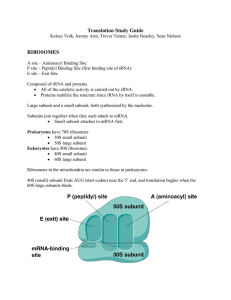
handout
... AUG start codon. 2. Next, the tRNA and small sub-unit complex bind to translation initiation factors and attach to the 5’ cap of the mature mRNA. 3. Next, the entire complex scans in the 3’ direction until it finds the AUG start codon of the mRNA 4. Lastly, the 60S large sub-unit binds to the comple ...
... AUG start codon. 2. Next, the tRNA and small sub-unit complex bind to translation initiation factors and attach to the 5’ cap of the mature mRNA. 3. Next, the entire complex scans in the 3’ direction until it finds the AUG start codon of the mRNA 4. Lastly, the 60S large sub-unit binds to the comple ...
Divergent Functional Properties of the Ribosome
... To determine the minimal sequences of Ssb1 required for its function, a series of C-terminal truncation mutants of Ssb1 were generated (Figure 1A). Truncation clones were transformed into a ⌬ssb strain and tested for their ability to rescue the phenotypes associated with the lack of Ssb function: co ...
... To determine the minimal sequences of Ssb1 required for its function, a series of C-terminal truncation mutants of Ssb1 were generated (Figure 1A). Truncation clones were transformed into a ⌬ssb strain and tested for their ability to rescue the phenotypes associated with the lack of Ssb function: co ...
Purine Biosynthesis. Big in Cell Division, Even
... plants has focused on its role in N assimilation. Because expression of some of the pur genes is significantly increased in nodules after N fixation begins (Smith et al., 1998), a question that has received substantial attention is whether the products of N assimilation are involved in regulating th ...
... plants has focused on its role in N assimilation. Because expression of some of the pur genes is significantly increased in nodules after N fixation begins (Smith et al., 1998), a question that has received substantial attention is whether the products of N assimilation are involved in regulating th ...
Brewing biochemistry
... describe metabolic processes in yeast, in particular those involved during the fermentation processes By the end of this activity, the student is able to manipulate yeasts and to conduct analyses which are essential to the processes of beer production. This means ...
... describe metabolic processes in yeast, in particular those involved during the fermentation processes By the end of this activity, the student is able to manipulate yeasts and to conduct analyses which are essential to the processes of beer production. This means ...
Regulation of Glycolysis - Valdosta State University
... Regulation of Metabolic Pathways • Systems must respond to conditions • Homeostasis is not equilibrium • Dynamic Steady State – Flux - Rate of metabolic flow of material through pathways • Many ways to regulate – for example – At the protein level (e.g. allosteric control) – At the gene level – At t ...
... Regulation of Metabolic Pathways • Systems must respond to conditions • Homeostasis is not equilibrium • Dynamic Steady State – Flux - Rate of metabolic flow of material through pathways • Many ways to regulate – for example – At the protein level (e.g. allosteric control) – At the gene level – At t ...
Heptad repeat sequences are located adjacent to hydrophobic
... paramyxovirus fusion and coronavirus peplomer glycoproteins are reasonably hydrophilic despite the regular pattern of hydrophobic amino acids in positions a and d, consistent with the formation of an extended structure (Cohen & Parry, 1986). The heptad regions of some retroviruses, for example human ...
... paramyxovirus fusion and coronavirus peplomer glycoproteins are reasonably hydrophilic despite the regular pattern of hydrophobic amino acids in positions a and d, consistent with the formation of an extended structure (Cohen & Parry, 1986). The heptad regions of some retroviruses, for example human ...
Hereditary Myopathy with Lactic Acidosis
... coded for the Fe-S cluster assembly protein ISCU and an intronic base pair substitution (g.7044G>C) was identified in the last intron of this gene. The mutation gave rise to the insertion of intron sequence into the mRNA, leading to a protein containing 15 abberant amino acids and a premature stop. ...
... coded for the Fe-S cluster assembly protein ISCU and an intronic base pair substitution (g.7044G>C) was identified in the last intron of this gene. The mutation gave rise to the insertion of intron sequence into the mRNA, leading to a protein containing 15 abberant amino acids and a premature stop. ...
Protein relative abundance patterns associated with sucrose
... to catalog the functional potential of all microbial genes within a smaller subset of subjects. One of the key findings was that healthy sites from different people were broadly similar with respect to their functional profiles, even though there was extensive individual variation in their taxonomic ...
... to catalog the functional potential of all microbial genes within a smaller subset of subjects. One of the key findings was that healthy sites from different people were broadly similar with respect to their functional profiles, even though there was extensive individual variation in their taxonomic ...
Welcome to Class 14 - (canvas.brown.edu).
... Net loss of NH3 from amino acids requires oxidation:! α-keto acids are 2 equivalents more oxidized than amino acids! ...
... Net loss of NH3 from amino acids requires oxidation:! α-keto acids are 2 equivalents more oxidized than amino acids! ...
Cell Biophysics II - Univerzita Pavla Jozefa Šafárika v Košiciach
... Cell compartments and organelles Cell compartments and intracellular transport Molecular motors - Intracellular transport of vesicles Mitochondria Mitochondria and cell death Cell cycle & apoptosis References ...
... Cell compartments and organelles Cell compartments and intracellular transport Molecular motors - Intracellular transport of vesicles Mitochondria Mitochondria and cell death Cell cycle & apoptosis References ...
The nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding the attachment
... All the sequences (existing cDNA clones and the PCR product) were merged to give the complete sequence of the end of the F gene, the H gene and the beginning of the L gene of CDV (see Fig. 1). The numbering in this sequence begins at the conserved gene start sequence in the H gene and ends at positi ...
... All the sequences (existing cDNA clones and the PCR product) were merged to give the complete sequence of the end of the F gene, the H gene and the beginning of the L gene of CDV (see Fig. 1). The numbering in this sequence begins at the conserved gene start sequence in the H gene and ends at positi ...
Test Example
... (a) List the types of noncovalent interactions that are important in providing stability to the threedimensional structures of macromolecules. (b) Why is it important that these interactions be noncovalent, rather than covalent, bonds? Ans: (a) Noncovalent interactions include hydrogen bonds, ionic ...
... (a) List the types of noncovalent interactions that are important in providing stability to the threedimensional structures of macromolecules. (b) Why is it important that these interactions be noncovalent, rather than covalent, bonds? Ans: (a) Noncovalent interactions include hydrogen bonds, ionic ...
A perturbation-based method for calculating explicit likelihood of
... Their interdependence should be apparent in the evolutionary record of each protein family: positions in the sequence of a protein family that are intimately associated in space or in function should co-vary in evolution. A recent approach by Ranganathan and colleagues proposes to look at subsets of ...
... Their interdependence should be apparent in the evolutionary record of each protein family: positions in the sequence of a protein family that are intimately associated in space or in function should co-vary in evolution. A recent approach by Ranganathan and colleagues proposes to look at subsets of ...
A specific domain in α-catenin mediates binding to β
... with 20 mM Hepes-NaOH, pH 7.4, and ultracentrifuged for 30 minutes at 4°C at 45,000 rpm in an AH650 swing-out rotor. The supernatant was applied to 2 ml amylose resin (New England Biolabs) and incubated for 15 minutes at 4°C on a rotatory shaker. To achieve complete binding the flow-through was reap ...
... with 20 mM Hepes-NaOH, pH 7.4, and ultracentrifuged for 30 minutes at 4°C at 45,000 rpm in an AH650 swing-out rotor. The supernatant was applied to 2 ml amylose resin (New England Biolabs) and incubated for 15 minutes at 4°C on a rotatory shaker. To achieve complete binding the flow-through was reap ...
PDF - Biotechnology for Biofuels
... particular the use of fermentative microorganisms, have attracted scientific interest in recent years. However the low overall yield obtained is a major challenge in biological H2 production. Thus, a thorough and detailed understanding of the relationships between genome content, gene expression pat ...
... particular the use of fermentative microorganisms, have attracted scientific interest in recent years. However the low overall yield obtained is a major challenge in biological H2 production. Thus, a thorough and detailed understanding of the relationships between genome content, gene expression pat ...
Introduction - ART
... Cells are continuously exposed to diverse external stimuli, ranging from soluble endocrine and paracrine factors to signaling molecules on neighboring cells. The cell must interpret these extracellular signals to produce an appropriate developmental or proliferative response. Receptors of the tyrosi ...
... Cells are continuously exposed to diverse external stimuli, ranging from soluble endocrine and paracrine factors to signaling molecules on neighboring cells. The cell must interpret these extracellular signals to produce an appropriate developmental or proliferative response. Receptors of the tyrosi ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.























