CT1 - hullrad
... Consider cylindrical uniform body with a hole down the centre A beam passing through this body from one direction will have a transmitted profile in its central region This single measurement cannot determine the position of the hole other than identifying that it is in the line of the pencil beam p ...
... Consider cylindrical uniform body with a hole down the centre A beam passing through this body from one direction will have a transmitted profile in its central region This single measurement cannot determine the position of the hole other than identifying that it is in the line of the pencil beam p ...
Low cost digital detector technology for emerging economies
... • Cheaper film-screen and CR systems are being increasingly sold to developing nations and to hospitals in underserved populations • Both technologies do not provide the many benefits of digital and can be leapfrogged • However, digital is expensive making the cost-benefit argument relevant only ...
... • Cheaper film-screen and CR systems are being increasingly sold to developing nations and to hospitals in underserved populations • Both technologies do not provide the many benefits of digital and can be leapfrogged • However, digital is expensive making the cost-benefit argument relevant only ...
ACR Practice Parameter For The Performance Of
... tubes, and peritoneal cavity during injection of contrast media with fluoroscopic visualization. It should be done with the minimum radiation exposure necessary to provide sufficient anatomic detail for diagnosis of normal or abnormal findings. Adherence to the following practice parameters will max ...
... tubes, and peritoneal cavity during injection of contrast media with fluoroscopic visualization. It should be done with the minimum radiation exposure necessary to provide sufficient anatomic detail for diagnosis of normal or abnormal findings. Adherence to the following practice parameters will max ...
diabetes - NC State University
... 2. Differentiate between particulate and electromagnetic (non-particulate) forms of radiation (3.1.2) 3. Differentiate between the sites of origin of gamma rays and x-rays (3.1.3) 4. Know the basic forms of particulate radiations and their interactions or potential interactions with matter, includin ...
... 2. Differentiate between particulate and electromagnetic (non-particulate) forms of radiation (3.1.2) 3. Differentiate between the sites of origin of gamma rays and x-rays (3.1.3) 4. Know the basic forms of particulate radiations and their interactions or potential interactions with matter, includin ...
The History of X-Rays and Their Use in Diagnostic Medicine
... of the British public at the time.[5] Bizarre claims began to crop up, including the idea that they were the “philosopher's stone” and could turn metal into gold.[5] One enterprising company in London took advantage of the public's fear that the discovery would aid Peeping Toms and produced “X-Ray P ...
... of the British public at the time.[5] Bizarre claims began to crop up, including the idea that they were the “philosopher's stone” and could turn metal into gold.[5] One enterprising company in London took advantage of the public's fear that the discovery would aid Peeping Toms and produced “X-Ray P ...
Radiation Safety and Physics
... In digital mammography the x-ray photons strike a digital detector that converts absorbed energy into an electronic signal. A charge coupled device (CCD) is an integrated circuit containing an array of linked, or coupled, capacitors. The pixels in the CCD collect the electrons as they are created. T ...
... In digital mammography the x-ray photons strike a digital detector that converts absorbed energy into an electronic signal. A charge coupled device (CCD) is an integrated circuit containing an array of linked, or coupled, capacitors. The pixels in the CCD collect the electrons as they are created. T ...
Slice Wars vs Dose Wars in Multiple
... force behind the slice wars. However, the increasing number of slices and the increasing complexity in the performance of cardiac CT imaging has led to the development of protocols that can yield high radiation dose (expressed in terms of “effective dose”). In general, the demand for shorter scan ti ...
... force behind the slice wars. However, the increasing number of slices and the increasing complexity in the performance of cardiac CT imaging has led to the development of protocols that can yield high radiation dose (expressed in terms of “effective dose”). In general, the demand for shorter scan ti ...
syngo Workplaces
... clinical outcomes and greater financial success. The success of this philosophy is easily recognized with over 7,000 satisfied and knowledgeable customers worldwide. We are now continuing this unparalleled success story in an increasingly competitive and rapidly changing healthcare market. While pat ...
... clinical outcomes and greater financial success. The success of this philosophy is easily recognized with over 7,000 satisfied and knowledgeable customers worldwide. We are now continuing this unparalleled success story in an increasingly competitive and rapidly changing healthcare market. While pat ...
Attenuation
... Interaction of xrays by absorption and scatter is called attenuation. In this example, the x-ray beam ...
... Interaction of xrays by absorption and scatter is called attenuation. In this example, the x-ray beam ...
X-ray imaging: Fundamentals and planar imaging - English
... X-rays. The Bremsstrahlung originates from the sudden deacceleration and direction changes of the primary electrons in the field of the anode atoms, the characteristics X-rays originates from the knockout and subsequent level filling of inner electrons in the atoms of the anode material. The highest ...
... X-rays. The Bremsstrahlung originates from the sudden deacceleration and direction changes of the primary electrons in the field of the anode atoms, the characteristics X-rays originates from the knockout and subsequent level filling of inner electrons in the atoms of the anode material. The highest ...
Feasibility Study of Dual Energy Radiographic Imaging for Target
... types or tissue-selection for generating high contrast images of targeted structures, which can be applied to improve tumor detection for diagnostic interpretation. Planar kilovoltage (kV) imaging plays an important role in image guidance in radiation therapy (RT) systems, such as CyberKnife (Accura ...
... types or tissue-selection for generating high contrast images of targeted structures, which can be applied to improve tumor detection for diagnostic interpretation. Planar kilovoltage (kV) imaging plays an important role in image guidance in radiation therapy (RT) systems, such as CyberKnife (Accura ...
Dual Energy Imaging : Clinical applications for musculoskeletal
... The dual-energy CT scanner has no increased radiation dose compared to a singleenergy CT scanner at 120kVp. How to reduce beam hardening? CT plays a key role in evaluating orthopedic implants after surgery due to its high spatial resolution and 3D reconstruction. Metal hardware causes beam-hardening ...
... The dual-energy CT scanner has no increased radiation dose compared to a singleenergy CT scanner at 120kVp. How to reduce beam hardening? CT plays a key role in evaluating orthopedic implants after surgery due to its high spatial resolution and 3D reconstruction. Metal hardware causes beam-hardening ...
Intervention Conceptual example of the “fusion map”
... Position patient as close as possible to image receptor Maximize distance from x-ray tube to patient Use collimation to minimize irradiated area Lowest acceptable magnification, fluoroscopy dose rate Lowest acceptable cine, DSA dose and pulse rates Limit fluoroscopy to real time imaging guidance Las ...
... Position patient as close as possible to image receptor Maximize distance from x-ray tube to patient Use collimation to minimize irradiated area Lowest acceptable magnification, fluoroscopy dose rate Lowest acceptable cine, DSA dose and pulse rates Limit fluoroscopy to real time imaging guidance Las ...
Paediatric Dose and Image quality
... patient in an attempt to reduce scattered radiation artefacts. • The diagnostic image was assessed Qualitatively by a Radiologist and the effect of noise was assessed Quantitatively by one of the team. • Both forms of analysis determined there to be no difference between shielded and non-shielded im ...
... patient in an attempt to reduce scattered radiation artefacts. • The diagnostic image was assessed Qualitatively by a Radiologist and the effect of noise was assessed Quantitatively by one of the team. • Both forms of analysis determined there to be no difference between shielded and non-shielded im ...
master`s programme in medical physics
... with the basic knowledge needed to embark on a career in the regulatory, industry, metrology, research and development or innovation through research sectors, for instance. The major outcome of the academ ...
... with the basic knowledge needed to embark on a career in the regulatory, industry, metrology, research and development or innovation through research sectors, for instance. The major outcome of the academ ...
DRAFT TEMPLATE - American College of Radiology
... provide a benchmark for comparison, not to define a maximum or minimum dose limit. II. ...
... provide a benchmark for comparison, not to define a maximum or minimum dose limit. II. ...
Topic 2 X-rays and ECGs
... British border guards in Calais have been banned from using X-rays to search for illegal immigrants in lorries - unless they ask for the stowaways' written permission. French authorities have blocked the use of the scanners, claiming they could breach European health and safety laws. ...
... British border guards in Calais have been banned from using X-rays to search for illegal immigrants in lorries - unless they ask for the stowaways' written permission. French authorities have blocked the use of the scanners, claiming they could breach European health and safety laws. ...
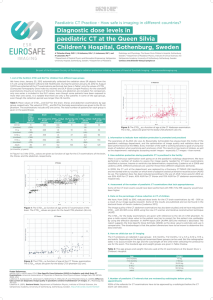
Diagnostic dose levels in paediatric CT at the
... levels of radiation when examining each and every child. This results in low levels of retakes, as well as the department’s radiologists accepting nosier images – especially CT images - than normal. 3. How radiation protection during paediatric CT is practised in the facility There is continuous opt ...
... levels of radiation when examining each and every child. This results in low levels of retakes, as well as the department’s radiologists accepting nosier images – especially CT images - than normal. 3. How radiation protection during paediatric CT is practised in the facility There is continuous opt ...
Image Management and Communications Technology
... Medical imaging technologies can be categorised according to their temporal resolution, with all of the above techniques essentially providing static images. In contrast, dynamic images are provided by ultrasound (US) where a continuously transmitting and receiving probe (transceiver) provides conti ...
... Medical imaging technologies can be categorised according to their temporal resolution, with all of the above techniques essentially providing static images. In contrast, dynamic images are provided by ultrasound (US) where a continuously transmitting and receiving probe (transceiver) provides conti ...
Chapter 7 Body Systems
... The typical sensor is more sensitive to xrays than conventional film. ...
... The typical sensor is more sensitive to xrays than conventional film. ...
Imaging Physics Recommendations for Routine Testing and Quality
... Daily testing is not required unless a specific imaging quality problem has arisen. Use a phantom which can monitor detail/contrast as a minimum for tracking image quality. ...
... Daily testing is not required unless a specific imaging quality problem has arisen. Use a phantom which can monitor detail/contrast as a minimum for tracking image quality. ...
dicom, hl7, ris, pacs
... radiotherapy device (X‐ray, CT, MRI, ultrasound, etc.), and increasingly in devices in other medical domains such as ophthalmology and dentistry. With tens of thousands of imaging devices in use, DICOM is one of the most widely deployed healthcare messaging standards in the world. There are lite ...
... radiotherapy device (X‐ray, CT, MRI, ultrasound, etc.), and increasingly in devices in other medical domains such as ophthalmology and dentistry. With tens of thousands of imaging devices in use, DICOM is one of the most widely deployed healthcare messaging standards in the world. There are lite ...
Fluoroscopy

Fluoroscopy /flɔrˈɒskəpi/ is an imaging technique that uses X-rays to obtain real-time moving images of the interior of an object. In its primary application of medical imaging, a fluoroscope /ˈflɔrɵˌskoʊp/ allows a physician to see the internal structure and function of a patient, so that the pumping action of the heart or the motion of swallowing, for example, can be watched. This is useful for both diagnosis and therapy and occurs in general radiology, interventional radiology, and image-guided surgery. In its simplest form, a fluoroscope consists of an X-ray source and a fluorescent screen, between which a patient is placed. However, since the 1950s most fluoroscopes have included X-ray image intensifiers and cameras as well, to improve the image's visibility and make it available on a remote display screen. For many decades fluoroscopy tended to produce live pictures that were not recorded, but since the 1960s, as technology improved, recording and playback became the norm.Fluoroscopy is similar to radiography and X-ray computed tomography (X-ray CT) in that it generates images using X-rays. The original difference was that radiography fixed still images on film whereas fluoroscopy provided live moving pictures that were not stored. However, today radiography, CT, and fluoroscopy are all digital imaging modes with image analysis software and data storage and retrieval. The use of X-rays, a form of ionizing radiation, requires the potential risks from a procedure to be carefully balanced with the benefits of the procedure to the patient. Because the patient must be exposed to a continuous source of x-rays instead of a momentary pulse, a fluoroscopy procedure generally subjects a patient to a higher absorbed dose of radiation than an ordinary (still) radiograph. Much research has been directed toward reducing radiation exposure, and recent advances in fluoroscopy technology such as digital image processing and flat panel detectors, have resulted in much lower radiation doses than former procedures.The type of fluoroscopy used in airport security (to check for hidden weapons or bombs) uses lower doses of radiation than medical fluoroscopy. It was formerly also used in retail stores in the form of shoe-fitting fluoroscopes, but such use was discontinued because it is no longer considered acceptable to use radiation exposure, however small the dose, for nonessential purposes. Only important applications such as health care, bodily safety, food safety, nondestructive testing, and scientific research meet the risk-benefit threshold for use. The reason for higher doses in medical applications is that they are more demanding about tissue contrast, and for the same reason they sometimes require contrast media.