Why we act when we act: How brain, body, and environment interact
... making is that decisions-to-act are formed in the brain and then transmitted to the body to be carried out; and that the “when” of the action corresponds to a decision about when to act. However, recent evidence shows that the “when” of self-initiated action might be determined in part by ongoing st ...
... making is that decisions-to-act are formed in the brain and then transmitted to the body to be carried out; and that the “when” of the action corresponds to a decision about when to act. However, recent evidence shows that the “when” of self-initiated action might be determined in part by ongoing st ...
Direct Electrode Stimulation Direct electrode stimulation involves
... Transcranial magnetic stimulation is a direct brain stimulation technique that delivers a magnetic field pulse through the skull and temporarily activates or disrupts the normal activity of neurons in a specific area of the cerebral cortex. In this procedure, patients are sat in a chair while a magn ...
... Transcranial magnetic stimulation is a direct brain stimulation technique that delivers a magnetic field pulse through the skull and temporarily activates or disrupts the normal activity of neurons in a specific area of the cerebral cortex. In this procedure, patients are sat in a chair while a magn ...
Study Concepts for Exam V - Nervous System
... Motor pathways that descend the spinal cord to the PNS The specialized cells, location, and function associated with vision, taste buds, olfaction, hearing, static equilibrium, and dynamic equilibrium. The wrappings of a nerve Nervous system defects arising during pregnancy Divisions of the CNS and ...
... Motor pathways that descend the spinal cord to the PNS The specialized cells, location, and function associated with vision, taste buds, olfaction, hearing, static equilibrium, and dynamic equilibrium. The wrappings of a nerve Nervous system defects arising during pregnancy Divisions of the CNS and ...
Nervous filled
... • The brain requires oxygen for aerobic metabolism. Lack of oxygen for more than 5 minutes can kill brain cells. • The brain requires glucose for metabolism. Lack of glucose for more than 15 minutes kills brain cells. • Neurons cannot undergo mitosis. ...
... • The brain requires oxygen for aerobic metabolism. Lack of oxygen for more than 5 minutes can kill brain cells. • The brain requires glucose for metabolism. Lack of glucose for more than 15 minutes kills brain cells. • Neurons cannot undergo mitosis. ...
File
... • Homeostasis – control blood pressure, heart rate, temperature and emotions • Major link between N.S. and endocrine system ...
... • Homeostasis – control blood pressure, heart rate, temperature and emotions • Major link between N.S. and endocrine system ...
I. How Do Scientists Study the Nervous System?
... into regions or lobes with specialized functions: frontal lobe (planning and movement, speech production, working memory, moral reasoning, mood regulation), ...
... into regions or lobes with specialized functions: frontal lobe (planning and movement, speech production, working memory, moral reasoning, mood regulation), ...
Cerebral cortex (top brain): Heavily wrinkled outer layer (gray matter
... This illustration shows specific brain functions. We know that Post Trauma Disorder takes place in the oldest part of the brain, or the ‘Reptilian’ brain. The ‘fright and flight’ response takes place here when danger is present. Whenever there is severe trauma this part of the brain replays the even ...
... This illustration shows specific brain functions. We know that Post Trauma Disorder takes place in the oldest part of the brain, or the ‘Reptilian’ brain. The ‘fright and flight’ response takes place here when danger is present. Whenever there is severe trauma this part of the brain replays the even ...
Where does breathing start?
... skeletal muscle voluntarily, we have, in part, conscious control over it. The signals that neurons send to the diaphragm and the intercostals function as if they were autonomic, even though the respiratory centres are not part of the autonomic nervous system. This is due to the interplay of the neur ...
... skeletal muscle voluntarily, we have, in part, conscious control over it. The signals that neurons send to the diaphragm and the intercostals function as if they were autonomic, even though the respiratory centres are not part of the autonomic nervous system. This is due to the interplay of the neur ...
BRAiNBAsED LEARNiNG - Slone Chiropractic
... a BrainBased Learning Program and has been trained to evaluate and treat many neurologic conditions such as Dyslexia, Autism, ADD/ADHD and Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD). Treatment is designed to treat an area of the patient that is often overlooked… THE BRAIN. ...
... a BrainBased Learning Program and has been trained to evaluate and treat many neurologic conditions such as Dyslexia, Autism, ADD/ADHD and Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD). Treatment is designed to treat an area of the patient that is often overlooked… THE BRAIN. ...
Worksheet - Humble ISD
... ______________ neuron carries impulses from the brain to muscles or glands. The _________________ neuron connects the other two types together. Lastly, the ____________ neuron carries impulses from sense organs to the brain. The electrical signal of the neuron is carried toward the ________________ ...
... ______________ neuron carries impulses from the brain to muscles or glands. The _________________ neuron connects the other two types together. Lastly, the ____________ neuron carries impulses from sense organs to the brain. The electrical signal of the neuron is carried toward the ________________ ...
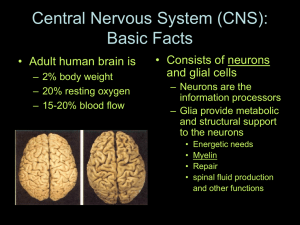
Central Nervous System (CNS): Basic Facts
... Central Nervous System (CNS): Basic Facts • Adult human brain is – 2% body weight – 20% resting oxygen – 15-20% blood flow ...
... Central Nervous System (CNS): Basic Facts • Adult human brain is – 2% body weight – 20% resting oxygen – 15-20% blood flow ...
Brain matters in multiple sclerosis
... This carries information from this neuron to other neurons ...
... This carries information from this neuron to other neurons ...
Document
... 1993: Meeting on Neural Modeling and Functional Brain Imaging • Brought together modelers and functional brain imagers for the first time. • Tried to determine what research questions modelers could address • The four questions: – Relation between neural activity and imaging signals – Effective con ...
... 1993: Meeting on Neural Modeling and Functional Brain Imaging • Brought together modelers and functional brain imagers for the first time. • Tried to determine what research questions modelers could address • The four questions: – Relation between neural activity and imaging signals – Effective con ...
The Nervous System
... • It is a semi-permeable capillary membrane; that is, it allows some materials to cross, but prevents others from crossing. In most parts of the body the capillaries, are lined with endothelial cells. The endothelial tissue has small spaces between each individual cell so substances can move readily ...
... • It is a semi-permeable capillary membrane; that is, it allows some materials to cross, but prevents others from crossing. In most parts of the body the capillaries, are lined with endothelial cells. The endothelial tissue has small spaces between each individual cell so substances can move readily ...
EXC 7770 Psychoneurological & Medical Issues in Special Education
... Axons to thalamus – gatekeeper forms units Primary processing – modality specific Secondary processing – modality specific Tertiary processing – integrate across ...
... Axons to thalamus – gatekeeper forms units Primary processing – modality specific Secondary processing – modality specific Tertiary processing – integrate across ...
TECHNIQUES2001
... – radioactively labeled 2-deoxy-d-glucose (2DG) ~ [“false glucose”] is absorbed by “active” neurons and accumulates in cells since it can’t be broken down like normal glucose. OR – radioactively labeled H2O (hydrogen with O15) carried by blood flow to “active” neurons. ...
... – radioactively labeled 2-deoxy-d-glucose (2DG) ~ [“false glucose”] is absorbed by “active” neurons and accumulates in cells since it can’t be broken down like normal glucose. OR – radioactively labeled H2O (hydrogen with O15) carried by blood flow to “active” neurons. ...
Brain Chips
... enabling. Brain cells enable users to see IR,UV and chemical spectra. It will enhance memory. It will enable “cyberthink”. It will enable consistent and constant access to information where and when it is needed The advantage of implants is that they take the decision making power away from the addi ...
... enabling. Brain cells enable users to see IR,UV and chemical spectra. It will enhance memory. It will enable “cyberthink”. It will enable consistent and constant access to information where and when it is needed The advantage of implants is that they take the decision making power away from the addi ...
• Ch 49 • Nervous Systems • Neuronal Circuits • Each single
... In the PNS, afferent neurons transmit information to the CNS and efferent neurons transmit information away from the CNSThe PNS has two efferent components: the motor system and the autonomic nervous system ...
... In the PNS, afferent neurons transmit information to the CNS and efferent neurons transmit information away from the CNSThe PNS has two efferent components: the motor system and the autonomic nervous system ...
Nervous System PowerPoint
... Buoyancy for the brain, c_____, chemical stability, f_____ system, clears out _____ (esp. when we sleep) Located between the _____ and _____ maters Flows uninterrupted through the CNS through the cerebrospinal canal of the spinal cord to the _____ in the _____ then exits CNS through veins draining ...
... Buoyancy for the brain, c_____, chemical stability, f_____ system, clears out _____ (esp. when we sleep) Located between the _____ and _____ maters Flows uninterrupted through the CNS through the cerebrospinal canal of the spinal cord to the _____ in the _____ then exits CNS through veins draining ...
Subthalamic High-frequency Deep Brain Stimulation Evaluated in a
... During the past decade, subthalamic high frequency deep brain stimulation (DBS) has proven effective in the treatment of Parkinson's disease complicated with motor fluctuations and L-dopa induced dyskinesias. The current claim holds that the electrical stimulation inhibits neural activity in the sub ...
... During the past decade, subthalamic high frequency deep brain stimulation (DBS) has proven effective in the treatment of Parkinson's disease complicated with motor fluctuations and L-dopa induced dyskinesias. The current claim holds that the electrical stimulation inhibits neural activity in the sub ...
Brain-Class Notes
... sleep/wake cycle), homeostasis (inner balance in body, including temperature), appetite, thirst, other bodily urges and also plays a role in emotions, autonomic functions, and motor functions ...
... sleep/wake cycle), homeostasis (inner balance in body, including temperature), appetite, thirst, other bodily urges and also plays a role in emotions, autonomic functions, and motor functions ...
The Academy Professional Development Session
... anything that did not engage any of your senses? How? ...
... anything that did not engage any of your senses? How? ...
Haemodynamic response
In haemodynamics, the body must respond to physical activities, external temperature, and other factors by homeostatically adjusting its blood flow to deliver nutrients such as oxygen and glucose to stressed tissues and allow them to function. Haemodynamic response (HR) allows the rapid delivery of blood to active neuronal tissues. Since higher processes in the brain occur almost constantly, cerebral blood flow is essential for the maintenance of neurons, astrocytes, and other cells of the brain.