meiotic division ...
Gene Expression, Inheritance Patterns, and DNA Technology
... located on an autosome Genetic Marker (short section of DNA known to have close association with a particular gene located nearby) Cystic Fibrosis (CF) and sickle cell anemia are single, recessive allele: only fully expressed when the individual has two copies of the recessive allele (homozygous ...
... located on an autosome Genetic Marker (short section of DNA known to have close association with a particular gene located nearby) Cystic Fibrosis (CF) and sickle cell anemia are single, recessive allele: only fully expressed when the individual has two copies of the recessive allele (homozygous ...
doc summer 2010 lecture 1 pg. 1-27
... Genetics is the study of genes at all levels from molecules to populations A gene is a functional region of the long DNA molecule composed of 4 nucleotides: A, G, T, C In replication, the 2 chains separate, and their exposed bases are used as templates for the synthesis of 2 identical daughter DNA m ...
... Genetics is the study of genes at all levels from molecules to populations A gene is a functional region of the long DNA molecule composed of 4 nucleotides: A, G, T, C In replication, the 2 chains separate, and their exposed bases are used as templates for the synthesis of 2 identical daughter DNA m ...
LE 3
... Special enzyme molecules read DNA instructions in cell nucleus. Special enzymes create a “messenger molecule”, RNA, to carry instructions to Ribosome. The RNA carries the instructions through the cytoplasm to the Ribosome. Transfer molecules gather up amino acids in cytoplasm and deliver them to Rib ...
... Special enzyme molecules read DNA instructions in cell nucleus. Special enzymes create a “messenger molecule”, RNA, to carry instructions to Ribosome. The RNA carries the instructions through the cytoplasm to the Ribosome. Transfer molecules gather up amino acids in cytoplasm and deliver them to Rib ...
The Universal Genetic Code - Willimon-PHS
... • Karyotype – photograph of arranged chromosomes from a cell • Patient karyotype compared to normal karyotype to determine presence of genetic diseases DNA fingerprinting – technique that creates a pattern of DNA fragments • Used to identify individual organisms or compare individuals • Procedure 1. ...
... • Karyotype – photograph of arranged chromosomes from a cell • Patient karyotype compared to normal karyotype to determine presence of genetic diseases DNA fingerprinting – technique that creates a pattern of DNA fragments • Used to identify individual organisms or compare individuals • Procedure 1. ...
Isolation of the plc1 gene from the fission yeast
... the X-region from several PLCs is shown as the single letter code - residues identical to those in the S.cerevisiae enzyme are indicated) was used to design two degenerate oligonucleotide primers that would be expected to amplify this region from S.pombe genomic DNA. A single PCRproduct was obtained ...
... the X-region from several PLCs is shown as the single letter code - residues identical to those in the S.cerevisiae enzyme are indicated) was used to design two degenerate oligonucleotide primers that would be expected to amplify this region from S.pombe genomic DNA. A single PCRproduct was obtained ...
Protein Synthesis Word Scramble
... notebook What does translate mean? Read message and create new message! mRNA to Protein! (the whole goal of PROTEIN synthesis!) ...
... notebook What does translate mean? Read message and create new message! mRNA to Protein! (the whole goal of PROTEIN synthesis!) ...
DNA PPT - McKinney ISD Staff Sites
... • Humans have 20,000-25,000 genes. • Only about 2% of our DNA is genes – The noncoding regions function to provide chromosomal structural integrity and to regulate where, when, and in what quantity proteins are made. ...
... • Humans have 20,000-25,000 genes. • Only about 2% of our DNA is genes – The noncoding regions function to provide chromosomal structural integrity and to regulate where, when, and in what quantity proteins are made. ...
Logan Rayborns Biology CrosswordsM
... 3. dominance a form of intermediate inheritance in which one allele for a specific trait is not completely expressed over its paired allele. 4. assortment formation of random combinations of chromosomes in meiosis and of genes on different pairs of homologous chromosomes by the passage according to ...
... 3. dominance a form of intermediate inheritance in which one allele for a specific trait is not completely expressed over its paired allele. 4. assortment formation of random combinations of chromosomes in meiosis and of genes on different pairs of homologous chromosomes by the passage according to ...
File - Intermediate School Biology
... 4. (a) Shields the –ve DNA from the +ve proteins causing the DNA to clump. (b) Inactivates any enzymes not denatured.(c) removes cellular debris ( cell walls and membranes) (d) removes the protein associated with DNA. (e) DNA is insoluble in ice cold ethanol and comes out of solution 5. (i) DNA is i ...
... 4. (a) Shields the –ve DNA from the +ve proteins causing the DNA to clump. (b) Inactivates any enzymes not denatured.(c) removes cellular debris ( cell walls and membranes) (d) removes the protein associated with DNA. (e) DNA is insoluble in ice cold ethanol and comes out of solution 5. (i) DNA is i ...
Biotechnology
... nonchromosomal DNA molecules called plasmids. Plasmids usually contain between 5 and 100 genes. Plasmids are not essential for normal bacterial growth and bacteria may lose or gain them without harm Transposons (transposable elements or "jumping genes") are small pieces of DNA that encode enzymes th ...
... nonchromosomal DNA molecules called plasmids. Plasmids usually contain between 5 and 100 genes. Plasmids are not essential for normal bacterial growth and bacteria may lose or gain them without harm Transposons (transposable elements or "jumping genes") are small pieces of DNA that encode enzymes th ...
lecture 03b
... Long thin molecule: if as thick as spaghetti, a bacterial DNA molecule would stretch from here to Bono ...
... Long thin molecule: if as thick as spaghetti, a bacterial DNA molecule would stretch from here to Bono ...
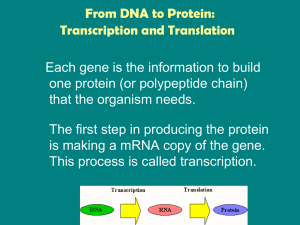
From DNA to Protein: Transcription and Translation
... The Process of Transcription The process of transcription is similar to DNA replication in that the DNA is unwound and complementary nucleotides are added. Differences: • Only a gene is copied, not the whole chromosome. • RNA nucleotides are added instead of DNA nucleotides. – Uracil is paired wit ...
... The Process of Transcription The process of transcription is similar to DNA replication in that the DNA is unwound and complementary nucleotides are added. Differences: • Only a gene is copied, not the whole chromosome. • RNA nucleotides are added instead of DNA nucleotides. – Uracil is paired wit ...
Section 1.3 Name:
... complementary base pair nucleotides until it reaches a region of DNA called the _______________ _______________. All __________ types of RNA are transcribed in this process. • Following transcription, the __________ moves through the pores of the nuclear membrane into the cytosol of the cell, where ...
... complementary base pair nucleotides until it reaches a region of DNA called the _______________ _______________. All __________ types of RNA are transcribed in this process. • Following transcription, the __________ moves through the pores of the nuclear membrane into the cytosol of the cell, where ...
Freeman 1e: How we got there
... • Genes carried by certain plasmids (such as the F plasmid) control conjugation, and the process involves transfer of the plasmid from a donor cell to a recipient cell (Figure 10.22). Plasmid DNA transfer involves replication via the rolling circle mechanism. ...
... • Genes carried by certain plasmids (such as the F plasmid) control conjugation, and the process involves transfer of the plasmid from a donor cell to a recipient cell (Figure 10.22). Plasmid DNA transfer involves replication via the rolling circle mechanism. ...
1) Definition of the gene
... A HOUSKEEPING GENE! The PDH gene, beta-subunit is active at the same time on EACH chromosome (maternal and paternal): this protein is made from the PDH gene on each chromosome. As a general rule, both copies of each gene in your DNA are active (unless one copy is defective). If you have one good cop ...
... A HOUSKEEPING GENE! The PDH gene, beta-subunit is active at the same time on EACH chromosome (maternal and paternal): this protein is made from the PDH gene on each chromosome. As a general rule, both copies of each gene in your DNA are active (unless one copy is defective). If you have one good cop ...
Genomics and Gene Recognition
... bacterial species to another • s can vary (less well conserved) Several variants often found in a cell The ability to use several different s factors allows a cell to turn on or off expression of whole sets of genes For example, s32 turns on gene expressions for genes associated with heat shoc ...
... bacterial species to another • s can vary (less well conserved) Several variants often found in a cell The ability to use several different s factors allows a cell to turn on or off expression of whole sets of genes For example, s32 turns on gene expressions for genes associated with heat shoc ...
What determines who we are?
... • Each chromosome is made up of DNA • A segment of DNA which controls a trait or body function is called a gene • When the information in genes is mixed up it is called mutation • Mutations may or may not change an individual for better or for worse ...
... • Each chromosome is made up of DNA • A segment of DNA which controls a trait or body function is called a gene • When the information in genes is mixed up it is called mutation • Mutations may or may not change an individual for better or for worse ...
Chapter 10
... • Untwists and replicates both strands simultaneously • Rapid process – Efficient – Builds in two directions ...
... • Untwists and replicates both strands simultaneously • Rapid process – Efficient – Builds in two directions ...
Transgenic Organisms
... Transgenic organisms contain genes from another species; possible because of the universal nature of the genetic code – Fig. 13-12 1. Microorganisms – easy to grow, divide rapidly, can be used to produce human proteins 2. Animals can be used to improve food supply, or to study effect of human disea ...
... Transgenic organisms contain genes from another species; possible because of the universal nature of the genetic code – Fig. 13-12 1. Microorganisms – easy to grow, divide rapidly, can be used to produce human proteins 2. Animals can be used to improve food supply, or to study effect of human disea ...
LEQ: How do we splice new genes into DNA?
... positive end; smaller pieces travel farther faster; DNA fragments are separated based on the size of the fragment (# of base pairs). ...
... positive end; smaller pieces travel farther faster; DNA fragments are separated based on the size of the fragment (# of base pairs). ...