4-Nervous system I: Structure and organization
... West, L. J., C. M. Pierce and W. D. Thomas. 1962. Lysergic acid diethylamide: its effects on a male Asiatic elephant. Science 138:1100-1103. Harwood, P. 1963. Therapeutic dosage in small and large mammals . Science 139: 684-685. ...
... West, L. J., C. M. Pierce and W. D. Thomas. 1962. Lysergic acid diethylamide: its effects on a male Asiatic elephant. Science 138:1100-1103. Harwood, P. 1963. Therapeutic dosage in small and large mammals . Science 139: 684-685. ...
Viscoelastic Properties of the Rat Brain in the Horizontal Plane
... CT scans, and the resulting high degree of freedom models can typically be solved in a reasonable time frame with modern computing resources. A tolerance criterion is also necessary to relate tissue strain to loss of function[5]. Finally, accurate mechanical properties for ...
... CT scans, and the resulting high degree of freedom models can typically be solved in a reasonable time frame with modern computing resources. A tolerance criterion is also necessary to relate tissue strain to loss of function[5]. Finally, accurate mechanical properties for ...
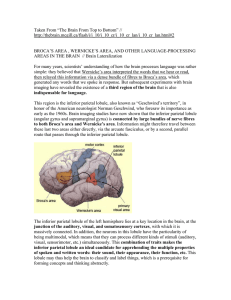
Language Processing in the Brain
... otherwise be needed to connect regions on opposite sides of the brain. Also, when two symmetrical areas on opposite sides of the brain perform two different functions, the brain’s cognitive capacities are in a sense doubled. Handedness and language are two highly lateralized functions. Though there ...
... otherwise be needed to connect regions on opposite sides of the brain. Also, when two symmetrical areas on opposite sides of the brain perform two different functions, the brain’s cognitive capacities are in a sense doubled. Handedness and language are two highly lateralized functions. Though there ...
The Nervous System How your body responds to a stimulus
... Each second, your body fires off about five trillion nerve impulses. • Your emotions, decisions, and physical actions all happen through nerve impulses traveling through neurons in your brain, spinal cord and ...
... Each second, your body fires off about five trillion nerve impulses. • Your emotions, decisions, and physical actions all happen through nerve impulses traveling through neurons in your brain, spinal cord and ...
Nervous System - Mrs. Riggs Online
... • cerebrospinal fluid circulates through fibers of arachnoid; cushions brain • glial cells: support and insulate nerve tissue • neurons: actual nerve cells; long fibers branch out from cell bodies • cell body: contains nucleus and most of nerve cell's cytoplasm; found only in brain, spinal cord or i ...
... • cerebrospinal fluid circulates through fibers of arachnoid; cushions brain • glial cells: support and insulate nerve tissue • neurons: actual nerve cells; long fibers branch out from cell bodies • cell body: contains nucleus and most of nerve cell's cytoplasm; found only in brain, spinal cord or i ...
Bringing the Brain of the Child with Autism Back on Track
... research has shown that autism may be a component of several genetic disorders, including fragile X syndrome, phenylketonuria, tuberous sclerosis complex, and Rett syndrome. But even in cases where genes are identical (such as when identical twins have the disorder), the symptoms may manifest themse ...
... research has shown that autism may be a component of several genetic disorders, including fragile X syndrome, phenylketonuria, tuberous sclerosis complex, and Rett syndrome. But even in cases where genes are identical (such as when identical twins have the disorder), the symptoms may manifest themse ...
Brain Sturcture and Function
... The occipital lobe is the visual processing centre of the mammalian brain containing most of the anatomical region of the visual cortex. The primary visual cortex is Brodmann area 17, commonly called V1 (visual one) ...
... The occipital lobe is the visual processing centre of the mammalian brain containing most of the anatomical region of the visual cortex. The primary visual cortex is Brodmann area 17, commonly called V1 (visual one) ...
Nervous system summary
... After repeated drug use, the brain starts to adjust to the surges of dopamine. Neurons may begin to reduce the number of dopamine receptors or simply make less dopamine. The result is less dopamine signaling in the brain—like turning down the volume on the dopamine signal. Because some drugs are tox ...
... After repeated drug use, the brain starts to adjust to the surges of dopamine. Neurons may begin to reduce the number of dopamine receptors or simply make less dopamine. The result is less dopamine signaling in the brain—like turning down the volume on the dopamine signal. Because some drugs are tox ...
Lecture Suggestions and Guidelines
... 2. Discuss factors which may affect impulse conduction. 3. Introduce the terms presynaptic neuron and postsynaptic neuron. 4. Discuss the release of neurotransmitters by exocytosis as a result of increased calcium concentration inside the cell. Application Question(s) 1. Ask students to devise a set ...
... 2. Discuss factors which may affect impulse conduction. 3. Introduce the terms presynaptic neuron and postsynaptic neuron. 4. Discuss the release of neurotransmitters by exocytosis as a result of increased calcium concentration inside the cell. Application Question(s) 1. Ask students to devise a set ...
laboratory manual - Neuroanatomy - University of Illinois at Chicago
... Arachnoid mater Thin trabeculae connect it to the pia mater. Arachnoid granulations (near superior sagittal sinus) Subarachnoid space (circulating CSF, and where space is enlarged called cisterns; The arteries and veins on the surface of the brain are in this space. Subarachnoid bleeding, e.g. from ...
... Arachnoid mater Thin trabeculae connect it to the pia mater. Arachnoid granulations (near superior sagittal sinus) Subarachnoid space (circulating CSF, and where space is enlarged called cisterns; The arteries and veins on the surface of the brain are in this space. Subarachnoid bleeding, e.g. from ...
Outline14 Efferent NS
... stimulated directly by preganglionic sympathetic fibers secretes epinephrine (E) and norepinephrine (NE) as hormones b. Parasympathetic Division - craniosacral outflow vagus nerve (cranial nerve X) is the major parasympathetic nerve to visceral organs - long preganglionic, short postganglionic fiber ...
... stimulated directly by preganglionic sympathetic fibers secretes epinephrine (E) and norepinephrine (NE) as hormones b. Parasympathetic Division - craniosacral outflow vagus nerve (cranial nerve X) is the major parasympathetic nerve to visceral organs - long preganglionic, short postganglionic fiber ...
Balancing the brain: resting state networks and deep brain stimulation
... the underlying neural mechanisms is still missing. We have previously proposed that efficacious DBS works by restoring the balance of the brain’s resting state networks. Here, we extend this proposal by reviewing how detailed investigations of the highly coherent functional and structural brain netw ...
... the underlying neural mechanisms is still missing. We have previously proposed that efficacious DBS works by restoring the balance of the brain’s resting state networks. Here, we extend this proposal by reviewing how detailed investigations of the highly coherent functional and structural brain netw ...
Abstract Browser - Journal of Neuroscience
... Our understanding of mammalian olfactory coding has been impeded by the paucity of information about the odorant receptors (ORs) that respond to a given odorant ligand in awake, freely behaving animals. Identifying the ORs that respond in vivo to a given odorant ligand from among the ⬃1100 ORs in mi ...
... Our understanding of mammalian olfactory coding has been impeded by the paucity of information about the odorant receptors (ORs) that respond to a given odorant ligand in awake, freely behaving animals. Identifying the ORs that respond in vivo to a given odorant ligand from among the ⬃1100 ORs in mi ...
Characterization of the Bed Nucleus of the Stria Terminalis
... The bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (BNST) is part of the extended amygdala which receives heavy projections from the basolateral amygdala and other areas, and projects to hypothalamic and brainstem target areas that mediate autonomic and behavioral responses to aversive or threatening stimuli. ...
... The bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (BNST) is part of the extended amygdala which receives heavy projections from the basolateral amygdala and other areas, and projects to hypothalamic and brainstem target areas that mediate autonomic and behavioral responses to aversive or threatening stimuli. ...
Selective loss of 20S proteasome a-subunits in the substantia nigra
... content of b-subunits were similar in the various brain regions studied and these levels did not change significantly in PD (Fig. 1B). The content of a-subunits were different in the various regions of control brains and this may reflect tissue-specific differences in the expression of this componen ...
... content of b-subunits were similar in the various brain regions studied and these levels did not change significantly in PD (Fig. 1B). The content of a-subunits were different in the various regions of control brains and this may reflect tissue-specific differences in the expression of this componen ...
A Brain-Based Approach to Teaching
... multiple risk factors received the benefits of established nurturing relationships while obtaining certain protective factors that promote health. The impact of relationship and these protective factors have been show to have a positive impact on brain function, resulting in children who are better ...
... multiple risk factors received the benefits of established nurturing relationships while obtaining certain protective factors that promote health. The impact of relationship and these protective factors have been show to have a positive impact on brain function, resulting in children who are better ...
regular course syllabus
... 1. Anatomy of male and female reproductive system 2. Female reproductive cycle 11. Laboratory Outline (taught with diagrams, laboratory manual, specimens and computers) A. Circulatory System (dissection of Sheep heart and cat blood vessels) B. Pulse Rate and Blood Pressure C. Respiratory System (dis ...
... 1. Anatomy of male and female reproductive system 2. Female reproductive cycle 11. Laboratory Outline (taught with diagrams, laboratory manual, specimens and computers) A. Circulatory System (dissection of Sheep heart and cat blood vessels) B. Pulse Rate and Blood Pressure C. Respiratory System (dis ...
neurons
... Function: Dreams provide the sleeping brain with periodic stimulation to develop and preserve ...
... Function: Dreams provide the sleeping brain with periodic stimulation to develop and preserve ...
General integration and regulation of metabolism at the organ level
... one of the largest perfusion changes observed in mammalian tissues. This increase is even more remarkable when one considers that contractile tissues such as heart and skeletal muscle, both arterial and venous vessels, become occluded during the contraction phase, which typically accounts for about ...
... one of the largest perfusion changes observed in mammalian tissues. This increase is even more remarkable when one considers that contractile tissues such as heart and skeletal muscle, both arterial and venous vessels, become occluded during the contraction phase, which typically accounts for about ...
Respiratory Physiology
... The most important function of the lungs is to make arterial blood with PO2 and PCO2 values within normal limits (see Fig. 13-21). Ventilation plays an important role in this process. Bottom line: Alveolar ventilation, relative to the body’s metabolism and considering the composition of the inspired ...
... The most important function of the lungs is to make arterial blood with PO2 and PCO2 values within normal limits (see Fig. 13-21). Ventilation plays an important role in this process. Bottom line: Alveolar ventilation, relative to the body’s metabolism and considering the composition of the inspired ...
Alzheimer`s Disease and it`s Treatment
... accumulation of beta amyloid peptides as the central event triggering neuron degeneration. Accumulation of aggregated amyloid fibrils, which are believed to be the toxic form of the protein responsible for disrupting the cell's calcium ion homeostasis, induces programmed cell death (apoptosis). It i ...
... accumulation of beta amyloid peptides as the central event triggering neuron degeneration. Accumulation of aggregated amyloid fibrils, which are believed to be the toxic form of the protein responsible for disrupting the cell's calcium ion homeostasis, induces programmed cell death (apoptosis). It i ...
The Nervous System
... The symptoms of a shaking palsy were described by a London physician, James Parkinson, in 1817 (Kolb & Whishaw, 1985), and the syndrome was named for him. The incidence of the disease is about 100 per 100,000 people, and it is higher in older people (Thompson, 1985). Symptoms of Parkinson’s disease ...
... The symptoms of a shaking palsy were described by a London physician, James Parkinson, in 1817 (Kolb & Whishaw, 1985), and the syndrome was named for him. The incidence of the disease is about 100 per 100,000 people, and it is higher in older people (Thompson, 1985). Symptoms of Parkinson’s disease ...
02biologya
... • Axon terminals release neurotransmitter. • Neurotransmitter enters synaptic gap. • Neurotransmitter binds to receptors that it fits. ...
... • Axon terminals release neurotransmitter. • Neurotransmitter enters synaptic gap. • Neurotransmitter binds to receptors that it fits. ...
Haemodynamic response
In haemodynamics, the body must respond to physical activities, external temperature, and other factors by homeostatically adjusting its blood flow to deliver nutrients such as oxygen and glucose to stressed tissues and allow them to function. Haemodynamic response (HR) allows the rapid delivery of blood to active neuronal tissues. Since higher processes in the brain occur almost constantly, cerebral blood flow is essential for the maintenance of neurons, astrocytes, and other cells of the brain.