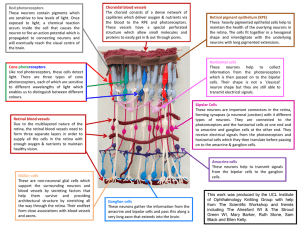
Click here to view a labelled image of the Knitted Retina
... will eventually reach the visual centre of the brain. ...
... will eventually reach the visual centre of the brain. ...
Draft Proposal to the Keck Foundation KECK CENTER FOR
... multiphoton microscopy, and lifetime resolved microscopy, are combined with genetic or exogenous optical markers to provide new ways to study processes such as cellular trafficking, vesicle membrane fusion, locally regulated dendritic ionic flows and protein synthesis, and rhythmic activities of ind ...
... multiphoton microscopy, and lifetime resolved microscopy, are combined with genetic or exogenous optical markers to provide new ways to study processes such as cellular trafficking, vesicle membrane fusion, locally regulated dendritic ionic flows and protein synthesis, and rhythmic activities of ind ...
The Brain - Central Connecticut State University
... Dopamine has been found in animal studies to be released when certain pleasures are taking place, e.g. sex, drinking, etc. ...
... Dopamine has been found in animal studies to be released when certain pleasures are taking place, e.g. sex, drinking, etc. ...
Vocab: Unit 3 Handout made by: Jessica Jones and Hanna Cho
... Lesion: tissue destruction, brain lesions are naturally or experimentally caused Electroencephalogram: (EEG) amplified recording of the waves, measured by electrodes placed on the scalp. CT computed tomography scan: X-ray photographs taken from different angles and combined by the computer to compos ...
... Lesion: tissue destruction, brain lesions are naturally or experimentally caused Electroencephalogram: (EEG) amplified recording of the waves, measured by electrodes placed on the scalp. CT computed tomography scan: X-ray photographs taken from different angles and combined by the computer to compos ...
ANATOMY
... • Neurons do not connect with each other but send impulses over spaces called synapses. ...
... • Neurons do not connect with each other but send impulses over spaces called synapses. ...
Neuronal Development
... • Neurons that divide are located next to the ventricles • Where is the gray matter (soma) in the cerebral cortex? • Neurons will either migrate by: – Sending out processes – Follow radial glia ...
... • Neurons that divide are located next to the ventricles • Where is the gray matter (soma) in the cerebral cortex? • Neurons will either migrate by: – Sending out processes – Follow radial glia ...
Neurotransmitters
... connecting motor nerves to muscles. The paralytic arrow-poison curare acts by blocking transmission at these synapses. Acetylcholine also operates in many regions of the brain, but using different types of receptors. Dopamine has a number of important functions in the brain. It plays a critical role ...
... connecting motor nerves to muscles. The paralytic arrow-poison curare acts by blocking transmission at these synapses. Acetylcholine also operates in many regions of the brain, but using different types of receptors. Dopamine has a number of important functions in the brain. It plays a critical role ...
Chapter 51 Disorders of Brain Function
... • The brain floats freely in the CSF. Blunt force to the head accelerates the brain within the skull, and then the brain decelerates abruptly upon hitting the inner skull surfaces. • Coup: direct contusion of the brain at the site of external force • Contrecoup: rebound injury on the opposite side o ...
... • The brain floats freely in the CSF. Blunt force to the head accelerates the brain within the skull, and then the brain decelerates abruptly upon hitting the inner skull surfaces. • Coup: direct contusion of the brain at the site of external force • Contrecoup: rebound injury on the opposite side o ...
Abstract
... However, in the last decade optical methods and optical tracers are developing rapidly. Optical methods can determine concentrations in vivo in a sub-second time frame. They can map drug distribution. Experiments that would take days or months using chemical measurements take minutes to do and in ve ...
... However, in the last decade optical methods and optical tracers are developing rapidly. Optical methods can determine concentrations in vivo in a sub-second time frame. They can map drug distribution. Experiments that would take days or months using chemical measurements take minutes to do and in ve ...
Chapter 12-13 Summary
... change allows sodium ions to enter the cell, causing depolarization. Once begun the action potential or nerve impulse continues over the entire surface of the axon. Electrical condition of resting state are restored by the diffusion of potassium ions out of the cell (repolarization) ion concentratio ...
... change allows sodium ions to enter the cell, causing depolarization. Once begun the action potential or nerve impulse continues over the entire surface of the axon. Electrical condition of resting state are restored by the diffusion of potassium ions out of the cell (repolarization) ion concentratio ...
PSY 301 – Summer 2004
... Introduction to Psychology Class 8: Neuroscience 1 Myers: 38-51 June 22, 2006 ...
... Introduction to Psychology Class 8: Neuroscience 1 Myers: 38-51 June 22, 2006 ...
brain - The Institute of Mathematical Sciences
... thought that glia simply held neurons together. (Indeed, “glia” take their name from the Greek word for glue.) But recent research by Fields, Bukalo’s colleague at the National Institutes of Child Health and Human Development, reveals that glial cells also become active during learning. One type of ...
... thought that glia simply held neurons together. (Indeed, “glia” take their name from the Greek word for glue.) But recent research by Fields, Bukalo’s colleague at the National Institutes of Child Health and Human Development, reveals that glial cells also become active during learning. One type of ...
Document
... • The various dimensions and divisions of the CNS are defined in the neural tube • Development of the neural tube cavity becomes the ventricles of the brain and canal of the cord • Development of the neural tube wall provides an early organization of the CNS ...
... • The various dimensions and divisions of the CNS are defined in the neural tube • Development of the neural tube cavity becomes the ventricles of the brain and canal of the cord • Development of the neural tube wall provides an early organization of the CNS ...
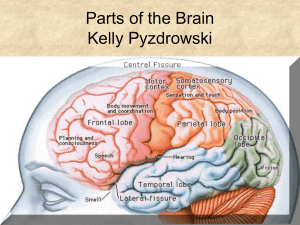
Parts of the Brain - Bellarmine University
... between the brain and spinal cord Various nuclei of the medulla transmits nerve impulses that control: Heart rate Constriction Dilation of blood vessels Blood pressure Swallowing sneezing ...
... between the brain and spinal cord Various nuclei of the medulla transmits nerve impulses that control: Heart rate Constriction Dilation of blood vessels Blood pressure Swallowing sneezing ...
Biology and Behaviour
... accept that the brain controls it, we must understand the brain The nervous system is built out of neurons or nerve cells, and glial cells, which are sort of the glue Glial cells do other support functions too ...
... accept that the brain controls it, we must understand the brain The nervous system is built out of neurons or nerve cells, and glial cells, which are sort of the glue Glial cells do other support functions too ...
The building blocks of matter (elements and molecules) form the
... Integumentary system - The integumentary system is an animal’s outer covering, such as skin, scales, feathers, fur, and other body parts, that protect the animal and prevent it from drying out. This system is the first barrier to disease and is responsible for controlling body temperature. Lymphati ...
... Integumentary system - The integumentary system is an animal’s outer covering, such as skin, scales, feathers, fur, and other body parts, that protect the animal and prevent it from drying out. This system is the first barrier to disease and is responsible for controlling body temperature. Lymphati ...
The Brain
... listening, speaking, looking at images, etc. Oxyhaemoglobin doesn’t absorb radio waves, deoxyhaemoglobin does and these appear differently on scans. 3. Active areas of the brain result in increased blood flow. Higher amounts of oxyhaemoglobin indicate increased blood flow. Less signal is absor ...
... listening, speaking, looking at images, etc. Oxyhaemoglobin doesn’t absorb radio waves, deoxyhaemoglobin does and these appear differently on scans. 3. Active areas of the brain result in increased blood flow. Higher amounts of oxyhaemoglobin indicate increased blood flow. Less signal is absor ...
University of Split Danica Škara, PhD e
... The human brain is the center of the human nervous system and is a highly complex organ. It has the same general structure as the brains of other mammals, but is over three times as large as the brain of a typical mammal. Especially expanded are the frontal lobes, which are involved in executive fun ...
... The human brain is the center of the human nervous system and is a highly complex organ. It has the same general structure as the brains of other mammals, but is over three times as large as the brain of a typical mammal. Especially expanded are the frontal lobes, which are involved in executive fun ...
File
... 2. The Hypothalamus- monitors the internal systems to maintain the normal state of the body (homeostasis) by controlling the release of hormones it can moderate body functions (sleep, food intake, and liquid intake) WARNING- if out of balance difficult to concentrate ...
... 2. The Hypothalamus- monitors the internal systems to maintain the normal state of the body (homeostasis) by controlling the release of hormones it can moderate body functions (sleep, food intake, and liquid intake) WARNING- if out of balance difficult to concentrate ...
Nervous System - Creston High School
... make up central nervous tissue? Known as neuroglia or glial cells 1. Astrocytes-star shaped cells that connect neurons together and to their blood supply. 2. Microglia- function as phagocytes by engulfing foreign invaders. 3. Ependymal- (epithelial-like) provide a barrier between brain and spinal fl ...
... make up central nervous tissue? Known as neuroglia or glial cells 1. Astrocytes-star shaped cells that connect neurons together and to their blood supply. 2. Microglia- function as phagocytes by engulfing foreign invaders. 3. Ependymal- (epithelial-like) provide a barrier between brain and spinal fl ...
Nervous Systems - manorlakesscience
... sensory detectors to the brain and impulses that pass from the brain to other parts of the body travel along the spinal cord. ...
... sensory detectors to the brain and impulses that pass from the brain to other parts of the body travel along the spinal cord. ...
Chapter 2 Vocabulary
... computer-generated images that show brain structures more clearly. (p. 59) 30. The __________________ , the oldest and innermost region of the brain, is an extension of the spinal cord and is the central core of the brain; its structures direct automatic survival functions. (p. 61) 31. Located in t ...
... computer-generated images that show brain structures more clearly. (p. 59) 30. The __________________ , the oldest and innermost region of the brain, is an extension of the spinal cord and is the central core of the brain; its structures direct automatic survival functions. (p. 61) 31. Located in t ...
Learning Styles PowerPoint
... Rational thinking and organization come easily A left brain thinker can be seen as very serious ...
... Rational thinking and organization come easily A left brain thinker can be seen as very serious ...
Haemodynamic response
In haemodynamics, the body must respond to physical activities, external temperature, and other factors by homeostatically adjusting its blood flow to deliver nutrients such as oxygen and glucose to stressed tissues and allow them to function. Haemodynamic response (HR) allows the rapid delivery of blood to active neuronal tissues. Since higher processes in the brain occur almost constantly, cerebral blood flow is essential for the maintenance of neurons, astrocytes, and other cells of the brain.