Ghost in Your Genes Response
... 4. The epigenome ______________ gene expression. 5. How are identical twins evidence that the environment affects the organism’s epigenome? ...
... 4. The epigenome ______________ gene expression. 5. How are identical twins evidence that the environment affects the organism’s epigenome? ...
RC 2 Student Notes
... A gene is a segment of DNA; carries instructions for expression of traits (eye color, hair color, etc.) A pair of inherited genes controls a trait One member of the inherited pair of genes comes from each parent, often called alleles. Alleles are represented as letters: B b T t The alleles are the r ...
... A gene is a segment of DNA; carries instructions for expression of traits (eye color, hair color, etc.) A pair of inherited genes controls a trait One member of the inherited pair of genes comes from each parent, often called alleles. Alleles are represented as letters: B b T t The alleles are the r ...
Information flow within the cell
... ….so that you do not tangle it up and are able to separate p it every y time the cell divides? …and so that each part of it can be accessed for transcription? ...
... ….so that you do not tangle it up and are able to separate p it every y time the cell divides? …and so that each part of it can be accessed for transcription? ...
Bio1100Ch19W
... • are temporarily displaced by polymerases during transcription and replication ...
... • are temporarily displaced by polymerases during transcription and replication ...
Genetic Technology
... genotype individual would you need to perform a test cross with to determine your genotype? Draw a punnett square and determine what ratio of genotypes your offspring would have. If you did not have any blonde hair children, what does that mean your genotype must be? ...
... genotype individual would you need to perform a test cross with to determine your genotype? Draw a punnett square and determine what ratio of genotypes your offspring would have. If you did not have any blonde hair children, what does that mean your genotype must be? ...
Transgenic organisms - Ken Pitts` Biological Science Page
... 5) Patients die every year for lack of a replacement heart, liver, or kidney. For example, about 5,000 organs are needed each year in the United Kingdom alone.25 Transgenic pigs may provide the transplant organs needed to alleviate the shortfall.9 Currently, xenotransplantation is hampered by a pig ...
... 5) Patients die every year for lack of a replacement heart, liver, or kidney. For example, about 5,000 organs are needed each year in the United Kingdom alone.25 Transgenic pigs may provide the transplant organs needed to alleviate the shortfall.9 Currently, xenotransplantation is hampered by a pig ...
The Origins of Variation
... the translocation of genetic material between endosymbionts and their hosts or by bacteriophage vectors e.g., mitochondria - endosymbiotic origin, evidence from cell membranes, gene structure, origin of replication, the fact that mitochondrial rRNAs are more similar to endosymbiotic bacterial (Ricke ...
... the translocation of genetic material between endosymbionts and their hosts or by bacteriophage vectors e.g., mitochondria - endosymbiotic origin, evidence from cell membranes, gene structure, origin of replication, the fact that mitochondrial rRNAs are more similar to endosymbiotic bacterial (Ricke ...
DNA
... molecule, FRET, …), but toxicity and dynamic range compromise detection. • Electrical detection offers advantages over fluorescence: fluorescence robust, simultaneous detection of multiple analytes, extreme sensistivity and improved dynamic range. • Silicon Nanotechnology offers exquisite, sub-nanom ...
... molecule, FRET, …), but toxicity and dynamic range compromise detection. • Electrical detection offers advantages over fluorescence: fluorescence robust, simultaneous detection of multiple analytes, extreme sensistivity and improved dynamic range. • Silicon Nanotechnology offers exquisite, sub-nanom ...
document
... enhanced their observations. The Fly Room was the source of some of the most important research in the history of biology. Morgan and his students eventually elucidated many basic principles of heredity. ...
... enhanced their observations. The Fly Room was the source of some of the most important research in the history of biology. Morgan and his students eventually elucidated many basic principles of heredity. ...
Basic Principles of Genetics: Printable Crossword Puzzle
... 2. Mendel's principle of genetic inheritance stating that, for any particular trait, the pair of genes of each parent separate and only one gene from each parent passes on to an offspring. 5. Mendel's principle of genetic inheritance stating that different pairs of genes are passed to offspring inde ...
... 2. Mendel's principle of genetic inheritance stating that, for any particular trait, the pair of genes of each parent separate and only one gene from each parent passes on to an offspring. 5. Mendel's principle of genetic inheritance stating that different pairs of genes are passed to offspring inde ...
Glossary AV 121017
... A polymorphic DNA segment at a known chromosomal location. All exons from a genome together The most likely order of DNA segments on the chromosome based on analysis of co-segregation of DNA markers in pedigrees. The analysis of several hundreds of DNA markers (usually micro-satellites) which are mo ...
... A polymorphic DNA segment at a known chromosomal location. All exons from a genome together The most likely order of DNA segments on the chromosome based on analysis of co-segregation of DNA markers in pedigrees. The analysis of several hundreds of DNA markers (usually micro-satellites) which are mo ...
Citrus Breeding - Udayana University Official Website
... • Isolate cell protoplasts from callus or leaf tissue and fuse in vitro to form hybrids • Mostly polyploid plants regenerated from tissue culture- genetic hybrids • Overcome barriers to sexual reproduction ...
... • Isolate cell protoplasts from callus or leaf tissue and fuse in vitro to form hybrids • Mostly polyploid plants regenerated from tissue culture- genetic hybrids • Overcome barriers to sexual reproduction ...
Genetics Unit Study guide
... How many cells are produced as a result of mitosis? How many chromosomes are in each new cell as compared to the parent cell? What is the purpose of meiosis? What are the phases of meiosis? What happens during each phase? How many cells are produced as a result of meiosis? How may chromosomes are i ...
... How many cells are produced as a result of mitosis? How many chromosomes are in each new cell as compared to the parent cell? What is the purpose of meiosis? What are the phases of meiosis? What happens during each phase? How many cells are produced as a result of meiosis? How may chromosomes are i ...
Nedmolecularbio1of32013 40 KB
... Genomes: The genetic material of the whole organism **In bacteria or prokaryotes, genomes are ring-shaped (circular and coiled), and on average 20 Kbp. Extra DNA can be taken on by the bacterium (transformed) in the form of small plasmid rings and can be beneficial to the bacterium. **In animals and ...
... Genomes: The genetic material of the whole organism **In bacteria or prokaryotes, genomes are ring-shaped (circular and coiled), and on average 20 Kbp. Extra DNA can be taken on by the bacterium (transformed) in the form of small plasmid rings and can be beneficial to the bacterium. **In animals and ...
DNA, RNA and Protein
... DNA Secondary Structure The Double Helix • Two polynucleotide chains are wound together • Bases are located inside the helix • Sugar-phosphate groups are on the outside as a “backbone” • Bases are arranged like rungs on a ladder, perpendicular to the “backbone” • 10 base pairs per turn of the helix ...
... DNA Secondary Structure The Double Helix • Two polynucleotide chains are wound together • Bases are located inside the helix • Sugar-phosphate groups are on the outside as a “backbone” • Bases are arranged like rungs on a ladder, perpendicular to the “backbone” • 10 base pairs per turn of the helix ...
Biotechnology Techniques - Mercer Island School District
... Biotechnology Techniques Recombinant DNA: DNA made by connecting DNA from two different sources. ...
... Biotechnology Techniques Recombinant DNA: DNA made by connecting DNA from two different sources. ...
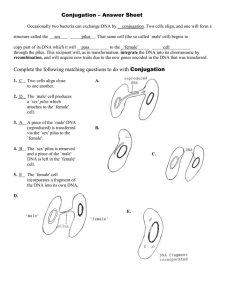
Conjugation Answer Sheet
... Conjugation – Answer Sheet Occasionally two bacteria can exchange DNA by structure called the ...
... Conjugation – Answer Sheet Occasionally two bacteria can exchange DNA by structure called the ...
BI0 10-3 P0WERPOINT
... • Those who plant genetically modified roses may find that these roses become too hardy and that the gardeners are unable to get rid of them using herbicides. This problem is an example of the unpredictable nature of genetically modifying plants and other organisms. Scientists do not always fully un ...
... • Those who plant genetically modified roses may find that these roses become too hardy and that the gardeners are unable to get rid of them using herbicides. This problem is an example of the unpredictable nature of genetically modifying plants and other organisms. Scientists do not always fully un ...
Molecular Genetics Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice
... b. fusion into circular forms known as e. fusion with other newly transcribed plasmids. mRNA. c. linkage to histone molecules. All of the following are directly involved in translation except a. mRNA. b. tRNA. c. ribosomes. d. DNA. The genetic code is essentially the same for all organisms. From thi ...
... b. fusion into circular forms known as e. fusion with other newly transcribed plasmids. mRNA. c. linkage to histone molecules. All of the following are directly involved in translation except a. mRNA. b. tRNA. c. ribosomes. d. DNA. The genetic code is essentially the same for all organisms. From thi ...
Protein Synthesis 1 - Transcription Translation
... 4) First, the DNA (genetic code) gets transcribed into mRNA. 5) Why do we need to make a coded copy of DNA? __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ ...
... 4) First, the DNA (genetic code) gets transcribed into mRNA. 5) Why do we need to make a coded copy of DNA? __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ ...