Chronic Inflammation
... aggregation of mononuclear inflammatory cells, or such a collection of modified macrophages resembling epithelial cells (epitheloid cells) usually surrounded by a rim of lymphocytes, often with multinucleated giant cells. Some granulomas contain eosinophils and plasma cells, and fibrosis is commonly ...
... aggregation of mononuclear inflammatory cells, or such a collection of modified macrophages resembling epithelial cells (epitheloid cells) usually surrounded by a rim of lymphocytes, often with multinucleated giant cells. Some granulomas contain eosinophils and plasma cells, and fibrosis is commonly ...
The elimination of bacteria and biofilms in periodontal disease via
... disease are dependent upon the presence of persistent bacterial plaque. ...
... disease are dependent upon the presence of persistent bacterial plaque. ...
Chronic inflammation
... • The best possible outcome following an inflammatory process is complete resolution, – leaving the tissues intact and undamaged. • However, chronic inflammation may occur in conjunction with some degree of scarring. • Here, chronic inflammation of the bronchi has led to dilation and scarringwith i ...
... • The best possible outcome following an inflammatory process is complete resolution, – leaving the tissues intact and undamaged. • However, chronic inflammation may occur in conjunction with some degree of scarring. • Here, chronic inflammation of the bronchi has led to dilation and scarringwith i ...
Chapter 18 Lecture Outline
... – Tissue hypoxia and necrosis • Patient is lethargic • Shortness of breath upon exertion • Life-threatening necrosis of brain, heart, or kidney ...
... – Tissue hypoxia and necrosis • Patient is lethargic • Shortness of breath upon exertion • Life-threatening necrosis of brain, heart, or kidney ...
Lymphatic system
... Blood pressure forces some of the blood plasma through the single-celled capillary walls Interstitial Fluid is in the spaces between cells Most is reabsorbed into the capillaries Some fluid is not and must be drained from the tissue spaces to prevent swelling or Edema. Lymphatic Capillaries – drain ...
... Blood pressure forces some of the blood plasma through the single-celled capillary walls Interstitial Fluid is in the spaces between cells Most is reabsorbed into the capillaries Some fluid is not and must be drained from the tissue spaces to prevent swelling or Edema. Lymphatic Capillaries – drain ...
Slide 1
... add antibodies to urine for particular drug add chemically labeled version of presumed drug competition between labeled and unlabeled amount of labeled drug left in test related to amount of original drug in sample • labeled drug left over means original drug combined with antibodies and was removed ...
... add antibodies to urine for particular drug add chemically labeled version of presumed drug competition between labeled and unlabeled amount of labeled drug left in test related to amount of original drug in sample • labeled drug left over means original drug combined with antibodies and was removed ...
Research on Orgono Silica
... Anti-inflamatory Action The anti-inflammatory and soothing action of monomethylsilanetriol has also been proved in several experiments. In vivo studies proved that Orgono Silica protects against cell infiltration and inflammation. In vitro studies showed a decrease in interleukins production. Anothe ...
... Anti-inflamatory Action The anti-inflammatory and soothing action of monomethylsilanetriol has also been proved in several experiments. In vivo studies proved that Orgono Silica protects against cell infiltration and inflammation. In vitro studies showed a decrease in interleukins production. Anothe ...
Hematopoietic Function Hematopoietic Function
... The blood-forming population of bone marrow is made up of three types of cells: self-renewing stem cells, differentiated progenitor (parent) cells, and functional mature blood cells. All of the blood cell precursors of the erythrocyte (i.e., red cell), myelocyte (i.e., granulocyte or monocyte), lymp ...
... The blood-forming population of bone marrow is made up of three types of cells: self-renewing stem cells, differentiated progenitor (parent) cells, and functional mature blood cells. All of the blood cell precursors of the erythrocyte (i.e., red cell), myelocyte (i.e., granulocyte or monocyte), lymp ...
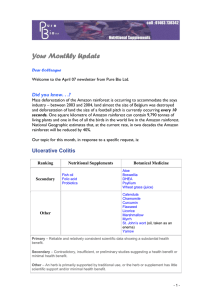
Ulcerative Colitis
... problems, including arthritis, eye infections, liver disease, skin rashes, blood clots, or gallstones. Although it is not clear why such problems occur outside the colon, some researchers speculate that they may be linked to a faulty immune response. ...
... problems, including arthritis, eye infections, liver disease, skin rashes, blood clots, or gallstones. Although it is not clear why such problems occur outside the colon, some researchers speculate that they may be linked to a faulty immune response. ...
Pulmonary Hypertension
... • 3 year girl with hypoplastic left heart syndrome (mitral and aortic valve atresia) • Followed closely by PMD, GI and myself since ...
... • 3 year girl with hypoplastic left heart syndrome (mitral and aortic valve atresia) • Followed closely by PMD, GI and myself since ...
Aromatherapy and the Immune System
... percent of all lymphocytes. Once a also involved in the fight against they find the invader, they can use stem cell produces a descendant, the parasites. these enzymes to drill holes on its shell stromal cells of the bone marrow causing its insides to pour out. decide whether this cell will become a ...
... percent of all lymphocytes. Once a also involved in the fight against they find the invader, they can use stem cell produces a descendant, the parasites. these enzymes to drill holes on its shell stromal cells of the bone marrow causing its insides to pour out. decide whether this cell will become a ...
Blood group change in acute myeloid leukemia
... Corresponding author: Geetha Narayanan, MD, DM, Professor and Head, Department of Medical Oncology, Regional Cancer Centre, Trivandrum 695011, ...
... Corresponding author: Geetha Narayanan, MD, DM, Professor and Head, Department of Medical Oncology, Regional Cancer Centre, Trivandrum 695011, ...
canine dentistry - Cottage Animal Hospital
... kidney and liver function are satisfactory for anesthesia. Sometimes antibiotic treatment is instituted before a full dental prophylaxis is carried out. Your veterinarian will discuss the specific pre-dental recommendations for your pet. Tooth scaling will be performed using both hand scalers and ul ...
... kidney and liver function are satisfactory for anesthesia. Sometimes antibiotic treatment is instituted before a full dental prophylaxis is carried out. Your veterinarian will discuss the specific pre-dental recommendations for your pet. Tooth scaling will be performed using both hand scalers and ul ...
Dentistry - Liles Animal Clinic
... kidney and liver function are satisfactory for anesthesia. Sometimes antibiotic treatment is instituted before a full dental prophylaxis is carried out. Your veterinarian will discuss the specific pre-dental recommendations for your pet. Tooth scaling will be performed using both hand scalers and ul ...
... kidney and liver function are satisfactory for anesthesia. Sometimes antibiotic treatment is instituted before a full dental prophylaxis is carried out. Your veterinarian will discuss the specific pre-dental recommendations for your pet. Tooth scaling will be performed using both hand scalers and ul ...
Post-Test Questions (PDF: 89KB/2 pages)
... 2. Which of the following are risk factors for the development of asymptomatic bacteriuria in long-term care residents? Answer: e a. Increased age b. Increased number of diagnoses c. Decreased ability to perform activities of daily living d. Indwelling urinary catheter e. All of the above 3. Is the ...
... 2. Which of the following are risk factors for the development of asymptomatic bacteriuria in long-term care residents? Answer: e a. Increased age b. Increased number of diagnoses c. Decreased ability to perform activities of daily living d. Indwelling urinary catheter e. All of the above 3. Is the ...
What Is Halitosis? Halitosis is the medical term for bad breath. It is
... surrounding the teeth. Combinations of these problems are the number one causes of strong bad breathe in your pet, drooling and discomfort. It is also suspected that dental disease be a primary cause of kidney and heart disease in older pets. This may be because the bacteria that live in the infecte ...
... surrounding the teeth. Combinations of these problems are the number one causes of strong bad breathe in your pet, drooling and discomfort. It is also suspected that dental disease be a primary cause of kidney and heart disease in older pets. This may be because the bacteria that live in the infecte ...
HG: Care of Patient with a Tunneled Central Venous Catheter of Implanted Port Hickman,Groshong)
... excessive PSI and possible rupture of catheter or dislodgement of clot. Blood may be drawn from central VADs by individuals with specialized training. a. On general care units (exception Oncology and Pediatrics) central line blood sampling should be performed by the VAT whenever possible. Blood cult ...
... excessive PSI and possible rupture of catheter or dislodgement of clot. Blood may be drawn from central VADs by individuals with specialized training. a. On general care units (exception Oncology and Pediatrics) central line blood sampling should be performed by the VAT whenever possible. Blood cult ...
Lymphatic System
... conditions required for proliferation of B lymphocytes can be met, and at intervals there will be germinal centers along it. ...
... conditions required for proliferation of B lymphocytes can be met, and at intervals there will be germinal centers along it. ...
What`s Your Type?
... system. It has long been recognized that some foods are capable of causing the cells of a certain blood type to agglutinate while having no impact on cells of another blood type. This reaction is dependent upon the interaction of human cells with the lectins found in food. ...
... system. It has long been recognized that some foods are capable of causing the cells of a certain blood type to agglutinate while having no impact on cells of another blood type. This reaction is dependent upon the interaction of human cells with the lectins found in food. ...
/2 0573 24 P2 :44 SEP 241997
... effects of cholesterol by inhibiting cholesterol deposits from forming in the elastin tissue of vascular walls. Masquelier’sw OPC strengthens the collagen against destructive enzymes and neutralizes free radicals, thus inhibiting LDL oxidation and plaque formation. Section 403(r)(6) of the act makes ...
... effects of cholesterol by inhibiting cholesterol deposits from forming in the elastin tissue of vascular walls. Masquelier’sw OPC strengthens the collagen against destructive enzymes and neutralizes free radicals, thus inhibiting LDL oxidation and plaque formation. Section 403(r)(6) of the act makes ...
Ch 12- Forensic Serology - Bio-Guru
... Usually when the immune system produces antibodies, they are a mixture of immunoglobulin molecules designed to recognize and bind to many different sites on an antigen molecule or different epitopes. In other words, they are made against a specific antigen, but each recognizing a different epitope o ...
... Usually when the immune system produces antibodies, they are a mixture of immunoglobulin molecules designed to recognize and bind to many different sites on an antigen molecule or different epitopes. In other words, they are made against a specific antigen, but each recognizing a different epitope o ...
Phytosterols and cardiovascular health
... The PS side chain is responsible for the selective secretion of sitosterol and other PS from the enterocyte into the intestinal lumen, mediated by the adenosine triphosphate (ATP) binding cassette (ABC) transporters ABCG5 and ABCG8 [7]. Recent findings suggest that ABCG5 and ABCG8 play a role also in ...
... The PS side chain is responsible for the selective secretion of sitosterol and other PS from the enterocyte into the intestinal lumen, mediated by the adenosine triphosphate (ATP) binding cassette (ABC) transporters ABCG5 and ABCG8 [7]. Recent findings suggest that ABCG5 and ABCG8 play a role also in ...
Forensic Serology - Bio-Guru
... Usually when the immune system produces antibodies, they are a mixture of immunoglobulin molecules designed to recognize and bind to many different sites on an antigen molecule or different epitopes. In other words, they are made against a specific antigen, but each recognizing a different epitope o ...
... Usually when the immune system produces antibodies, they are a mixture of immunoglobulin molecules designed to recognize and bind to many different sites on an antigen molecule or different epitopes. In other words, they are made against a specific antigen, but each recognizing a different epitope o ...
DIVERTICULITIS
... • Avoid Colonoscopy, Barium enema • Symptoms Should Resolve <48 Hours • <25% Have Recurrent Attacks • 6% Recovered Patients Need Operation • Long-Term- High Fiber Diet ...
... • Avoid Colonoscopy, Barium enema • Symptoms Should Resolve <48 Hours • <25% Have Recurrent Attacks • 6% Recovered Patients Need Operation • Long-Term- High Fiber Diet ...
Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis (also known as arteriosclerotic vascular disease or ASVD) is a specific form of arteriosclerosis in which an artery wall thickens as a result of invasion and accumulation of white blood cells (WBCs) (foam cell) and proliferation of intimal smooth muscle cell creating a fibrofatty plaque.The accumulation of the WBCs is termed ""fatty streaks"" early on because of the appearance being similar to that of marbled steak. These accumulations contain both living, active WBCs (producing inflammation) and remnants of dead cells, including cholesterol and triglycerides. The remnants eventually include calcium and other crystallized materials within the outermost and oldest plaque. The ""fatty streaks"" reduce the elasticity of the artery walls. However, they do not affect blood flow for decades because the artery muscular wall enlarges at the locations of plaque. The wall stiffening may eventually increase pulse pressure; widened pulse pressure is one possible result of advanced disease within the major arteries.Atherosclerosis is therefore a syndrome affecting arterial blood vessels due to a chronic inflammatory response of WBCs in the walls of arteries. This is promoted by low-density lipoproteins (LDL, plasma proteins that carry cholesterol and triglycerides) without adequate removal of fats and cholesterol from the macrophages by functional high-density lipoproteins (HDL). It is commonly referred to as a ""hardening"" or furring of the arteries. It is caused by the formation of multiple atheromatous plaques within the arteries.The plaque is divided into three distinct components: The atheroma (""lump of gruel"", from Greek ἀθήρα (athera), meaning ""gruel""), which is the nodular accumulation of a soft, flaky, yellowish material at the center of large plaques, composed of macrophages nearest the lumen of the artery Underlying areas of cholesterol crystals Calcification at the outer base of older or more advanced lesions.Atherosclerosis is a chronic disease that remains asymptomatic for decades. Atherosclerotic lesions, or atherosclerotic plaques, are separated into two broad categories: Stable and unstable (also called vulnerable). The pathobiology of atherosclerotic lesions is very complicated, but generally, stable atherosclerotic plaques, which tend to be asymptomatic, are rich in extracellular matrix and smooth muscle cells. On the other hand, unstable plaques are rich in macrophages and foam cells, and the extracellular matrix separating the lesion from the arterial lumen (also known as the fibrous cap) is usually weak and prone to rupture. Ruptures of the fibrous cap expose thrombogenic material, such as collagen, to the circulation and eventually induce thrombus formation in the lumen. Upon formation, intraluminal thrombi can occlude arteries outright (e.g., coronary occlusion), but more often they detach, move into the circulation, and eventually occlude smaller downstream branches causing thromboembolism. Apart from thromboembolism, chronically expanding atherosclerotic lesions can cause complete closure of the lumen. Chronically expanding lesions are often asymptomatic until lumen stenosis is so severe (usually over 80%) that blood supply to downstream tissue(s) is insufficient, resulting in ischemia.These complications of advanced atherosclerosis are chronic, slowly progressive and cumulative. Most commonly, soft plaque suddenly ruptures (see vulnerable plaque), causing the formation of a thrombus that will rapidly slow or stop blood flow, leading to death of the tissues fed by the artery in approximately five minutes. This catastrophic event is called an infarction. One of the most common recognized scenarios is called coronary thrombosis of a coronary artery, causing myocardial infarction (a heart attack). The same process in an artery to the brain is commonly called stroke. Another common scenario in very advanced disease is claudication from insufficient blood supply to the legs. Atherosclerosis affects the entire artery tree, but mostly larger, high-pressure vessels such as the coronary, renal, femoral, cerebral, and carotid arteries. These are termed ""clinically silent"" because the person having the infarction does not notice the problem and does not seek medical help, or when they do, physicians do not recognize what has happened.