Unit 3: Plate Tectonics: Test Review
... Divergent, because it is spreading. 30. Is new crust created, destroyed or neither? Created 31. What happens when continental crust meets continental crust? Mountains ...
... Divergent, because it is spreading. 30. Is new crust created, destroyed or neither? Created 31. What happens when continental crust meets continental crust? Mountains ...
An earthquake is the vibration of the Earth that results in a
... Earthquakes are caused mostly by rupture of geological faults, but also by volcanic activity, landslides, mine blasts, dams (waterquakes), and ...
... Earthquakes are caused mostly by rupture of geological faults, but also by volcanic activity, landslides, mine blasts, dams (waterquakes), and ...
PPT - California State University, Northridge
... - Second largest recorded on Earth - Major damage in Sumatra - Tsunami damage spread far to Indonesia, Thailand, Sri Lanka, India, East Africa - Death toll 220,000 from force of tsunami wave - Tsunami movie ...
... - Second largest recorded on Earth - Major damage in Sumatra - Tsunami damage spread far to Indonesia, Thailand, Sri Lanka, India, East Africa - Death toll 220,000 from force of tsunami wave - Tsunami movie ...
Unit 6 -- Earthquakes Vocabulary
... earthquake – vibrations in the earth caused by rocks under stress suddenly shifting along a fault focus – the source point of the earthquake epicenter – the surface location directly above the focus seismograph -- instrument that measures seismic waves seismogram – paper recording of seismic waves ...
... earthquake – vibrations in the earth caused by rocks under stress suddenly shifting along a fault focus – the source point of the earthquake epicenter – the surface location directly above the focus seismograph -- instrument that measures seismic waves seismogram – paper recording of seismic waves ...
Faults
... To put it another way, as the tectonic forces push on the "locked" blocks, potential energy builds When the plates are finally moved, this built-up energy becomes kinetic. Some fault shifts create visible changes at the earth's surface, but other shifts occur in rock well under the surface, and ...
... To put it another way, as the tectonic forces push on the "locked" blocks, potential energy builds When the plates are finally moved, this built-up energy becomes kinetic. Some fault shifts create visible changes at the earth's surface, but other shifts occur in rock well under the surface, and ...
Urška Slivšek, 1.E GIMB PACIFIC NORTHWEST OVERDUE FOR A
... southern portion along Oregon and California breaks every 230 years on average .This paper is important because it is an excellent synthesis of two widely divergent fields of Earth science," . One field is what's called microstratigraphy, which is what allowed for the deciphering of the tidal marshe ...
... southern portion along Oregon and California breaks every 230 years on average .This paper is important because it is an excellent synthesis of two widely divergent fields of Earth science," . One field is what's called microstratigraphy, which is what allowed for the deciphering of the tidal marshe ...
Plate Margin
... Tectonic Activity and Plate Margins– in the right hand column add EXTRA case studies in the empty spaces (with thanks to D McGuinness) Plate Margin NAME Constructive (Spreading or Divergent margins) ...
... Tectonic Activity and Plate Margins– in the right hand column add EXTRA case studies in the empty spaces (with thanks to D McGuinness) Plate Margin NAME Constructive (Spreading or Divergent margins) ...
Magnitude 7.1 MOLUCCA SEA
... Convergent plate boundary Divergent plate boundary Transform plate boundary ...
... Convergent plate boundary Divergent plate boundary Transform plate boundary ...
Lecture 9 Earthquakes
... A. Short answer: 1. Seismic velocities across the _________ - mantle boundary increase dramatically. The difference is referred to as the Mohorovicic Discontinuity. 2. Deeper than about 700 kilometers, higher temperatures and pressures cause stressed rocks to deform ______________, rather than ruptu ...
... A. Short answer: 1. Seismic velocities across the _________ - mantle boundary increase dramatically. The difference is referred to as the Mohorovicic Discontinuity. 2. Deeper than about 700 kilometers, higher temperatures and pressures cause stressed rocks to deform ______________, rather than ruptu ...
Earth Materials
... first movement occurs during an earthquake • Epicenter: The point on the Earth’s surface directly above the focus (this is usually the location reported in the media) ...
... first movement occurs during an earthquake • Epicenter: The point on the Earth’s surface directly above the focus (this is usually the location reported in the media) ...
Earthquakes - NewPathWorksheets.com
... earthquake shakes the “feet” out from under them. Construction engineers are using advanced techniques to minimize, and hopefully eliminate, such structural damage caused by earthquakes. This not only reduces damage and the costs related to that damage, but more importantly it reduces the chances of ...
... earthquake shakes the “feet” out from under them. Construction engineers are using advanced techniques to minimize, and hopefully eliminate, such structural damage caused by earthquakes. This not only reduces damage and the costs related to that damage, but more importantly it reduces the chances of ...
Overview of Technical Program
... Recent Moderate Oklahoma Earthquakes: Widely Felt and Often Damaging Induced Seismicity—The European Perspective Understanding and Modeling Ground Motions and Seismic Hazard from Induced Earthquakes The Future of Past Earthquakes Earthquake Complexities Revealed by Kinematic and Dynamic Modeling and ...
... Recent Moderate Oklahoma Earthquakes: Widely Felt and Often Damaging Induced Seismicity—The European Perspective Understanding and Modeling Ground Motions and Seismic Hazard from Induced Earthquakes The Future of Past Earthquakes Earthquake Complexities Revealed by Kinematic and Dynamic Modeling and ...
Ancient Crete - Hodder Education
... marker of the sea level before the uplift event. Radiocarbon dating of coral and shell samples from this palaeoshoreline show that the uplift is associated with the ad 365 earthquake. By dating such features we can use them to estimate long-term earthquake risk. ...
... marker of the sea level before the uplift event. Radiocarbon dating of coral and shell samples from this palaeoshoreline show that the uplift is associated with the ad 365 earthquake. By dating such features we can use them to estimate long-term earthquake risk. ...
Chapter 6 – Plate Tectonics and Earthquakes
... 2. The Pacific is the largest plate, covering one-fifth of Earth’s surface. ...
... 2. The Pacific is the largest plate, covering one-fifth of Earth’s surface. ...
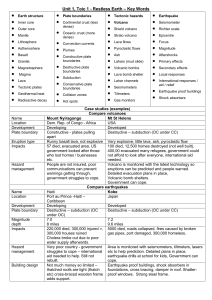
Unit 1 topic 1 revision
... Case studies (examples) Compare volcanoes Mount Nyiragongo Mt St Helens Dem. Rep. of Congo - Africa USA Developing Developed Constructive - plates pulling Destructive – subduction (OC under CC) apart Runny basalt lava, not explosive Very explosive, little lava, ash, pyroclastic flow 57 died, evacuat ...
... Case studies (examples) Compare volcanoes Mount Nyiragongo Mt St Helens Dem. Rep. of Congo - Africa USA Developing Developed Constructive - plates pulling Destructive – subduction (OC under CC) apart Runny basalt lava, not explosive Very explosive, little lava, ash, pyroclastic flow 57 died, evacuat ...
Geologic Time
... • Devised in 1935 by the seismologist C.F. Richter • The magnitude is based on multiples of 10, i.e.,101, 102, 103 each number on the scale is ten times greater than the previous number. For example magnitude 3 is ten times greater than magnitude ...
... • Devised in 1935 by the seismologist C.F. Richter • The magnitude is based on multiples of 10, i.e.,101, 102, 103 each number on the scale is ten times greater than the previous number. For example magnitude 3 is ten times greater than magnitude ...
3How Does Plate Tectonics Explain Earthquakes and Volcanoes?
... This volcano in Iceland gave a fiery display for four months. ...
... This volcano in Iceland gave a fiery display for four months. ...
Chapter 6 Study Guide
... Answer the following questions: 1. The rock most commonly found on oceanic crust is 2. The rock most commonly found on continental crust is 3. Which layer of the earth is partially made of magma? 4. Which physical layer of the earth is made up of tectonic plates? 5. Another name for crust is 6. What ...
... Answer the following questions: 1. The rock most commonly found on oceanic crust is 2. The rock most commonly found on continental crust is 3. Which layer of the earth is partially made of magma? 4. Which physical layer of the earth is made up of tectonic plates? 5. Another name for crust is 6. What ...
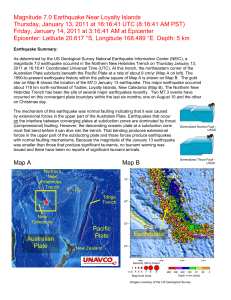
Magnitude 7.0 Earthquake Near Loyalty Islands Thursday
... about 118 km north-northeast of Tadine, Loyalty Islands, New Caledonia (Map B). The Northern New Hebrides Trench has been the site of several major earthquakes recently. Two M7.3 events have occurred on this convergent plate boundary within the last six months; one on August 10 and the other on Chri ...
... about 118 km north-northeast of Tadine, Loyalty Islands, New Caledonia (Map B). The Northern New Hebrides Trench has been the site of several major earthquakes recently. Two M7.3 events have occurred on this convergent plate boundary within the last six months; one on August 10 and the other on Chri ...
Earthquake-Volcano Research Project Rubric
... Clarification on what needs to be in your Project (earthquake/volcano powerpoint). Be sure to include: 1. Names of the main plates (ex. Pacific Plate), the direction of movement (convergent, divergent or transform fault), and the type of plates (ocean or continental). 2. The type of boundary and th ...
... Clarification on what needs to be in your Project (earthquake/volcano powerpoint). Be sure to include: 1. Names of the main plates (ex. Pacific Plate), the direction of movement (convergent, divergent or transform fault), and the type of plates (ocean or continental). 2. The type of boundary and th ...
Henry6SCI3 (H6SCIGEOLOGY)
... 1. The San Andreas Fault in Mexico and California is watched carefully for signs of an expected earthquake. Why do scientists think an earthquake might happen there? A. The chances of a major earthquake in California have increased greatly because there has been so much construction there. B. Everyp ...
... 1. The San Andreas Fault in Mexico and California is watched carefully for signs of an expected earthquake. Why do scientists think an earthquake might happen there? A. The chances of a major earthquake in California have increased greatly because there has been so much construction there. B. Everyp ...
earthquakes
... MAGNITUDE (Wave Amplitude) Richter Scale – based on largest amplitude of a seismic wave from seismograph during an earthquake An increase by 1 in magnitude equals 10x increase in amplitude Measure of the amount of energy released Energy released increases 32 x’s for each unit Charles Richter ...
... MAGNITUDE (Wave Amplitude) Richter Scale – based on largest amplitude of a seismic wave from seismograph during an earthquake An increase by 1 in magnitude equals 10x increase in amplitude Measure of the amount of energy released Energy released increases 32 x’s for each unit Charles Richter ...
Earthquake

An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the perceptible shaking of the surface of the Earth, which can be violent enough to destroy major buildings and kill thousands of people. The severity of the shaking can range from barely felt to violent enough to toss people around. Earthquakes have destroyed whole cities. They result from the sudden release of energy in the Earth's crust that creates seismic waves. The seismicity, seismism or seismic activity of an area refers to the frequency, type and size of earthquakes experienced over a period of time.Earthquakes are measured using observations from seismometers. The moment magnitude is the most common scale on which earthquakes larger than approximately 5 are reported for the entire globe. The more numerous earthquakes smaller than magnitude 5 reported by national seismological observatories are measured mostly on the local magnitude scale, also referred to as the Richter magnitude scale. These two scales are numerically similar over their range of validity. Magnitude 3 or lower earthquakes are mostly almost imperceptible or weak and magnitude 7 and over potentially cause serious damage over larger areas, depending on their depth. The largest earthquakes in historic times have been of magnitude slightly over 9, although there is no limit to the possible magnitude. The most recent large earthquake of magnitude 9.0 or larger was a 9.0 magnitude earthquake in Japan in 2011 (as of March 2014), and it was the largest Japanese earthquake since records began. Intensity of shaking is measured on the modified Mercalli scale. The shallower an earthquake, the more damage to structures it causes, all else being equal.At the Earth's surface, earthquakes manifest themselves by shaking and sometimes displacement of the ground. When the epicenter of a large earthquake is located offshore, the seabed may be displaced sufficiently to cause a tsunami. Earthquakes can also trigger landslides, and occasionally volcanic activity.In its most general sense, the word earthquake is used to describe any seismic event — whether natural or caused by humans — that generates seismic waves. Earthquakes are caused mostly by rupture of geological faults, but also by other events such as volcanic activity, landslides, mine blasts, and nuclear tests. An earthquake's point of initial rupture is called its focus or hypocenter. The epicenter is the point at ground level directly above the hypocenter.