
Lecture 11a Nervous System
... • Multipolar neurons: – common in the CNS – include all skeletal muscle motor neurons – cell body (soma) – short, branched dendrites ...
... • Multipolar neurons: – common in the CNS – include all skeletal muscle motor neurons – cell body (soma) – short, branched dendrites ...
BSSCA - Ch01
... increased, people are more likely to get both hits and false alarms. These types of tests are often useful as screening instruments that later more expensive and invasive tests will confirm or invalidate the original results (e.g., mammograms as a screening instrument for breast cancer). ➤ Selectivi ...
... increased, people are more likely to get both hits and false alarms. These types of tests are often useful as screening instruments that later more expensive and invasive tests will confirm or invalidate the original results (e.g., mammograms as a screening instrument for breast cancer). ➤ Selectivi ...
Morphological Basis of Learning and Memory: Vertebrates
... underlie learning and memory. Formation, and occasionally loss, of synapses occurs both during periods of development when the brain is storing information and during exposure to specific learning tasks. Various control procedures have largely ruled out the possibility that these synaptic changes ar ...
... underlie learning and memory. Formation, and occasionally loss, of synapses occurs both during periods of development when the brain is storing information and during exposure to specific learning tasks. Various control procedures have largely ruled out the possibility that these synaptic changes ar ...
Psy I Brain and Behavior PPT 2016
... •Any public performance or display, including transmission of any image over a network; •Preparation of any derivative work, including the extraction, in whole or in part, of any images •Any rental, lease or lending of the program. ...
... •Any public performance or display, including transmission of any image over a network; •Preparation of any derivative work, including the extraction, in whole or in part, of any images •Any rental, lease or lending of the program. ...
Warm up Cool down Flexibility
... Increase in temperature has other effects that are beneficial as ...
... Increase in temperature has other effects that are beneficial as ...
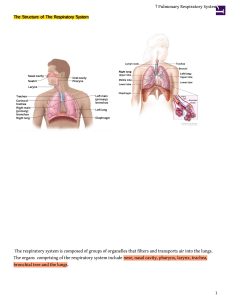
① Pulmonary Respiratory System
... The diaphragm is the most important muscle of inspiration, it inserts into the lower ribs, and is innervated by the phrenic nerves (Cervial plexus, brachial plexus C3-5). During inspiration, the diaphragm contracts and the abdomen moves downward and forward causing ribs to lift outward. This causes ...
... The diaphragm is the most important muscle of inspiration, it inserts into the lower ribs, and is innervated by the phrenic nerves (Cervial plexus, brachial plexus C3-5). During inspiration, the diaphragm contracts and the abdomen moves downward and forward causing ribs to lift outward. This causes ...
Neural control of the circulation - Advances in Physiology Education
... relative strength and pattern of sympathetic discharge (8). Like the autonomic nerves that innervate the heart, the sympathetic nerves innervating the vasculature also display tonic activity, which sets a background level of vasoconstriction. Increasing sympathetic outflow beyond this tonic level ca ...
... relative strength and pattern of sympathetic discharge (8). Like the autonomic nerves that innervate the heart, the sympathetic nerves innervating the vasculature also display tonic activity, which sets a background level of vasoconstriction. Increasing sympathetic outflow beyond this tonic level ca ...
Biosc_48_Chapter_8_lecture_part_1
... 5) Slow-wave is prominent in the first part of sleep, while REM is prominent in the second half ...
... 5) Slow-wave is prominent in the first part of sleep, while REM is prominent in the second half ...
Friday 3rd June - The University of Sydney
... is thought to be additionally influenced by genetic factors. In the past, various studies could show an association of genes such as APP or APOE with AD. In our experiments, we examined single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in three other genes: A2M, APOC1 and TNF. Genomic DNA was extracted from ne ...
... is thought to be additionally influenced by genetic factors. In the past, various studies could show an association of genes such as APP or APOE with AD. In our experiments, we examined single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in three other genes: A2M, APOC1 and TNF. Genomic DNA was extracted from ne ...
Changes in renal physiology
... Significant decrease in serum lamotrigine concentrations; increase in seizure activity unless monitoring and dose adjustment occurs ...
... Significant decrease in serum lamotrigine concentrations; increase in seizure activity unless monitoring and dose adjustment occurs ...
The Synergists: An Exploration of Choreography, Media, and Science
... addition of the live dancer served to create an artificial synapse between the video projection and the live performance which symbolized the dueling aspect between the axon on one end of the synapse and the dendrites on the other end. Both the video projection and the live dancer performed the sam ...
... addition of the live dancer served to create an artificial synapse between the video projection and the live performance which symbolized the dueling aspect between the axon on one end of the synapse and the dendrites on the other end. Both the video projection and the live dancer performed the sam ...
muscles
... • At death, calcium ions are released causing a partial contraction • No new ATP so the muscles can’t relax • Joints become fixed creating the condition known as rigor mortis ...
... • At death, calcium ions are released causing a partial contraction • No new ATP so the muscles can’t relax • Joints become fixed creating the condition known as rigor mortis ...
Nerve Cells - Dr Magrann
... Sensoroy Neurons (afferent neurons) transmit impulses toward the CNS. They originate in the PNS and terminate in the CNS. Motor Neurons (efferent neurons) transmit impulses from the CNS to effector organs (muscles and glands). They originate in the CNS and terminate in the PNS. Interneurons (a ...
... Sensoroy Neurons (afferent neurons) transmit impulses toward the CNS. They originate in the PNS and terminate in the CNS. Motor Neurons (efferent neurons) transmit impulses from the CNS to effector organs (muscles and glands). They originate in the CNS and terminate in the PNS. Interneurons (a ...
C Description of Symposium
... important b) relevant and c) interesting for more than a few specialists in the field. Describe the role of each speaker and what she/he will present and how it complements the other speakers. In other word, we would like to see an overall plan and coherence between the speakers. Like an NSF summary ...
... important b) relevant and c) interesting for more than a few specialists in the field. Describe the role of each speaker and what she/he will present and how it complements the other speakers. In other word, we would like to see an overall plan and coherence between the speakers. Like an NSF summary ...
Lecture Exam 2 Study Guide
... brain require in large quantities? How does the brain respond to hyper- and hypoglycemia? - What is the overall function of gray matter in the spinal cord? What functional types of neurons are found in the dorsal, lateral, and ventral horns? - What is the overall function of white matter in the spin ...
... brain require in large quantities? How does the brain respond to hyper- and hypoglycemia? - What is the overall function of gray matter in the spinal cord? What functional types of neurons are found in the dorsal, lateral, and ventral horns? - What is the overall function of white matter in the spin ...
Peripheral Nervous System
... At least MAG and Nogo are capable of causing growth cone collapse and inhibiting neurite outgrowth in vitro. ...
... At least MAG and Nogo are capable of causing growth cone collapse and inhibiting neurite outgrowth in vitro. ...
The Nervous and Endocrine Systems Review Set
... What type of neurons sent impulses to his muscles? • A. axon • B. motor • C. sensory • D. dendrite ...
... What type of neurons sent impulses to his muscles? • A. axon • B. motor • C. sensory • D. dendrite ...
Read the full press release
... How Many Friends Can a Brain Handle? A more extensive brain network underlies extensive social networks A new study shows that a large network of friends and the highly developed social skills needed to manage it corresponds to certain brain regions that are bigger and better connected than in peopl ...
... How Many Friends Can a Brain Handle? A more extensive brain network underlies extensive social networks A new study shows that a large network of friends and the highly developed social skills needed to manage it corresponds to certain brain regions that are bigger and better connected than in peopl ...
PDF
... were mixed to produce the GFP-loxP-nls sequence, a second loxP site added at the 3⬘ by PCR, and the resulting GFP-loxP-nls-loxP cassette cloned in the p6NST90 plasmid. Primers (supplementary material Table S1) were designed to express the GFP in frame with the nls, and stop codons were added to term ...
... were mixed to produce the GFP-loxP-nls sequence, a second loxP site added at the 3⬘ by PCR, and the resulting GFP-loxP-nls-loxP cassette cloned in the p6NST90 plasmid. Primers (supplementary material Table S1) were designed to express the GFP in frame with the nls, and stop codons were added to term ...
[j26]Chapter 8#
... specialized portions of the brain these action potentials are interpreted, giving us the ability to speak, express emotion, be motivated, move muscles, and remember things. The deeper structures of the brain, such as the thalamus, hypothalamus, and medulla oblongata, are critical interpretive areas ...
... specialized portions of the brain these action potentials are interpreted, giving us the ability to speak, express emotion, be motivated, move muscles, and remember things. The deeper structures of the brain, such as the thalamus, hypothalamus, and medulla oblongata, are critical interpretive areas ...
The nature of neuronal words and language
... period during which time the intracellular negative membrane K+/Na+ potential is restored using energy derived from intracellular stores of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) via a plasma membrane surface enzyme, Na+/K+ ATPase, in order to transport these ions against their respective gradients [4]. In si ...
... period during which time the intracellular negative membrane K+/Na+ potential is restored using energy derived from intracellular stores of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) via a plasma membrane surface enzyme, Na+/K+ ATPase, in order to transport these ions against their respective gradients [4]. In si ...
Inside the Brain
... Functional imaging From reconstructing YouTube clips from brain scans to ‘watching’ a person’s brain as they slip under an anaesthetic, functional brain imaging is producing fascinating insights into how our brains work. ...
... Functional imaging From reconstructing YouTube clips from brain scans to ‘watching’ a person’s brain as they slip under an anaesthetic, functional brain imaging is producing fascinating insights into how our brains work. ...
[j26]Chapter 8#
... specialized portions of the brain these action potentials are interpreted, giving us the ability to speak, express emotion, be motivated, move muscles, and remember things. The deeper structures of the brain, such as the thalamus, hypothalamus, and medulla oblongata, are critical interpretive areas ...
... specialized portions of the brain these action potentials are interpreted, giving us the ability to speak, express emotion, be motivated, move muscles, and remember things. The deeper structures of the brain, such as the thalamus, hypothalamus, and medulla oblongata, are critical interpretive areas ...
Haemodynamic response
In haemodynamics, the body must respond to physical activities, external temperature, and other factors by homeostatically adjusting its blood flow to deliver nutrients such as oxygen and glucose to stressed tissues and allow them to function. Haemodynamic response (HR) allows the rapid delivery of blood to active neuronal tissues. Since higher processes in the brain occur almost constantly, cerebral blood flow is essential for the maintenance of neurons, astrocytes, and other cells of the brain.
















![[j26]Chapter 8#](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015149816_1-9d495749ad340ee903e25aea78e4f4ae-300x300.png)


![[j26]Chapter 8#](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/010706021_1-9baf14474201fd4015c7c6d48d77223e-300x300.png)
