Field Trip Vocabulary List
... coast. They usually occur in chains, consisting of anything from a few islands to more than a dozen. A barrier chain may extend uninterrupted for over a hundred kilometers, the longest and widest being Padre Island. ...
... coast. They usually occur in chains, consisting of anything from a few islands to more than a dozen. A barrier chain may extend uninterrupted for over a hundred kilometers, the longest and widest being Padre Island. ...
Population Dynamics
... relationship between carrying capacity & changes in populations and ecosystems. The student is expected to: (A) relate carrying capacity to population dynamics. (B) Calculate birth rates & exponential growth of populations. (C) Analyze & predict the effects of nonrenewable resource depletion. (D) An ...
... relationship between carrying capacity & changes in populations and ecosystems. The student is expected to: (A) relate carrying capacity to population dynamics. (B) Calculate birth rates & exponential growth of populations. (C) Analyze & predict the effects of nonrenewable resource depletion. (D) An ...
BIOLOGY 4.2 Niches and Community Interactions The Niche • A
... every environmental factor. Beyond those limits, the organism cannot survive. ...
... every environmental factor. Beyond those limits, the organism cannot survive. ...
interactions in the ecosystem
... Elephants eat many tons of plants each day and need a lot water to drink and cool themselves with. Only one female in each family has a baby – the rest of the females help care for the young ...
... Elephants eat many tons of plants each day and need a lot water to drink and cool themselves with. Only one female in each family has a baby – the rest of the females help care for the young ...
Community Composition, Interactions, and Productivity
... 6) Productivity (timing and location coincident with recruitment). ...
... 6) Productivity (timing and location coincident with recruitment). ...
1 - Cloudfront.net
... as a population gets larger, it also grows larger; shown as a curve line how populations grow include five stages ...
... as a population gets larger, it also grows larger; shown as a curve line how populations grow include five stages ...
Ecological Relationship Notes
... common predator. o Mullerian mimcry - natural phenomenon in which two or more poisonous species, that may or may not be closely related and share one or more common predators, have come to mimic each other's warning signals. ...
... common predator. o Mullerian mimcry - natural phenomenon in which two or more poisonous species, that may or may not be closely related and share one or more common predators, have come to mimic each other's warning signals. ...
Life and the Environment
... • The non-living features or conditions of the environment. • Ex: soil, water, light, air and temperature. • Have effects on living things and often determine the organisms that are able to live in a certain environment. ...
... • The non-living features or conditions of the environment. • Ex: soil, water, light, air and temperature. • Have effects on living things and often determine the organisms that are able to live in a certain environment. ...
Title - Iowa State University
... C) The trophic structure of a community describes abiotic factors such as rainfall and temperature affecting members of the community. D) Ecologists refer to species richness as the number of species within a community. E) Many plant species in communities seem to be independently distributed. 8) Co ...
... C) The trophic structure of a community describes abiotic factors such as rainfall and temperature affecting members of the community. D) Ecologists refer to species richness as the number of species within a community. E) Many plant species in communities seem to be independently distributed. 8) Co ...
Carrying Capacity of Ecosystems
... Often competition results in the reduction or complete elimination of one species from the area due to competitive exclusion. ...
... Often competition results in the reduction or complete elimination of one species from the area due to competitive exclusion. ...
Unit 5
... Fundamental niche is the niche that an organism occupies in the absence of competing species. Realized niche is that part of their existence where niche overlap is absent. Distinguish between Batesian mimicry and Mullerian mimicry. Betesian mimicry occurs when an animal without any special defense ...
... Fundamental niche is the niche that an organism occupies in the absence of competing species. Realized niche is that part of their existence where niche overlap is absent. Distinguish between Batesian mimicry and Mullerian mimicry. Betesian mimicry occurs when an animal without any special defense ...
ecological succession
... Biotic potential: ظرفیت رشد جمعیت در شرایط ائده آل:توان حیات is the capacity for population growth under ideal conditions Generally large species have low B.P. Such as elephants and small individuals have high B.P. such as bacteria. ...
... Biotic potential: ظرفیت رشد جمعیت در شرایط ائده آل:توان حیات is the capacity for population growth under ideal conditions Generally large species have low B.P. Such as elephants and small individuals have high B.P. such as bacteria. ...
Chapter 53 - TeacherWeb
... 13. Explain the relationship between species richness and relative abundance and explain how both contribute to species diversity. 14. Distinguish between a food chain and a food web. 15. Describe two ways to simplify food webs. 16. Summarize two hypotheses that explain why food chains are relativel ...
... 13. Explain the relationship between species richness and relative abundance and explain how both contribute to species diversity. 14. Distinguish between a food chain and a food web. 15. Describe two ways to simplify food webs. 16. Summarize two hypotheses that explain why food chains are relativel ...
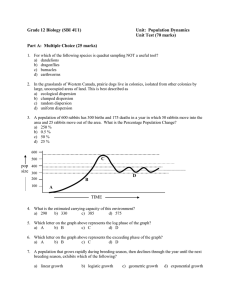
Grade 12 Biology (SBI 4U1)
... a) a type I survivorship pattern b) a type II survivorship pattern c) a type III survivorship pattern d) a type IV survivorship pattern 11. A population with very high mortality rates among the young and very low mortality rates among sexually mature adults exhibits which of the following? a) a type ...
... a) a type I survivorship pattern b) a type II survivorship pattern c) a type III survivorship pattern d) a type IV survivorship pattern 11. A population with very high mortality rates among the young and very low mortality rates among sexually mature adults exhibits which of the following? a) a type ...
Testing the Effects of Climate Change on the Competitive Ability of
... Canada, two invasive species, Spotted Knapweed (Centaurea stoebe) and, Yellow Toadflax (Linaria vulgaris) are of particular concern. The objective of this study was to determine the competitive effect of Spotted Knapweed, and Yellow Toadflax, on two native grasses and on each other under differen ...
... Canada, two invasive species, Spotted Knapweed (Centaurea stoebe) and, Yellow Toadflax (Linaria vulgaris) are of particular concern. The objective of this study was to determine the competitive effect of Spotted Knapweed, and Yellow Toadflax, on two native grasses and on each other under differen ...
Ecology
... Carrying Capacity When a population reaches a state where it can no longer grow, the population has reached it’s carrying capacity, or the maximum number of individuals that an ecosystem can support. An ecosystem’s carrying capacity is different for each population. ...
... Carrying Capacity When a population reaches a state where it can no longer grow, the population has reached it’s carrying capacity, or the maximum number of individuals that an ecosystem can support. An ecosystem’s carrying capacity is different for each population. ...
Ecology
... Carrying Capacity When a population reaches a state where it can no longer grow, the population has reached it’s carrying capacity, or the maximum number of individuals that an ecosystem can support. An ecosystem’s carrying capacity is different for each population. ...
... Carrying Capacity When a population reaches a state where it can no longer grow, the population has reached it’s carrying capacity, or the maximum number of individuals that an ecosystem can support. An ecosystem’s carrying capacity is different for each population. ...
biological diversity
... • Genetic diversity - occurs within organisms at a cellular level, as it describes the variety of genetic material in all living things. Genetic diversity is variation of individual genes, which provides an opportunity for populations of organisms to adapt to their ever-changing environment. The mor ...
... • Genetic diversity - occurs within organisms at a cellular level, as it describes the variety of genetic material in all living things. Genetic diversity is variation of individual genes, which provides an opportunity for populations of organisms to adapt to their ever-changing environment. The mor ...
Ecology Review Questions - Wahconah Science Department
... detritivores, decomposers) important in moving these elements from one form to another? f) How have humans influenced each cycle? 14. How are bioremediation and bioaugmentation used to restore degraded ecosystems? 15. What is biodiversity, what are the four main factors that threaten it, and what ro ...
... detritivores, decomposers) important in moving these elements from one form to another? f) How have humans influenced each cycle? 14. How are bioremediation and bioaugmentation used to restore degraded ecosystems? 15. What is biodiversity, what are the four main factors that threaten it, and what ro ...
Chapter 1 - Kennedy APES
... In order to study nature better, scientists have organized it into increasing levels of complexity. Distinguish between each level: What does this level consist of? What do scientists study at this level? Individual ...
... In order to study nature better, scientists have organized it into increasing levels of complexity. Distinguish between each level: What does this level consist of? What do scientists study at this level? Individual ...
Test Questions Biology
... 24. Elephants and other large herbivores trample many species of plants that are different from the plant species they eat. The relationship between the elephants and the trampled plant species is an example of a. predation. b. mutualism. c. parasitism. d. commensalism. e. amensalism. 25. A single b ...
... 24. Elephants and other large herbivores trample many species of plants that are different from the plant species they eat. The relationship between the elephants and the trampled plant species is an example of a. predation. b. mutualism. c. parasitism. d. commensalism. e. amensalism. 25. A single b ...
Populations and Communities
... 4. The potential growth of a population, if it could grow in perfect conditions with no limiting factors, is the population’s ...
... 4. The potential growth of a population, if it could grow in perfect conditions with no limiting factors, is the population’s ...
Chapter 24
... inference can you make about the climate there? How have plants adapted to that environment? How are those adaptations different from costal ...
... inference can you make about the climate there? How have plants adapted to that environment? How are those adaptations different from costal ...
Three Key Features of Populations Size
... • The maximum population size that can be supported by the available resources • There can only be as many organisms as the environmental resources can support ...
... • The maximum population size that can be supported by the available resources • There can only be as many organisms as the environmental resources can support ...