a comparative study of the histological changes in cerebral
... competitive inhibitor of the Ca transport at the level of Ca pump and channels and that’s how the lead induces its toxicity leading to the disturbance in the cellular homeostasis. The clinical manifestation of the lead toxicity popularly known as plumbism depends on the level of exposure, affinity o ...
... competitive inhibitor of the Ca transport at the level of Ca pump and channels and that’s how the lead induces its toxicity leading to the disturbance in the cellular homeostasis. The clinical manifestation of the lead toxicity popularly known as plumbism depends on the level of exposure, affinity o ...
Adrenocortical Hormones
... 90-95% of the cortisol in plasma binds to cortisol-binding globulin or transcortin, less to albumin – long half-life (60-90 min) 60% of circulating aldosterone combined with plasma proteins (half-life 20 min) degraded in liver – conjugation especially to glucuronic acid and sulfates (25% excreted in ...
... 90-95% of the cortisol in plasma binds to cortisol-binding globulin or transcortin, less to albumin – long half-life (60-90 min) 60% of circulating aldosterone combined with plasma proteins (half-life 20 min) degraded in liver – conjugation especially to glucuronic acid and sulfates (25% excreted in ...
Unit B6 Key Words
... brings about a slow change in the body A change in the environment that causes a response Cells that detect changes in the environment The long tine part of a neuron Tissues and organs in the body that control the body’s responses to stimuli A set of nerve impulses that causes a reflex action Made u ...
... brings about a slow change in the body A change in the environment that causes a response Cells that detect changes in the environment The long tine part of a neuron Tissues and organs in the body that control the body’s responses to stimuli A set of nerve impulses that causes a reflex action Made u ...
PAC01 Pulmonary Physiology
... Internal Respiration is gas exchange between the systemic capillaries and the metabolic tissues of the body. This is also passive and occurs via diffusion. Cellular Respiration is the metabolic use of oxygen to form ATP in the mitochondria. Anatomical decscriptions. There is a respiratory and conduc ...
... Internal Respiration is gas exchange between the systemic capillaries and the metabolic tissues of the body. This is also passive and occurs via diffusion. Cellular Respiration is the metabolic use of oxygen to form ATP in the mitochondria. Anatomical decscriptions. There is a respiratory and conduc ...
So it is the number of action potentials per second
... inhibitory. Between a neuron and a muscle cell it is excitatory but the receptors on cardiac muscle cells generate an inhibitory responses to reduce strength of contraction and rate of heart beat. 2. Epinephrine and norepinephrine a) can be both excitatory or inhibitory 3. Dopamine a) lack of dopami ...
... inhibitory. Between a neuron and a muscle cell it is excitatory but the receptors on cardiac muscle cells generate an inhibitory responses to reduce strength of contraction and rate of heart beat. 2. Epinephrine and norepinephrine a) can be both excitatory or inhibitory 3. Dopamine a) lack of dopami ...
Cardiovascular System: Vessels
... Blood Flow: Volume of blood flowing past a point per given time (ml / min) The velocity of blood flow is not related to proximity of heart, but depends on the diameter and cross-sectional area of blood vessels ...
... Blood Flow: Volume of blood flowing past a point per given time (ml / min) The velocity of blood flow is not related to proximity of heart, but depends on the diameter and cross-sectional area of blood vessels ...
Kevin
... the neuron is pumping the ions to their respective sides, it does not respond to incoming stimuli. After this is complete, the neuron is back to its polarized state and stays in resting potential until another impulse occurs. ...
... the neuron is pumping the ions to their respective sides, it does not respond to incoming stimuli. After this is complete, the neuron is back to its polarized state and stays in resting potential until another impulse occurs. ...
Cognitive DisordersRevisions
... No treatment for biological component Find cause and attempt to treat it first Focus on client management and environment Some types of medication may help Counseling for client and support group ...
... No treatment for biological component Find cause and attempt to treat it first Focus on client management and environment Some types of medication may help Counseling for client and support group ...
1 SCI 102 - Anatomy and Physiology
... Joints are classified in three main groups based upon their structure and the degree of movement they allow. ...
... Joints are classified in three main groups based upon their structure and the degree of movement they allow. ...
learning objectives chapter 2
... association cortex. (see “Sensory and Motor Cortex” and “Association Cortex”) 20. Explain the roles of Broca’s area and Wernicke’s area in language production and comprehension. (see “Association Cortex”) 21. Explain how split-brain studies provide insight into the specialized functions of the brain ...
... association cortex. (see “Sensory and Motor Cortex” and “Association Cortex”) 20. Explain the roles of Broca’s area and Wernicke’s area in language production and comprehension. (see “Association Cortex”) 21. Explain how split-brain studies provide insight into the specialized functions of the brain ...
Unit XIV: Regulation
... - Cerebrum – larger in humans than other organisms - many convolutions – increase surface area - senses, motor, associative functions (memory thought, reasoning) - voluntary movement ...
... - Cerebrum – larger in humans than other organisms - many convolutions – increase surface area - senses, motor, associative functions (memory thought, reasoning) - voluntary movement ...
Questions for Exam #3
... One of the TRP channels, call it TRPQ, opens in response to heat. TRPQ is a nonspecific cation channel. TRPQ is found in the sensory neurons that detect heat; these neurons can fire APs. Exposure to the compound capsaicin, the active ingredient in hot peppers, also opens TRPQ channels in sensory neu ...
... One of the TRP channels, call it TRPQ, opens in response to heat. TRPQ is a nonspecific cation channel. TRPQ is found in the sensory neurons that detect heat; these neurons can fire APs. Exposure to the compound capsaicin, the active ingredient in hot peppers, also opens TRPQ channels in sensory neu ...
Computational Intelligence in a Human Brain Model
... Smart interfaces defined for “sight, sound, taste, touch and hearing senses” are bidirectional and completed by input-output interfaces that ensure the communication for output actions like “speech, sound, movements” and other commands resulting in the thinking process. An important issue is the ‘eq ...
... Smart interfaces defined for “sight, sound, taste, touch and hearing senses” are bidirectional and completed by input-output interfaces that ensure the communication for output actions like “speech, sound, movements” and other commands resulting in the thinking process. An important issue is the ‘eq ...
Chapter 2 Power Point: The Biological Perspective
... • Parietal lobes - sections of the brain located at the top and back of each cerebral hemisphere containing the centers for touch, taste, and temperature sensations. • Somatosensory cortex - area of neurons running down the front of the parietal lobes responsible for processing information from the ...
... • Parietal lobes - sections of the brain located at the top and back of each cerebral hemisphere containing the centers for touch, taste, and temperature sensations. • Somatosensory cortex - area of neurons running down the front of the parietal lobes responsible for processing information from the ...
Autistic brains `organized differently`
... People with autism use their brains differently from other people, which may explain why some have extraordinary abilities to remember and draw objects in detail, according to new research. University of Montreal scientists say in autistic people, the brain areas that deal with visual information ar ...
... People with autism use their brains differently from other people, which may explain why some have extraordinary abilities to remember and draw objects in detail, according to new research. University of Montreal scientists say in autistic people, the brain areas that deal with visual information ar ...
1-DevelopmentMyogenesis
... • Primary myoblasts migrate from somites to muscle pools and fuse • Axons extend from neural tube to muscle ...
... • Primary myoblasts migrate from somites to muscle pools and fuse • Axons extend from neural tube to muscle ...
Introduction to Neuroscience: Systems Neuroscience – Concepts
... • Microglia: immune system cells in the CNS (central nervous system) • Macroglia: • Oligodendrocytes (in CNS) and Schwann cells (in PNS) form the Myelin Sheath (insulation of axons) Æ faster action potential propagation • Astrocytes – (1) bring nutrients to neurons, (2) form the BBB (bloodbrain barr ...
... • Microglia: immune system cells in the CNS (central nervous system) • Macroglia: • Oligodendrocytes (in CNS) and Schwann cells (in PNS) form the Myelin Sheath (insulation of axons) Æ faster action potential propagation • Astrocytes – (1) bring nutrients to neurons, (2) form the BBB (bloodbrain barr ...
Introduction to neural computation
... activated simultaneously (synchronously), then the strength of that synapse is selectively increased. 2. If two neurons on either side of a synapse are activated asynchronously, then that synapse is selectively weakened or eliminated.a ...
... activated simultaneously (synchronously), then the strength of that synapse is selectively increased. 2. If two neurons on either side of a synapse are activated asynchronously, then that synapse is selectively weakened or eliminated.a ...
Introduction and Summary - Cyprus Chiropractic Association
... known neurons which are essential to our development as fully functional humans. For further information see the section below on von Economo neurons (VENs), gigantopyramidal cells and Calcium Binding Calretinin cells. The prefrontal lobes are an integral part of what is called the neo-cortex (new b ...
... known neurons which are essential to our development as fully functional humans. For further information see the section below on von Economo neurons (VENs), gigantopyramidal cells and Calcium Binding Calretinin cells. The prefrontal lobes are an integral part of what is called the neo-cortex (new b ...
Physiology of Respiration - International Fire Training Centre
... absorbed, and then expel it. This process is known as respiration, and consists of two spontaneous actions, inhalation (breathing in) and exhalation (breathing out). Inhalation is effected by a muscular effort which raises the ribs and lowers the diaphragm, thus enlarging the chest cavity and creati ...
... absorbed, and then expel it. This process is known as respiration, and consists of two spontaneous actions, inhalation (breathing in) and exhalation (breathing out). Inhalation is effected by a muscular effort which raises the ribs and lowers the diaphragm, thus enlarging the chest cavity and creati ...
How Does the Brain Sense Osmolality?
... volume-regulatory increases or decreases in response to changes in extracellular tonicity, this would not allow for an absolute plasma osmolality around which body fluid homeostasis is maintained; that is, chronic hyperosmolality would not elicit sustained stimuli to AVP secretion and thirst. Result ...
... volume-regulatory increases or decreases in response to changes in extracellular tonicity, this would not allow for an absolute plasma osmolality around which body fluid homeostasis is maintained; that is, chronic hyperosmolality would not elicit sustained stimuli to AVP secretion and thirst. Result ...
Growth and Development
... As they grow, neurons become arranged by function. Some move into the CEREBRAL CORTEX Others move to subcortical levels, which regulate fundamental activities such as breathing and heart rate (and are below the cerebral cortex). Networks of neurons become more complex over the first few years of lif ...
... As they grow, neurons become arranged by function. Some move into the CEREBRAL CORTEX Others move to subcortical levels, which regulate fundamental activities such as breathing and heart rate (and are below the cerebral cortex). Networks of neurons become more complex over the first few years of lif ...
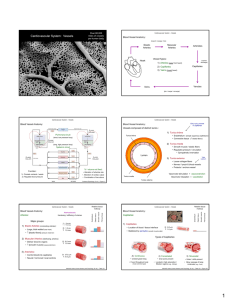
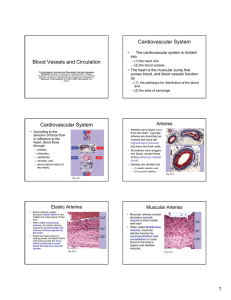
PowerPoint Notes for Blood Vessels
... walls expand to accommodate the increased volume. • When the left ventricle relaxes, the aortic (semilunar) valve closes, and the elastic recoil of the arteries produces the pressure that drives the blood onward through the remaining vascular system. During the recoil of the elastic arteries blood p ...
... walls expand to accommodate the increased volume. • When the left ventricle relaxes, the aortic (semilunar) valve closes, and the elastic recoil of the arteries produces the pressure that drives the blood onward through the remaining vascular system. During the recoil of the elastic arteries blood p ...
Haemodynamic response
In haemodynamics, the body must respond to physical activities, external temperature, and other factors by homeostatically adjusting its blood flow to deliver nutrients such as oxygen and glucose to stressed tissues and allow them to function. Haemodynamic response (HR) allows the rapid delivery of blood to active neuronal tissues. Since higher processes in the brain occur almost constantly, cerebral blood flow is essential for the maintenance of neurons, astrocytes, and other cells of the brain.