Vertebrate Nervous System
... cavity joining to which the csf flows, lining that central canal are ependymal cells which are epithelial cells, they also function in producing the csf ...
... cavity joining to which the csf flows, lining that central canal are ependymal cells which are epithelial cells, they also function in producing the csf ...
Blood - El Camino College
... D. Blood ______ - watery portion of blood, composes 55% of blood; consists of about 90% ______ and 10% solutes. _______ include: 1. Plasma __________ - 7% of solutes; 3 major types produced by the ________ are: a. ___________ (60%) - small protein that makes blood viscous to maintain blood _________ ...
... D. Blood ______ - watery portion of blood, composes 55% of blood; consists of about 90% ______ and 10% solutes. _______ include: 1. Plasma __________ - 7% of solutes; 3 major types produced by the ________ are: a. ___________ (60%) - small protein that makes blood viscous to maintain blood _________ ...
Slide 1 - Teachers TryScience
... 1. An action potential arrives at a presynaptic terminal. 2. The Calcium ion channel opens releasing calcium ions into the presynaptic terminal. 3. Calcium ions cause the synaptic vesicle to move to the synaptic cleft. 4. The synaptic vesicle releases ACH neurotransmitter into the cleft. 5. ACH diff ...
... 1. An action potential arrives at a presynaptic terminal. 2. The Calcium ion channel opens releasing calcium ions into the presynaptic terminal. 3. Calcium ions cause the synaptic vesicle to move to the synaptic cleft. 4. The synaptic vesicle releases ACH neurotransmitter into the cleft. 5. ACH diff ...
Basics of Neuroscience
... environment & coordinating bodily functions of its organ components 1. Central Nervous System (CNS) includes the brain and the spinal cord 2. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) 3. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS). ...
... environment & coordinating bodily functions of its organ components 1. Central Nervous System (CNS) includes the brain and the spinal cord 2. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) 3. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS). ...
Nerve Cells Images
... illustrations for ‘Big Picture’. He is happy for teachers and students to use his illustrations in a classroom setting, but for other uses, permission must be sought. • We source other images from photo libraries such as Science Photo Library, Corbis and iStock and will acknowledge in an image’s cre ...
... illustrations for ‘Big Picture’. He is happy for teachers and students to use his illustrations in a classroom setting, but for other uses, permission must be sought. • We source other images from photo libraries such as Science Photo Library, Corbis and iStock and will acknowledge in an image’s cre ...
Nervous & Endocrine Systems
... 2. Receptors in your ear pick the sound of a ringing phone 5. Receptors trigger nerve impulses in sensory neurons 1. The nerve impulses pass to interneurons in the brain. 6. Your brain interprets the impulses from many interneurons and you realize the phone is ringing. Your brain also decides that y ...
... 2. Receptors in your ear pick the sound of a ringing phone 5. Receptors trigger nerve impulses in sensory neurons 1. The nerve impulses pass to interneurons in the brain. 6. Your brain interprets the impulses from many interneurons and you realize the phone is ringing. Your brain also decides that y ...
1) Corticotropin releasing hormone secretion would not raise the
... Anatomy and Physiology 212: Quiz #1 ON YOUR SCANTRON, PUT YOUR NAME AND TEST FORM LETTER ON FRONT! Multiple Choice (2 pts each): Choose the one best answer for each question, use a pencil to mark answer on scantron (double check for smears). 1) A _______hormone only exerts its effects on cells with ...
... Anatomy and Physiology 212: Quiz #1 ON YOUR SCANTRON, PUT YOUR NAME AND TEST FORM LETTER ON FRONT! Multiple Choice (2 pts each): Choose the one best answer for each question, use a pencil to mark answer on scantron (double check for smears). 1) A _______hormone only exerts its effects on cells with ...
2nd class Nervous System
... Paragraph 1: What are the parts of the Nervous system and how do they work? Paragraph 2: What parts of the body need the nervous system? Paragraph 3: What are problems of the nervous system? Paragraph 4: What are some of the ways to care for the nervous system? Also the crossword puzzle Control Cent ...
... Paragraph 1: What are the parts of the Nervous system and how do they work? Paragraph 2: What parts of the body need the nervous system? Paragraph 3: What are problems of the nervous system? Paragraph 4: What are some of the ways to care for the nervous system? Also the crossword puzzle Control Cent ...
Unit 3
... • Discuss the effect of the endocrine system on behavior. • Describe the nervous system and its subdivisions and functions: — central and peripheral nervous systems; — major brain regions, lobes, and cortical areas; — brain lateralization and hemispheric specialization. • Recount historic and contem ...
... • Discuss the effect of the endocrine system on behavior. • Describe the nervous system and its subdivisions and functions: — central and peripheral nervous systems; — major brain regions, lobes, and cortical areas; — brain lateralization and hemispheric specialization. • Recount historic and contem ...
Chapter 13 - Las Positas College
... A. Embryonic development and congenital birth defects that involve the brain are anencephaly, spina bifida, and cerebral palsy. (pp. 419–420, Fig. 13.38) B. Postnatal changes in the brain represent many neuronal connections during childhood that are based on early experiences; brain growth stops in ...
... A. Embryonic development and congenital birth defects that involve the brain are anencephaly, spina bifida, and cerebral palsy. (pp. 419–420, Fig. 13.38) B. Postnatal changes in the brain represent many neuronal connections during childhood that are based on early experiences; brain growth stops in ...
Neurological Injuries - toggenburg ski patrol
... Review the anatomy and physiology of the nervous system and spinal column Identify the types and mechanisms of head and spine injuries, and describe their features Describe the assessment of head and spine injuries ...
... Review the anatomy and physiology of the nervous system and spinal column Identify the types and mechanisms of head and spine injuries, and describe their features Describe the assessment of head and spine injuries ...
Nervous System Poster
... 1. Membranes of neurons are polarized by the establishment of electrical potentials across the membranes. 2. In response to a stimulus, Na+ and K+ gated channels sequentially open and cause the membrane to become locally depolarized. 3. Na+/K+ pumps, powered by ATP, work to maintain membrane potenti ...
... 1. Membranes of neurons are polarized by the establishment of electrical potentials across the membranes. 2. In response to a stimulus, Na+ and K+ gated channels sequentially open and cause the membrane to become locally depolarized. 3. Na+/K+ pumps, powered by ATP, work to maintain membrane potenti ...
intro to psych ch3 biological bases of behavior
... buttons; nerve impulses travel down the axon; carries messages Myelin sheath: fatty layer covering the axon that helps nerve impulses move ...
... buttons; nerve impulses travel down the axon; carries messages Myelin sheath: fatty layer covering the axon that helps nerve impulses move ...
Perinatal Neuorscience and Skin to Skin Contact
... and then creates no more. Once born, the second to sixth month has more synapsis in its brain than any other stage of life. This period is significant for the imprinting period on the baby. The synapsis of the brain hard wire a bio-chemical reaction so a dance of hormones get excreted based on certa ...
... and then creates no more. Once born, the second to sixth month has more synapsis in its brain than any other stage of life. This period is significant for the imprinting period on the baby. The synapsis of the brain hard wire a bio-chemical reaction so a dance of hormones get excreted based on certa ...
Brain_stemCh45
... Origins from medial medullary reticular formation Function: inhibits cranial and spinal motor neurons => motor tone ...
... Origins from medial medullary reticular formation Function: inhibits cranial and spinal motor neurons => motor tone ...
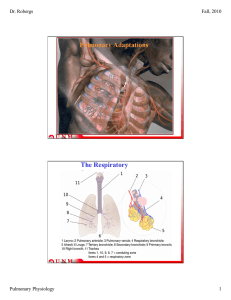
Pulmonary Adaptations The Respiratory System
... The fact that alveolar and blood gas partial pressures approximately reach equilibrium within the lung enables researchers to estimate arterial blood gas partial pressures from alveolar partial pressures! ...
... The fact that alveolar and blood gas partial pressures approximately reach equilibrium within the lung enables researchers to estimate arterial blood gas partial pressures from alveolar partial pressures! ...
How your brain and nervous system work
... Higher tier only: high demand • Recall that the gap between neurones is called a synapse. • Describe how an impulse triggers the release of a transmitter substance in a synapse and how it diffuses across to bind with receptor molecules in the membrane of the next neurone causing the impulse to conti ...
... Higher tier only: high demand • Recall that the gap between neurones is called a synapse. • Describe how an impulse triggers the release of a transmitter substance in a synapse and how it diffuses across to bind with receptor molecules in the membrane of the next neurone causing the impulse to conti ...
HLTH 102 Module C Notes
... However, in low doses, alcohol can also be a stimulant! o It activates (instead of inhibits) certain nerve cells o Also, it can send excitatory messages using GABA, which ultimately results in more inhibition occurring GABA and glutamate receptor responses: o So the increase of GABA is the reason wh ...
... However, in low doses, alcohol can also be a stimulant! o It activates (instead of inhibits) certain nerve cells o Also, it can send excitatory messages using GABA, which ultimately results in more inhibition occurring GABA and glutamate receptor responses: o So the increase of GABA is the reason wh ...
neurolinguistics: shakespeare and aphasia
... The brain processes information and sends instructions through an extremely complex system of nervecells, known as neurons. The travelling of information from one neuron to the other is a process called synapse, and the synapses can be chemical (indirect synapse, where messages are transferred throu ...
... The brain processes information and sends instructions through an extremely complex system of nervecells, known as neurons. The travelling of information from one neuron to the other is a process called synapse, and the synapses can be chemical (indirect synapse, where messages are transferred throu ...
Module 3 - yhernandez
... information away from the spinal cord to produce responses in various muscles and organs throughout the body ...
... information away from the spinal cord to produce responses in various muscles and organs throughout the body ...
CHAPTER OUTLINE
... photoreceptors, mechanoreceptors, and thermoreceptors, which respond to chemical substances, light energy, mechanical forces, and changes in temperature, respectively. How Sensation Occurs Sensory receptors respond to environmental stimuli by generating nerve impulses. Detection occurs when environm ...
... photoreceptors, mechanoreceptors, and thermoreceptors, which respond to chemical substances, light energy, mechanical forces, and changes in temperature, respectively. How Sensation Occurs Sensory receptors respond to environmental stimuli by generating nerve impulses. Detection occurs when environm ...
Chapter 12 – The Nervous System ()
... Today, innovations in technology have resulted in many ways of probing the structure and function of the brain. These include: 1. The electroencephalograph ( EEG ) which was invented in 1924 by Dr. Hans Borger. This device measures the electrical activity of the brain and produces a printout ( See F ...
... Today, innovations in technology have resulted in many ways of probing the structure and function of the brain. These include: 1. The electroencephalograph ( EEG ) which was invented in 1924 by Dr. Hans Borger. This device measures the electrical activity of the brain and produces a printout ( See F ...
12-nervoussystemintro - Alexmac
... system don’t regenerate easily. • Some neurons in peripheral nervous system can regrow and repair a small gap. ...
... system don’t regenerate easily. • Some neurons in peripheral nervous system can regrow and repair a small gap. ...
Nervous System Introduction
... piling up layers of lipid/protein cell membranes • - one Schwann cell associates with and myelinates a segment of only one axon • - Schwann cell, myelin, axon are all surrounded by a basement membrane (covers whole unit) • - help to buffer excess extracellular K+ (prevent rampant depolarization) ...
... piling up layers of lipid/protein cell membranes • - one Schwann cell associates with and myelinates a segment of only one axon • - Schwann cell, myelin, axon are all surrounded by a basement membrane (covers whole unit) • - help to buffer excess extracellular K+ (prevent rampant depolarization) ...
Haemodynamic response
In haemodynamics, the body must respond to physical activities, external temperature, and other factors by homeostatically adjusting its blood flow to deliver nutrients such as oxygen and glucose to stressed tissues and allow them to function. Haemodynamic response (HR) allows the rapid delivery of blood to active neuronal tissues. Since higher processes in the brain occur almost constantly, cerebral blood flow is essential for the maintenance of neurons, astrocytes, and other cells of the brain.