Chapter 8 Earthquakes and Earth’s Interior
... Based on the height of the largest wave Familiar but outdated tool A tenfold increase in wave height equals an increase of 1 on the magnitude scale For example: a 5.0 quake is ten times greater than a 4.0 quake ...
... Based on the height of the largest wave Familiar but outdated tool A tenfold increase in wave height equals an increase of 1 on the magnitude scale For example: a 5.0 quake is ten times greater than a 4.0 quake ...
Earthquake Epicenters Plate Tectonics
... movement. (push-pull like a slinky) • Travel faster than any other wave (6-8 km./s) • Travel through solids, liquids, and gases ...
... movement. (push-pull like a slinky) • Travel faster than any other wave (6-8 km./s) • Travel through solids, liquids, and gases ...
Section 19.1 Forces Within Earth
... floors to fall one on top of the other like a stack of pancakes. • If the shaking caused by an earthquake has the same frequency of vibration as the natural sway of buildings of certain heights, those buildings will sway the most during the earthquake. • Shorter and taller buildings are less likely ...
... floors to fall one on top of the other like a stack of pancakes. • If the shaking caused by an earthquake has the same frequency of vibration as the natural sway of buildings of certain heights, those buildings will sway the most during the earthquake. • Shorter and taller buildings are less likely ...
Chapter 8 Earthquakes and Volcanoes
... Different types of eruptions produce different types of volcanoes. The composition of the magma plays a big part in determining the manner in which energy is released during a volcanic ...
... Different types of eruptions produce different types of volcanoes. The composition of the magma plays a big part in determining the manner in which energy is released during a volcanic ...
guide to earthquakes - part i
... illustrates that the majority of earthquakes are concentrated along the main plate boundaries, particularly larger magnitude events. However, earth surface deformation can also occur across older continental plates causing intraplate earthquakes, such as along the Trans-Alpine belt that extends from ...
... illustrates that the majority of earthquakes are concentrated along the main plate boundaries, particularly larger magnitude events. However, earth surface deformation can also occur across older continental plates causing intraplate earthquakes, such as along the Trans-Alpine belt that extends from ...
Bio-Precursors of Earthquakes and Their Possible Mechanism
... Therefore, we can assume, that prior to powerful earthquakes an increase in speed of vertical shift of Earth’s crust can be observed. In recent years scientists got interested in the anomalous behavior of animals prior to powerful earthquakes. Even though anomalous behavior of animals is long known, ...
... Therefore, we can assume, that prior to powerful earthquakes an increase in speed of vertical shift of Earth’s crust can be observed. In recent years scientists got interested in the anomalous behavior of animals prior to powerful earthquakes. Even though anomalous behavior of animals is long known, ...
B.C. Earthquake
... ACTIVITY: Thinking About the Northern Gateway Pipeline The Northern Gateway project is a proposed $6.5-billion twin pipeline that would carry crude oil from the Athabasca oil sands near Edmonton, Alberta to a marine terminal in Kitimat, British Columbia. From there the oil would be transported to A ...
... ACTIVITY: Thinking About the Northern Gateway Pipeline The Northern Gateway project is a proposed $6.5-billion twin pipeline that would carry crude oil from the Athabasca oil sands near Edmonton, Alberta to a marine terminal in Kitimat, British Columbia. From there the oil would be transported to A ...
JANUARY 2013 — B.C. EARTHQUAKE SETTING THE STAGE On
... The Northern Gateway project is a proposed $6.5-billion twin pipeline that would carry crude oil from the Athabasca oil sands near Edmonton, Alberta to a marine terminal in Kitimat, British Columbia. From there the oil would be transported to Asia via tankers. The pipeline project was first introduc ...
... The Northern Gateway project is a proposed $6.5-billion twin pipeline that would carry crude oil from the Athabasca oil sands near Edmonton, Alberta to a marine terminal in Kitimat, British Columbia. From there the oil would be transported to Asia via tankers. The pipeline project was first introduc ...
plate tectonics - British Academy Wiki
... •Stress builds up at a constant rate but only released periodically. •As the build-up pressure is constant, it is expected the released of pressure (earthquake) occurs regularly. •By using historical records and geological evidence (i.e. fault) scientist able to plot recurrences of earthquakes and u ...
... •Stress builds up at a constant rate but only released periodically. •As the build-up pressure is constant, it is expected the released of pressure (earthquake) occurs regularly. •By using historical records and geological evidence (i.e. fault) scientist able to plot recurrences of earthquakes and u ...
the File
... Write a sentence summarizing the relationship between the location of most earthquakes, volcanoes, mountain ranges and plate boundaries. ...
... Write a sentence summarizing the relationship between the location of most earthquakes, volcanoes, mountain ranges and plate boundaries. ...
Regents Earth Science – Unit 11: The Dynamic Crust
... Fossils of shallow water animals found at great depths in the oceans indicate crust “submergence” ...
... Fossils of shallow water animals found at great depths in the oceans indicate crust “submergence” ...
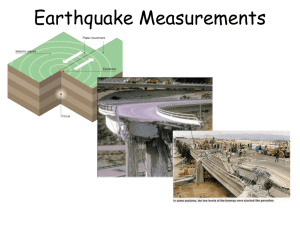
Earthquake Measurements
... A value of 7.7 is from the ______, while a value of VII is from the ______. Richter Scale/MMS or MMS/Richter Scale ...
... A value of 7.7 is from the ______, while a value of VII is from the ______. Richter Scale/MMS or MMS/Richter Scale ...
2How Do Volcanoes and Earthquakes Change Landforms?
... deep inside the earth. The magma is squeezed up through the crust. Sometimes, the magma breaks through the ground. Magma that comes above ground is called lava.' As lava cools, it hardens. This hardened lava can build a mountain called a volcano. Volcanoes erupt in different ways. When the volcano b ...
... deep inside the earth. The magma is squeezed up through the crust. Sometimes, the magma breaks through the ground. Magma that comes above ground is called lava.' As lava cools, it hardens. This hardened lava can build a mountain called a volcano. Volcanoes erupt in different ways. When the volcano b ...
131025japan - earthjay science
... This convergent plate boundary hosts moderate to large earthquakes fairly regularly. Historic events include the M9.0 Tohoku earthquake of March 11, 2011 that ruptured a large area of the plate boundary northwest of this earthquake. ...
... This convergent plate boundary hosts moderate to large earthquakes fairly regularly. Historic events include the M9.0 Tohoku earthquake of March 11, 2011 that ruptured a large area of the plate boundary northwest of this earthquake. ...
Lecture 12 Earthquake Magnitude October 20th
... Some facts and figures: Area involved was along the boundary of the N. American and Pacific plates for about 500 miles (subduction zone). Largest recorded disturbance of the earth’s surface in an arc 500 miles long and 200 miles wide (100,000 sq. miles). Average uplift = 6 feet; maximum uplift ...
... Some facts and figures: Area involved was along the boundary of the N. American and Pacific plates for about 500 miles (subduction zone). Largest recorded disturbance of the earth’s surface in an arc 500 miles long and 200 miles wide (100,000 sq. miles). Average uplift = 6 feet; maximum uplift ...
Classroom Activities KS2 A3
... facts about the August 2016 Italy Earthquake. 3. Cut out and use this map to describe the location of the earthquake. Convergent Boundary ...
... facts about the August 2016 Italy Earthquake. 3. Cut out and use this map to describe the location of the earthquake. Convergent Boundary ...
Impact on Landscape and Population
... Earthquakes are mainly found along the boundaries of tectonic plates as shown on the map above. There are bands of earthquakes found all around the Pacific Ocean e.g. Japan which is known as the Pacific ring of fire. The West coasts of North and South America are in earthquake zones as is the midAtl ...
... Earthquakes are mainly found along the boundaries of tectonic plates as shown on the map above. There are bands of earthquakes found all around the Pacific Ocean e.g. Japan which is known as the Pacific ring of fire. The West coasts of North and South America are in earthquake zones as is the midAtl ...
The Effects of Plate Movements
... • Faulting - a __________________________ where there has been movement and displacement. Caused by a shifting or dislodging of the ____________________, in which adjacent surfaces are displaced. Earthquakes: • Occur when two plates that are locked suddenly rub passed each other ...
... • Faulting - a __________________________ where there has been movement and displacement. Caused by a shifting or dislodging of the ____________________, in which adjacent surfaces are displaced. Earthquakes: • Occur when two plates that are locked suddenly rub passed each other ...
Integrated Science Chapter 19 Name
... 12. A cinder cone volcano is caused by a. converging plates b. diverging plates c. large amounts of gas trapped in t he magma d. vents 13. The breakage of rocks along a fault releases energy in the form of a. P waves b. Seismic waves c. Heat d. Light 14. Waves that cause the most damage during an ea ...
... 12. A cinder cone volcano is caused by a. converging plates b. diverging plates c. large amounts of gas trapped in t he magma d. vents 13. The breakage of rocks along a fault releases energy in the form of a. P waves b. Seismic waves c. Heat d. Light 14. Waves that cause the most damage during an ea ...
Mount Pinatubo and the Ring of Fire
... earthquake devastated cities for hundreds of miles around, and killed more than 1,600 people. Yet the destruction was not over. Two weeks later, residents of Luzon discovered steam coming out of a volcano called Mount Pinatubo. But when scientists inspected the volcano, they did not ...
... earthquake devastated cities for hundreds of miles around, and killed more than 1,600 people. Yet the destruction was not over. Two weeks later, residents of Luzon discovered steam coming out of a volcano called Mount Pinatubo. But when scientists inspected the volcano, they did not ...
What is an earthquake - GDTL CDU E
... Earthquakes are the shaking, rolling or sudden shock of the earth’s surface. They are the Earth's natural means of releasing stress. More than a million earthquakes rattle the world each year. The epicentre of an earthquake is the point on the Earth's surface directly above the source of the earthqu ...
... Earthquakes are the shaking, rolling or sudden shock of the earth’s surface. They are the Earth's natural means of releasing stress. More than a million earthquakes rattle the world each year. The epicentre of an earthquake is the point on the Earth's surface directly above the source of the earthqu ...
Earthquake

An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the perceptible shaking of the surface of the Earth, which can be violent enough to destroy major buildings and kill thousands of people. The severity of the shaking can range from barely felt to violent enough to toss people around. Earthquakes have destroyed whole cities. They result from the sudden release of energy in the Earth's crust that creates seismic waves. The seismicity, seismism or seismic activity of an area refers to the frequency, type and size of earthquakes experienced over a period of time.Earthquakes are measured using observations from seismometers. The moment magnitude is the most common scale on which earthquakes larger than approximately 5 are reported for the entire globe. The more numerous earthquakes smaller than magnitude 5 reported by national seismological observatories are measured mostly on the local magnitude scale, also referred to as the Richter magnitude scale. These two scales are numerically similar over their range of validity. Magnitude 3 or lower earthquakes are mostly almost imperceptible or weak and magnitude 7 and over potentially cause serious damage over larger areas, depending on their depth. The largest earthquakes in historic times have been of magnitude slightly over 9, although there is no limit to the possible magnitude. The most recent large earthquake of magnitude 9.0 or larger was a 9.0 magnitude earthquake in Japan in 2011 (as of March 2014), and it was the largest Japanese earthquake since records began. Intensity of shaking is measured on the modified Mercalli scale. The shallower an earthquake, the more damage to structures it causes, all else being equal.At the Earth's surface, earthquakes manifest themselves by shaking and sometimes displacement of the ground. When the epicenter of a large earthquake is located offshore, the seabed may be displaced sufficiently to cause a tsunami. Earthquakes can also trigger landslides, and occasionally volcanic activity.In its most general sense, the word earthquake is used to describe any seismic event — whether natural or caused by humans — that generates seismic waves. Earthquakes are caused mostly by rupture of geological faults, but also by other events such as volcanic activity, landslides, mine blasts, and nuclear tests. An earthquake's point of initial rupture is called its focus or hypocenter. The epicenter is the point at ground level directly above the hypocenter.