The Human brain
... • Most posterior portion of the brain stem • Continuous with the spinal cord • Consists of white matter (nerve tracts) and gray matter (cell bodies), carries messages to and from spinal cord • Motor fibers cross here, right brain controls lefts side of body, left brain controls right side. ...
... • Most posterior portion of the brain stem • Continuous with the spinal cord • Consists of white matter (nerve tracts) and gray matter (cell bodies), carries messages to and from spinal cord • Motor fibers cross here, right brain controls lefts side of body, left brain controls right side. ...
Ch 3 biology and Behavioir Notes
... New information is received by the senses, and it is processed in the frontal lobe into short term memory for about 5-20 seconds. Most new information is never remembered If it is deemed important, it is sent to the ...
... New information is received by the senses, and it is processed in the frontal lobe into short term memory for about 5-20 seconds. Most new information is never remembered If it is deemed important, it is sent to the ...
Unit 01 Biology and the Brain_Part 2
... • Involved in how we process memory. • More involved in volatile emotions like The emotion of anger has anger. not changed much throughout evolution. ...
... • Involved in how we process memory. • More involved in volatile emotions like The emotion of anger has anger. not changed much throughout evolution. ...
Chapter 2—Biological Bases of Behavior I. Neuroanatomy-
... Chapter 2—Biological Bases of Behavior I. Neuroanatomy-A. Neurons—individual nerve cells; the building blocks of the nervous system 1. parts of a neuron Dendrites— Soma— Axon— Myelin Sheath— Terminal Buttons— Synapse— 2. how a neuron fires (neuron has slightly negative charge in its rest ...
... Chapter 2—Biological Bases of Behavior I. Neuroanatomy-A. Neurons—individual nerve cells; the building blocks of the nervous system 1. parts of a neuron Dendrites— Soma— Axon— Myelin Sheath— Terminal Buttons— Synapse— 2. how a neuron fires (neuron has slightly negative charge in its rest ...
GEOTRAN - Life Solutions Institute
... In the human brain, there are more than several hundred million neurons. In these neurons ion currents flow. The ion currents produce the magnetic field. This magnetic field emerges out of the head through the brain, the scalp and the head. ...
... In the human brain, there are more than several hundred million neurons. In these neurons ion currents flow. The ion currents produce the magnetic field. This magnetic field emerges out of the head through the brain, the scalp and the head. ...
Pasko Rakic`s Autobiography
... discovery of a single signaling molecule that we share with other creatures, but from unraveling the neuronal circuitry that underlies our mental capacity. He also believed, like Einstein, that the meaning of a finding is as important as the finding itself. My original twoyear fellowship transformed ...
... discovery of a single signaling molecule that we share with other creatures, but from unraveling the neuronal circuitry that underlies our mental capacity. He also believed, like Einstein, that the meaning of a finding is as important as the finding itself. My original twoyear fellowship transformed ...
The Nervous System - Needham.K12.ma.us
... • Parasympathetic—Normal Body Maintenance – Moderates breathing and heart rate – Allows for digestion and urination – Constricts Pupils ...
... • Parasympathetic—Normal Body Maintenance – Moderates breathing and heart rate – Allows for digestion and urination – Constricts Pupils ...
Chapter 13 and 16
... A. Astrocyte- function in creating bloodbrain barrier, provide structure B. Oligodendocyte- produce myelin sheath C. Microglia- immune cells of CNS, similar to macrophages D. Ependymal- found in ventricles of brain, produce cerebrospinal fluid ...
... A. Astrocyte- function in creating bloodbrain barrier, provide structure B. Oligodendocyte- produce myelin sheath C. Microglia- immune cells of CNS, similar to macrophages D. Ependymal- found in ventricles of brain, produce cerebrospinal fluid ...
COURSE: 7065
... Cerebellum---controls muscular coordination, balance, and posture Pituitary gland---releases hormones that control metabolism and sexual development Spinal cord---controls simple reflexes that do not involve the brain Thalamus---controls the way emotions are expressed How the brain works N ...
... Cerebellum---controls muscular coordination, balance, and posture Pituitary gland---releases hormones that control metabolism and sexual development Spinal cord---controls simple reflexes that do not involve the brain Thalamus---controls the way emotions are expressed How the brain works N ...
A1984SK79600002
... 1. Feldberg W & Vogt M. Acetylcholine synthesis in different regions of the central nervous system. J. Physiology 107:372-81, 1948. (Cited 265 times since 1955.) 2. Carisson A. The occurrence, distribution and physiological role of catecholamines in the nervous system. Pharmacol Rev. 11:490-3, 1959 ...
... 1. Feldberg W & Vogt M. Acetylcholine synthesis in different regions of the central nervous system. J. Physiology 107:372-81, 1948. (Cited 265 times since 1955.) 2. Carisson A. The occurrence, distribution and physiological role of catecholamines in the nervous system. Pharmacol Rev. 11:490-3, 1959 ...
Crisis Response 101
... What happens when a person experiences inescapable, repeated, life-threatening, overwhelming stress ...
... What happens when a person experiences inescapable, repeated, life-threatening, overwhelming stress ...
mapping the brain - Scholastic Heads Up
... and bones absorb and then release the energy from the radio waves. A computer maps and measures these changes to create an image. Changes in the size of tissues (such as from diseases like cancer that cause tumors) can increase the amount of water in different parts of the body, which can be detecte ...
... and bones absorb and then release the energy from the radio waves. A computer maps and measures these changes to create an image. Changes in the size of tissues (such as from diseases like cancer that cause tumors) can increase the amount of water in different parts of the body, which can be detecte ...
NEUROTRANSMITTER TEST KIT (13 vials) - Life
... Acts on both the peripheral nervous system and central nervous system and is the only neurotransmitter used in the motor division of the somatic nervous system. Also the principal neurotransmitter in all autonomic ganglia. In cortex increases responsiveness to sensory stimuli; decreases heart rate a ...
... Acts on both the peripheral nervous system and central nervous system and is the only neurotransmitter used in the motor division of the somatic nervous system. Also the principal neurotransmitter in all autonomic ganglia. In cortex increases responsiveness to sensory stimuli; decreases heart rate a ...
The Brilliant Resilient Adolescent Brain
... The “use it or lose it principle” refers to the idea that the cells (neurons) and connections (synapses) that are used during adolescence grow and get stronger (use it!) and the ones that are not used will wither and die (lose it!). If a young person is getting exercise, playing an instrument or lea ...
... The “use it or lose it principle” refers to the idea that the cells (neurons) and connections (synapses) that are used during adolescence grow and get stronger (use it!) and the ones that are not used will wither and die (lose it!). If a young person is getting exercise, playing an instrument or lea ...
The Nervous System
... Nervous System Injuries Concussions • Bruise-like injury of brain • Occurs when soft tissue collides against skull • Can cause headache, dizziness, confusion, memory loss, brain damage ...
... Nervous System Injuries Concussions • Bruise-like injury of brain • Occurs when soft tissue collides against skull • Can cause headache, dizziness, confusion, memory loss, brain damage ...
Nutrition and the Brain
... person thinks something will have an effect. In other words, if a person thinks a change in diet will affect behavior, it may actually affect behavior even if the nutrients are not causing the change. Therefore, experiments must have a placebo control and be performed in a double-blind manner where ...
... person thinks something will have an effect. In other words, if a person thinks a change in diet will affect behavior, it may actually affect behavior even if the nutrients are not causing the change. Therefore, experiments must have a placebo control and be performed in a double-blind manner where ...
Intro Chap 2n.ppt
... Each Neuron consists of 3 structural parts 1. Soma or cell body 2. Axon 3. Dendrites Some axons are coated with myelin (for speed), and some may also be coated with neurilemma (allows for healing). 90% of nervous system cells are Glial Cells These provide structural support, nutrition, fuel, insulat ...
... Each Neuron consists of 3 structural parts 1. Soma or cell body 2. Axon 3. Dendrites Some axons are coated with myelin (for speed), and some may also be coated with neurilemma (allows for healing). 90% of nervous system cells are Glial Cells These provide structural support, nutrition, fuel, insulat ...
Chapter 6
... called cannabinoid receptors, many of which coordinate movement. The ______, a structure involved with memory storage and learning, also contains many receptors for THC. (54) 8. Scientists recently discovered that cannabinoid receptors normally bind to natural internal chemicals termed _____________ ...
... called cannabinoid receptors, many of which coordinate movement. The ______, a structure involved with memory storage and learning, also contains many receptors for THC. (54) 8. Scientists recently discovered that cannabinoid receptors normally bind to natural internal chemicals termed _____________ ...
Stereological estimates of neuronal loss in the primary motor cortex
... Introduction Whilst inflammatory demyelination (ID) is an important feature in the clinical and pathological diagnosis of MS, evidence suggests mechanisms other than ID may play an important role for the deterioration of function in people with progressive MS (pwPMS) (Trapp & Nave. Annu Rev Neurosci ...
... Introduction Whilst inflammatory demyelination (ID) is an important feature in the clinical and pathological diagnosis of MS, evidence suggests mechanisms other than ID may play an important role for the deterioration of function in people with progressive MS (pwPMS) (Trapp & Nave. Annu Rev Neurosci ...
Chapter 6 Notes
... and say it was a ball, but not holding it in their left hand c. Shows how unique and the specialize functions and skills of each hemisphere d. Remained practically unchanged in intelligence, emotion and personality E. How Psychologists study the brain a. Recording i. Putting electrodes into the brai ...
... and say it was a ball, but not holding it in their left hand c. Shows how unique and the specialize functions and skills of each hemisphere d. Remained practically unchanged in intelligence, emotion and personality E. How Psychologists study the brain a. Recording i. Putting electrodes into the brai ...
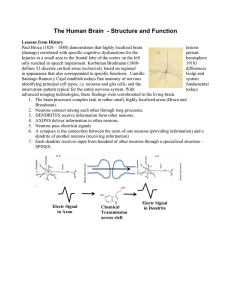
The Human Brain - Structure and Function
... defines 52 discrete cortical areas exclusively based on regional differences in appearance that also corresponded to specific functions. Camillo Golgi and Santiago Ramon y Cajal establish todays fine anatomy of nervous system identifying principal cell types, i.e. neurons and glia cells, and the fun ...
... defines 52 discrete cortical areas exclusively based on regional differences in appearance that also corresponded to specific functions. Camillo Golgi and Santiago Ramon y Cajal establish todays fine anatomy of nervous system identifying principal cell types, i.e. neurons and glia cells, and the fun ...
Document
... • Cerebrum= The largest part of the brain; it is responsible for learning and other conscious mental functions. • Thalamus= A midbrain structure that plays a major role in relaying information from the various sensory receptors to other ...
... • Cerebrum= The largest part of the brain; it is responsible for learning and other conscious mental functions. • Thalamus= A midbrain structure that plays a major role in relaying information from the various sensory receptors to other ...
Haemodynamic response
In haemodynamics, the body must respond to physical activities, external temperature, and other factors by homeostatically adjusting its blood flow to deliver nutrients such as oxygen and glucose to stressed tissues and allow them to function. Haemodynamic response (HR) allows the rapid delivery of blood to active neuronal tissues. Since higher processes in the brain occur almost constantly, cerebral blood flow is essential for the maintenance of neurons, astrocytes, and other cells of the brain.