Consciousness and Creativity in Brain
... commercially almost successful, but never become massively parallel and the company went bankrupt. CAM Brain (ATR Kyoto) – failed attempt to evolve the large-scale cellular neural network; based on a bad idea that one can evolve functions without knowing them. Evolutionary algorithms require supervi ...
... commercially almost successful, but never become massively parallel and the company went bankrupt. CAM Brain (ATR Kyoto) – failed attempt to evolve the large-scale cellular neural network; based on a bad idea that one can evolve functions without knowing them. Evolutionary algorithms require supervi ...
Nervous System
... somata and dendritic structures. They are often interconnected with each other to form a complex known as a plexus. 21 The ________ nervous system is the part of the peripheral nervous system that acts as a control system, maintaining homeostasis in the body. 25 The ________ mater is one of the thre ...
... somata and dendritic structures. They are often interconnected with each other to form a complex known as a plexus. 21 The ________ nervous system is the part of the peripheral nervous system that acts as a control system, maintaining homeostasis in the body. 25 The ________ mater is one of the thre ...
D - VCOMcc
... 30. Which of the following is an extrinsic factor that may increase SV? A. decreased LVEDV B. decreased preload C. increased adrenergic stimulation D. increased afterload E. increased heart rate 31. Dr. Reilly is given two agents and a large supply of laboratory rats. He divides the rat population i ...
... 30. Which of the following is an extrinsic factor that may increase SV? A. decreased LVEDV B. decreased preload C. increased adrenergic stimulation D. increased afterload E. increased heart rate 31. Dr. Reilly is given two agents and a large supply of laboratory rats. He divides the rat population i ...
Neuroscience Flash Cards, Second Edition
... to the corresponding figure number in the Atlas can be found on the front of each card. Relevant structures are labeled on the front of each flash card illustration with A, B, C, and so forth. On the back of the flash card is a list of all labeled structures. In some instances, such as the illustrat ...
... to the corresponding figure number in the Atlas can be found on the front of each card. Relevant structures are labeled on the front of each flash card illustration with A, B, C, and so forth. On the back of the flash card is a list of all labeled structures. In some instances, such as the illustrat ...
Slide 1
... Health Significance • Headaches are usually caused by tension in the neck or by dilation of the blood vessels of the head • Migraine headaches are caused by an imbalance in the brain’s chemistry ...
... Health Significance • Headaches are usually caused by tension in the neck or by dilation of the blood vessels of the head • Migraine headaches are caused by an imbalance in the brain’s chemistry ...
File - LC Biology 2012-2013
... • What is the function of the [a] humours, [b] optic nerve? • If you are longsighted, what does it mean? • What could be a possible cause? • What type of lens can rectify it? ...
... • What is the function of the [a] humours, [b] optic nerve? • If you are longsighted, what does it mean? • What could be a possible cause? • What type of lens can rectify it? ...
PDF
... done with respect to such detailed connectivity data. The intriguing results of the paper—and the questions regarding routing the paper raises—deserve attention. Mišić et al. (2014) compare simulated activity on the CoCoMac network with activity on two surrogate network topologies: a generic small ...
... done with respect to such detailed connectivity data. The intriguing results of the paper—and the questions regarding routing the paper raises—deserve attention. Mišić et al. (2014) compare simulated activity on the CoCoMac network with activity on two surrogate network topologies: a generic small ...
Chapter 16
... is decreased by increasing the size of the thoracic cavity; due to surface tension between the two layers of pleura, the lungs follow with the chest wall and expand. 4. Muscles involved in expanding the thoracic cavity include the diaphragm and the external intercostal muscles. Respiratory muscles c ...
... is decreased by increasing the size of the thoracic cavity; due to surface tension between the two layers of pleura, the lungs follow with the chest wall and expand. 4. Muscles involved in expanding the thoracic cavity include the diaphragm and the external intercostal muscles. Respiratory muscles c ...
The Nervous System
... • I can describe how the role and function of the nervous system • I can list and describe the individual organs that make up the nervous system, and how they work together • I can describe how the nervous system responds to changing ...
... • I can describe how the role and function of the nervous system • I can list and describe the individual organs that make up the nervous system, and how they work together • I can describe how the nervous system responds to changing ...
Chapter 9 Part 3 Central Nervous System
... – Brain Stem contains control centers for many automatic life functions: • Breathing • Blood pressure • Etc. • Brain Stem receives sensory information from body • Relays motor commands to peripheral muscles and glands ...
... – Brain Stem contains control centers for many automatic life functions: • Breathing • Blood pressure • Etc. • Brain Stem receives sensory information from body • Relays motor commands to peripheral muscles and glands ...
Central Nervous System CNS
... of visual field is on left side) Map of visual space If damaged: functionally blind because no conscious awareness of sight ...
... of visual field is on left side) Map of visual space If damaged: functionally blind because no conscious awareness of sight ...
Biology Option E
... E.3.5 Draw the gross structure of the brain including the medulla oblongata, cerebellum, hypothalamus, pituitary gland and cerebral hemispheres. Drawing will be inserted at a later date ...
... E.3.5 Draw the gross structure of the brain including the medulla oblongata, cerebellum, hypothalamus, pituitary gland and cerebral hemispheres. Drawing will be inserted at a later date ...
Neuron Unit 3A
... • The best understood NT. Plays a role in learning and memory. ACh is the messenger at every junction of a motor neuron & skeletal muscle. If Ach transmission is blocked like anesthesia, muscles can’t contract ...
... • The best understood NT. Plays a role in learning and memory. ACh is the messenger at every junction of a motor neuron & skeletal muscle. If Ach transmission is blocked like anesthesia, muscles can’t contract ...
Keshara Senanayake Towle Notes Chapter 50 "Nervous System
... >molecules diffuse across the short distance of the synaptic cleft and bind to receptor molecules embedded in the postsynaptic membrane - the interaction of neurotransmitters molecules and receptor molecules changes the permeability of the postsynaptic membrane by affecting chemical-gate ion channel ...
... >molecules diffuse across the short distance of the synaptic cleft and bind to receptor molecules embedded in the postsynaptic membrane - the interaction of neurotransmitters molecules and receptor molecules changes the permeability of the postsynaptic membrane by affecting chemical-gate ion channel ...
READING And YOUR BRAIN YOUR BRAIN YOUR BRAIN
... So with this very small in-focus viewing area how is anybody able to read more than 10 words per minute? Efficient readers are able to read quickly because of the top-down flow of information as depicted in the transactive model described in the last chapter. When we read, we use the information in ...
... So with this very small in-focus viewing area how is anybody able to read more than 10 words per minute? Efficient readers are able to read quickly because of the top-down flow of information as depicted in the transactive model described in the last chapter. When we read, we use the information in ...
Document
... exciting the neuron to fire more action potentials causing an increase in dopamine release. •Nicotine also affects neurons by increasing the number of synaptic vesicles released. ...
... exciting the neuron to fire more action potentials causing an increase in dopamine release. •Nicotine also affects neurons by increasing the number of synaptic vesicles released. ...
The Nanostructure of the Nervous System and the Impact
... gradients between the inside and outside of the neuron separated by the cell membrane of the axon. Na+, which is actively pumped out of the neuron and is at much higher concentrations extracellularly, enters the cell through Na+ specific ion channels while K+, whose situation is reversed, flows out. ...
... gradients between the inside and outside of the neuron separated by the cell membrane of the axon. Na+, which is actively pumped out of the neuron and is at much higher concentrations extracellularly, enters the cell through Na+ specific ion channels while K+, whose situation is reversed, flows out. ...
Biology 231
... cranial nerves – 12 pairs emerging from brainstem mainly detect sensations and control functions of head and neck (vagus nerve controls functions of thoracic and abdominal organs) may be mixed nerves or only sensory or motor SOMATIC VS AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Somatic Nervous System – controls move ...
... cranial nerves – 12 pairs emerging from brainstem mainly detect sensations and control functions of head and neck (vagus nerve controls functions of thoracic and abdominal organs) may be mixed nerves or only sensory or motor SOMATIC VS AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Somatic Nervous System – controls move ...
BIOLOGICAL AND CULTURAL SHAPING OF MIND AND BEHAVIOUR
... (3) The axon is a long fibre that leads away from the cell body. The axons send signals to the dendrites, other neurons or to muscles and glands. The axons make neural pathways in the (CNS). The axons are insulated by myelin sheath. Myelin sheath is made up of glial cells. The Nerve Impulse An infor ...
... (3) The axon is a long fibre that leads away from the cell body. The axons send signals to the dendrites, other neurons or to muscles and glands. The axons make neural pathways in the (CNS). The axons are insulated by myelin sheath. Myelin sheath is made up of glial cells. The Nerve Impulse An infor ...
The Ten-Percent Myth
... the subject, see Barry Beyerstein's chapter in the new book Mind Myths: Exploring Everyday Mysteries of the Mind [1999].) 1. Brain imaging research techniques such as PET scans (positron emission tomography) and fMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging) clearly show that the vast majority of the ...
... the subject, see Barry Beyerstein's chapter in the new book Mind Myths: Exploring Everyday Mysteries of the Mind [1999].) 1. Brain imaging research techniques such as PET scans (positron emission tomography) and fMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging) clearly show that the vast majority of the ...
FULL TEXT - RS Publication
... (MRI) of the brain is to correctly label certain areas of the image to highlight the brain tissues, both healthy and pathological. In practice, however, you come across often in images suffer from various kinds of artifacts that do fail the classification algorithms. Also the effect of noise, often ...
... (MRI) of the brain is to correctly label certain areas of the image to highlight the brain tissues, both healthy and pathological. In practice, however, you come across often in images suffer from various kinds of artifacts that do fail the classification algorithms. Also the effect of noise, often ...
Regulation of Respiration
... Reflexes originating from body movement Increase in body temperature Adrenaline release Impulses from the cerebral cortex Later: accumulation of CO2 and H+ generated by active muscles ...
... Reflexes originating from body movement Increase in body temperature Adrenaline release Impulses from the cerebral cortex Later: accumulation of CO2 and H+ generated by active muscles ...
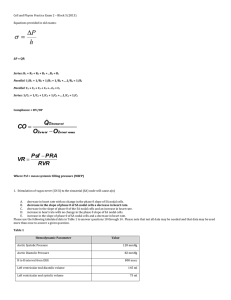
Haemodynamic response
In haemodynamics, the body must respond to physical activities, external temperature, and other factors by homeostatically adjusting its blood flow to deliver nutrients such as oxygen and glucose to stressed tissues and allow them to function. Haemodynamic response (HR) allows the rapid delivery of blood to active neuronal tissues. Since higher processes in the brain occur almost constantly, cerebral blood flow is essential for the maintenance of neurons, astrocytes, and other cells of the brain.