Characteristics of Living Things (Essay
... Stages. What happens? When? Spermatogenesis & Oogenesis 2. DNA in different forms DNA basic structure. Remember nucleotides? Drawings? What is a gene? Centromere? Homologous Chromosomes 3. Mutations & Cancer & Aging Mutations: Good? Bad? Indifferent? Mutations: Caused by what? Cancer ...
... Stages. What happens? When? Spermatogenesis & Oogenesis 2. DNA in different forms DNA basic structure. Remember nucleotides? Drawings? What is a gene? Centromere? Homologous Chromosomes 3. Mutations & Cancer & Aging Mutations: Good? Bad? Indifferent? Mutations: Caused by what? Cancer ...
Guidelines and Assignments
... 1. (MT1) A. How is the 5-mC distributed within the human genome? B. Do all human genes have CpG island at their promoters? C. How bisulfite treatment may affect the CpG methylation status? D. What methods can be used to detect the methylation status of DNA? Please describe at least four different me ...
... 1. (MT1) A. How is the 5-mC distributed within the human genome? B. Do all human genes have CpG island at their promoters? C. How bisulfite treatment may affect the CpG methylation status? D. What methods can be used to detect the methylation status of DNA? Please describe at least four different me ...
File
... What is the result? • Recombinant DNA: DNA in which genes from two different sources, often different species, are combined in one organism ...
... What is the result? • Recombinant DNA: DNA in which genes from two different sources, often different species, are combined in one organism ...
What is Genetic Engineering?
... _______ gene from one creature into other creature’s DNA _______ new chromosome into organism organism _______ new gene as if it were its own organism _______ gene as if it were its own _____________________________________: Remember: we all use the same genetic code! ...
... _______ gene from one creature into other creature’s DNA _______ new chromosome into organism organism _______ new gene as if it were its own organism _______ gene as if it were its own _____________________________________: Remember: we all use the same genetic code! ...
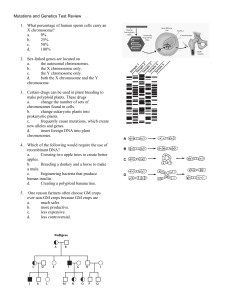
Mutations and Genetics Test Review 1. What percentage of human
... change the number of sets of chromosomes found in cells. b. change eukaryotic plants into prokaryotic plants. c. frequently cause mutations, which create new alleles and genes. d. insert foreign DNA into plant chromosomes. 4. Which of the following would require the use of recombinant DNA? a. Crossi ...
... change the number of sets of chromosomes found in cells. b. change eukaryotic plants into prokaryotic plants. c. frequently cause mutations, which create new alleles and genes. d. insert foreign DNA into plant chromosomes. 4. Which of the following would require the use of recombinant DNA? a. Crossi ...
Protein Synthesis - science4warriors
... amino acids into proteins from DNA to the rest of the cell • Ribosomal RNA (rRNA): makes up the major part of the ribosome • Transfer RNA (tRNA): transfers amino acids to ribosomes during protein ...
... amino acids into proteins from DNA to the rest of the cell • Ribosomal RNA (rRNA): makes up the major part of the ribosome • Transfer RNA (tRNA): transfers amino acids to ribosomes during protein ...
CP Biology
... d. all of these ______ 6) If the chromatid labeled C has a gene sequence that codes for normal hemoglobin, which of the following chromatids will USUALLY have the exact same gene sequence? a. A b. B c. D d. all of these 7. Is the homologous pair of chromosomes above in a dividing or non-dividing cel ...
... d. all of these ______ 6) If the chromatid labeled C has a gene sequence that codes for normal hemoglobin, which of the following chromatids will USUALLY have the exact same gene sequence? a. A b. B c. D d. all of these 7. Is the homologous pair of chromosomes above in a dividing or non-dividing cel ...
lec#18
... • Nonlethal: so cells can still multiply! • Genetic damage: mutations or non-mutational damages (epigenetic changes) • uncontrolled proliferation… not all genetic damages produce tumors, they only do so if they result in a crazy cell that can multiply continuously in an uncontrolled, uninhibited fas ...
... • Nonlethal: so cells can still multiply! • Genetic damage: mutations or non-mutational damages (epigenetic changes) • uncontrolled proliferation… not all genetic damages produce tumors, they only do so if they result in a crazy cell that can multiply continuously in an uncontrolled, uninhibited fas ...
From Genes to Proteins
... • The building blocks of proteins are amino acids. • They have many different functions. They can be enzymes, hormones, or any of a number of substances your body needs. • Ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis. ...
... • The building blocks of proteins are amino acids. • They have many different functions. They can be enzymes, hormones, or any of a number of substances your body needs. • Ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis. ...
Father of Modern Genetics
... Protein Synthesis: Translation mRNA carries a series of codons that code for specific amino acids A codon is a sequence of three nucleotide bases on mRNA Since there are only four RNA bases and there are three in each codon, there are 64 condon ...
... Protein Synthesis: Translation mRNA carries a series of codons that code for specific amino acids A codon is a sequence of three nucleotide bases on mRNA Since there are only four RNA bases and there are three in each codon, there are 64 condon ...
Norwich_Cyle
... The first two genes were not in the final set because their p-values were not small enough. Therefore these genes did not fluctuate as much as I thought they would ...
... The first two genes were not in the final set because their p-values were not small enough. Therefore these genes did not fluctuate as much as I thought they would ...
Topic 4.4 genetic engineering
... involving plasmids, a host cell ( bacterium, yeast or other cell), restriction enzymes and DNA ligase. [ The use of E. coli in gene technology is well documented. Most of its DNA is in one circular chromosome, but it also has plasmids ( smaller circles of DNA). These plasmids can be removed and clea ...
... involving plasmids, a host cell ( bacterium, yeast or other cell), restriction enzymes and DNA ligase. [ The use of E. coli in gene technology is well documented. Most of its DNA is in one circular chromosome, but it also has plasmids ( smaller circles of DNA). These plasmids can be removed and clea ...
CAP5510 - Bioinformatics - UF CISE
... http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Education/BLASTinfo/milestones.html ...
... http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Education/BLASTinfo/milestones.html ...
DNA_Technology_part2
... • The plasmids must be reintroduced into the host cell e.g. bacteria • This process is called transformation. • The bacteria, plasmids and calcium are mixed together. • By altering the temperature the bacteria become permeable and the plasmid can pass through the cell membrane. ...
... • The plasmids must be reintroduced into the host cell e.g. bacteria • This process is called transformation. • The bacteria, plasmids and calcium are mixed together. • By altering the temperature the bacteria become permeable and the plasmid can pass through the cell membrane. ...
The genetic engineers toolkit
... • A lot of DNA consists of long stretches of repeated nucleotides . • These vary between individuals and can be separated using gel electrophoresis. • Dna profiling usually uses about 10 STR’s ...
... • A lot of DNA consists of long stretches of repeated nucleotides . • These vary between individuals and can be separated using gel electrophoresis. • Dna profiling usually uses about 10 STR’s ...
Apr. 5 Presentation Mutagenesis Methods
... Transposon: a piece of short DNA that replicates by inserting into other pieces of DNA (plasmids, chromosomes, etc…) Useful for studying gene function because when the transposon moves into different location in the DNA it may cause a disruption in a gene or a set of genes. Transposons also have man ...
... Transposon: a piece of short DNA that replicates by inserting into other pieces of DNA (plasmids, chromosomes, etc…) Useful for studying gene function because when the transposon moves into different location in the DNA it may cause a disruption in a gene or a set of genes. Transposons also have man ...
Self Assessment
... DIRECTIONS: Write the letter of the BEST ANSWER beside each number of each the question. 1. Genes for medically important proteins can be cloned and inserted into bacteria, as shown in the diagram on the right. Why can bacteria recognize a human gene and then produce a human protein? A. DNA replicat ...
... DIRECTIONS: Write the letter of the BEST ANSWER beside each number of each the question. 1. Genes for medically important proteins can be cloned and inserted into bacteria, as shown in the diagram on the right. Why can bacteria recognize a human gene and then produce a human protein? A. DNA replicat ...
DNA Replication Pre
... B. The number of subunits in a DNA molecule C. The sequence of subunits in a protein molecule D. The number of subunits in a protein molecule 4. Humans, butterflies, and trees are all living things. In which of these organisms would you find DNA molecules? A. Only in humans B. Only in humans a ...
... B. The number of subunits in a DNA molecule C. The sequence of subunits in a protein molecule D. The number of subunits in a protein molecule 4. Humans, butterflies, and trees are all living things. In which of these organisms would you find DNA molecules? A. Only in humans B. Only in humans a ...
The Major Transitions in Evolution
... • Occasionally the mutant reverts phenotypically during somatic development, correlating with demethylation of Lcyc and restoration of gene expression. • It is surprising that the first natural morphological mutant to be characterized should trace to methylation, given the rarity of this mutational ...
... • Occasionally the mutant reverts phenotypically during somatic development, correlating with demethylation of Lcyc and restoration of gene expression. • It is surprising that the first natural morphological mutant to be characterized should trace to methylation, given the rarity of this mutational ...
iGEM Goals Past & Future
... acetate does not contain any cyanide. Nevertheless, it is legally considered an artificial flavor and sells at a much lower price. Feb 2005 the FDA issued an unprecedented warning to the cosmetics industry stating that the Agency is serious about enforcing the law requiring companies to inform consu ...
... acetate does not contain any cyanide. Nevertheless, it is legally considered an artificial flavor and sells at a much lower price. Feb 2005 the FDA issued an unprecedented warning to the cosmetics industry stating that the Agency is serious about enforcing the law requiring companies to inform consu ...
Biology and Society, Exam II
... D) They can develop into any different type of cell in the body. 48. Reproductive cloning is different than therapeutic in that reproductive cloning A) Uses eggs. B) Uses fertilized embryos. C) Can produce an embryo with stem cells. D) Produces fully-developed organisms. 49. True/False: During thera ...
... D) They can develop into any different type of cell in the body. 48. Reproductive cloning is different than therapeutic in that reproductive cloning A) Uses eggs. B) Uses fertilized embryos. C) Can produce an embryo with stem cells. D) Produces fully-developed organisms. 49. True/False: During thera ...