Glial cell biology in Drosophila and vertebrates
... support of neurons, blood–brain barrier formation, and modulation of neuronal activity) are probably very similar at the molecular level. Key aspects of neuronal development – from axon pathfinding to the sculpting of synaptic connections – are also regulated by glia in Drosophila and mammals. These ...
... support of neurons, blood–brain barrier formation, and modulation of neuronal activity) are probably very similar at the molecular level. Key aspects of neuronal development – from axon pathfinding to the sculpting of synaptic connections – are also regulated by glia in Drosophila and mammals. These ...
Cystatin C prevents degeneration of rat nigral dopaminergic neurons
... loss in the fetal mesencephalic cultures, an effect which could be partially reversed by treatment with cystatin C. Moreover, in vivo DA neurons survival study showed that administration of cystatin C in rats with 6OHDA-induced lesion partially rescued the nigral DA neurons. The results indicate tha ...
... loss in the fetal mesencephalic cultures, an effect which could be partially reversed by treatment with cystatin C. Moreover, in vivo DA neurons survival study showed that administration of cystatin C in rats with 6OHDA-induced lesion partially rescued the nigral DA neurons. The results indicate tha ...
Full PDF
... inputs; the ratio of excitatory to inhibitory synaptic contacts is ⬃10:1, which is unprecedented in the CNS (71). This pattern of synaptic organization, which results in noise assuming the characteristics of signal, allows hypocretinergic neurons to be easily activated, leading to rapid arousal (71) ...
... inputs; the ratio of excitatory to inhibitory synaptic contacts is ⬃10:1, which is unprecedented in the CNS (71). This pattern of synaptic organization, which results in noise assuming the characteristics of signal, allows hypocretinergic neurons to be easily activated, leading to rapid arousal (71) ...
The Pituitary Gland and Hypothalamus
... Figure 4: Growth hormone (GH) directly accelerates the rate of protein synthesis in skeletal muscle and bones. Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) is activated by growth hormone and indirectly supports the formation of new proteins in muscle cells and bone. ...
... Figure 4: Growth hormone (GH) directly accelerates the rate of protein synthesis in skeletal muscle and bones. Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) is activated by growth hormone and indirectly supports the formation of new proteins in muscle cells and bone. ...
Sound processing by local neural populations in the
... is transduced into an electrical signal. This signal propagates along various stations of the auditory pathway, through the thalamus, eventually reaching the auditory cortex (AC). The AC is the primary cortical region devoted to processing of sounds, and as such, it is believed to be involved in hig ...
... is transduced into an electrical signal. This signal propagates along various stations of the auditory pathway, through the thalamus, eventually reaching the auditory cortex (AC). The AC is the primary cortical region devoted to processing of sounds, and as such, it is believed to be involved in hig ...
A quantitative link between face discrimination deficits and neuronal
... an initial 10.2 s fixation period, 50 grayscale images of faces, houses, and scrambled faces were presented to participants in blocks of 30.6 s (each image was displayed for 512 ms and followed by a 100 ms blank screen), and were separated by a 20.4 s fixation block (Fig. 2). Each block was repeated t ...
... an initial 10.2 s fixation period, 50 grayscale images of faces, houses, and scrambled faces were presented to participants in blocks of 30.6 s (each image was displayed for 512 ms and followed by a 100 ms blank screen), and were separated by a 20.4 s fixation block (Fig. 2). Each block was repeated t ...
Move to the rhythm: oscillations in the subthalamic nucleus–external
... rebound depolarization, which generates a single spike, restores rhythmic spiking and/or generates a burst of activity (Fig. 2g,h) [63]. Multiple IPSPs can also reduce and/or prevent action-potential generation (Fig. 2f) [63]. The pattern and rate of inhibitory input are, therefore, crucial in deter ...
... rebound depolarization, which generates a single spike, restores rhythmic spiking and/or generates a burst of activity (Fig. 2g,h) [63]. Multiple IPSPs can also reduce and/or prevent action-potential generation (Fig. 2f) [63]. The pattern and rate of inhibitory input are, therefore, crucial in deter ...
PDF - Bentham Open
... low trait anxiety exhibit greater vmPFC activation compared to participants with high trait anxiety during cued fear conditioning [34]. In contrast, individuals with high trait anxiety showed a diminished vmPFC response that was associated with greater fear conditioned SCRs compared to participants ...
... low trait anxiety exhibit greater vmPFC activation compared to participants with high trait anxiety during cued fear conditioning [34]. In contrast, individuals with high trait anxiety showed a diminished vmPFC response that was associated with greater fear conditioned SCRs compared to participants ...
Electronic Realization of Human Brain`s Neo
... to get close to VLSI mimicry of the brain power efficiency. The brain consisting of 1010 neurons with 1014 neural connections is a very power efficient system that is still the most complex system to date [16]. Comparison of hardware/software implementation and software simulations shows how faraway ...
... to get close to VLSI mimicry of the brain power efficiency. The brain consisting of 1010 neurons with 1014 neural connections is a very power efficient system that is still the most complex system to date [16]. Comparison of hardware/software implementation and software simulations shows how faraway ...
ANS: c, p. 46, F, LO=2.1, (1)
... b) axon terminals, dendrites, cell body, axon c) cell body, dendrites, axon terminals, axon Incorrect. Every part of this answer is out of the correct order. d) axon, cell body, dendrites, axon terminals ANS: a, pp. 46–47, C, LO=2.1, (2) APA=1.1 14. Your teacher asks you to describe the sequence of ...
... b) axon terminals, dendrites, cell body, axon c) cell body, dendrites, axon terminals, axon Incorrect. Every part of this answer is out of the correct order. d) axon, cell body, dendrites, axon terminals ANS: a, pp. 46–47, C, LO=2.1, (2) APA=1.1 14. Your teacher asks you to describe the sequence of ...
ANS: c, p. 46, F, LO=2.1, (1) - test bank and solution manual for your
... 13. The function of the neuron’s axon is to ______. a) carry messages to other cells Correct. The function of the axon is to carry messages to other cells. b) regulate the neuron’s life processes c) receive messages from neighboring neurons Incorrect. Dendrites, not axons, receive messages. d) insul ...
... 13. The function of the neuron’s axon is to ______. a) carry messages to other cells Correct. The function of the axon is to carry messages to other cells. b) regulate the neuron’s life processes c) receive messages from neighboring neurons Incorrect. Dendrites, not axons, receive messages. d) insul ...
CHAPTER TWO - Test Bank 1
... 13. The function of the neuron’s axon is to ______. a) carry messages to other cells Correct. The function of the axon is to carry messages to other cells. b) regulate the neuron’s life processes c) receive messages from neighboring neurons Incorrect. Dendrites, not axons, receive messages. d) insu ...
... 13. The function of the neuron’s axon is to ______. a) carry messages to other cells Correct. The function of the axon is to carry messages to other cells. b) regulate the neuron’s life processes c) receive messages from neighboring neurons Incorrect. Dendrites, not axons, receive messages. d) insu ...
EEG & Sleep
... • It is characterized by emotional outburst such as abnormal rage,anxiety,fear or discomfort. • There is amnesia or confused mental state for some period. • The cause, are the abnormalities in temporal lobe & tumor in hypothalamus and limbic system. ...
... • It is characterized by emotional outburst such as abnormal rage,anxiety,fear or discomfort. • There is amnesia or confused mental state for some period. • The cause, are the abnormalities in temporal lobe & tumor in hypothalamus and limbic system. ...
Topic - We can offer most test bank and solution manual you need.
... called the ______________ nervous system. a) central c) sympathetic b) somatic d) parasympathetic 6. Hormones are___________. a) the female gonads b) chemicals released into the bloodstream by the endocrine glands c) chemicals found in the synaptic vesicles, which when released have an effect on the ...
... called the ______________ nervous system. a) central c) sympathetic b) somatic d) parasympathetic 6. Hormones are___________. a) the female gonads b) chemicals released into the bloodstream by the endocrine glands c) chemicals found in the synaptic vesicles, which when released have an effect on the ...
Full-Text PDF
... The vast majority of prothrombin is produced in the liver and released into the plasma. It circulates within the bloodstream until it is converted into mature thrombin in the the coagulation cascade [10]. Thrombin is a large, spherical molecule, with a major groove around its equatorial axis, that i ...
... The vast majority of prothrombin is produced in the liver and released into the plasma. It circulates within the bloodstream until it is converted into mature thrombin in the the coagulation cascade [10]. Thrombin is a large, spherical molecule, with a major groove around its equatorial axis, that i ...
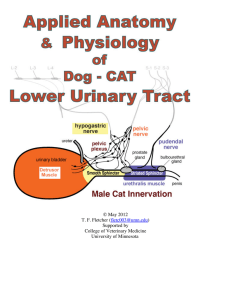
May 2012 TF Fletcher ()
... 1. Detrusor muscle = the smooth muscle coat of the bladder apex & body which expels urine, when activated by parasympathetic innervation conveyed by the pelvic nerve. 2. Smooth muscle sphincter (internal urethral sphincter) = smooth muscle of the bladder neck and, in the case of females and male c ...
... 1. Detrusor muscle = the smooth muscle coat of the bladder apex & body which expels urine, when activated by parasympathetic innervation conveyed by the pelvic nerve. 2. Smooth muscle sphincter (internal urethral sphincter) = smooth muscle of the bladder neck and, in the case of females and male c ...
Morphine effects on monetary reward - DUO
... The µ-opioid receptor system is central to reward and pain relief across species. In rodents, injection of opioids into striatum amplifies ‘liking’ responses to and/or motivation for rewards. In humans, opioid agonists can induce euphoria, whereas antagonists reduce food reward. Brain regions implic ...
... The µ-opioid receptor system is central to reward and pain relief across species. In rodents, injection of opioids into striatum amplifies ‘liking’ responses to and/or motivation for rewards. In humans, opioid agonists can induce euphoria, whereas antagonists reduce food reward. Brain regions implic ...
Section 2 Lactation Physiology
... Other mechanisms for milk ejection: Myoepithelial cells will also contract in response to vasopressin Milk ejection may be a condition response Stimulation of the genital tract such as vaginal distention causes release of large amounts of oxytocin The mechanical tap stimulus does not invol ...
... Other mechanisms for milk ejection: Myoepithelial cells will also contract in response to vasopressin Milk ejection may be a condition response Stimulation of the genital tract such as vaginal distention causes release of large amounts of oxytocin The mechanical tap stimulus does not invol ...
Resting-State Connectivity Predictors of Response to
... monitoring of emotional salience (Ressler and Mayberg, 2007; Seminowicz et al, 2004); (2) the subcortical brain regions that process affective stimuli (Kumar et al, 2008; Pizzagalli et al, 2009) and that modulate emotional memory formation and retrieval (Dillon et al, 2013); and (3) the coordinated ...
... monitoring of emotional salience (Ressler and Mayberg, 2007; Seminowicz et al, 2004); (2) the subcortical brain regions that process affective stimuli (Kumar et al, 2008; Pizzagalli et al, 2009) and that modulate emotional memory formation and retrieval (Dillon et al, 2013); and (3) the coordinated ...
Functional Organization in the Motor Cortex
... showed directly that when aligning the tuning curve of voxels to their PD (defined as the direction in which activation was highest) there was a gradual decrease in activation, as direction was farther away from that PD. (2) I used multi-voxel pattern analysis to show that spatial patterns of activa ...
... showed directly that when aligning the tuning curve of voxels to their PD (defined as the direction in which activation was highest) there was a gradual decrease in activation, as direction was farther away from that PD. (2) I used multi-voxel pattern analysis to show that spatial patterns of activa ...
Vesicular glutamate transporters (VGLUTs): The three musketeers of
... Glutamate was discovered by Kikunae Ikeda, a professor of Tokyo Imperial University in 1908, while looking for the flavor common to foods like cheese, meat, and mushrooms. He was able to extract the acid glutamate from seaweed, but it took about five decades for scientists to discover that this subs ...
... Glutamate was discovered by Kikunae Ikeda, a professor of Tokyo Imperial University in 1908, while looking for the flavor common to foods like cheese, meat, and mushrooms. He was able to extract the acid glutamate from seaweed, but it took about five decades for scientists to discover that this subs ...
Haemodynamic response
In haemodynamics, the body must respond to physical activities, external temperature, and other factors by homeostatically adjusting its blood flow to deliver nutrients such as oxygen and glucose to stressed tissues and allow them to function. Haemodynamic response (HR) allows the rapid delivery of blood to active neuronal tissues. Since higher processes in the brain occur almost constantly, cerebral blood flow is essential for the maintenance of neurons, astrocytes, and other cells of the brain.