Hotspot volcanoes
... The Hawaiian island chain are examples of hotspot volcanoes. Photo: Tom Pfeiffer / www.volcanodiscovery.com ...
... The Hawaiian island chain are examples of hotspot volcanoes. Photo: Tom Pfeiffer / www.volcanodiscovery.com ...
GCSE Revision session.
... • TOURISM - Potential income from people watching eruptions (eg Stromboli) or visiting dormant and extinct volcanoes. • GEOTHERMAL POWER - Countries like Iceland can generate most of the power they need through geothermal energy. • Other reasons: People do not realise the risk of an eruption. In ma ...
... • TOURISM - Potential income from people watching eruptions (eg Stromboli) or visiting dormant and extinct volcanoes. • GEOTHERMAL POWER - Countries like Iceland can generate most of the power they need through geothermal energy. • Other reasons: People do not realise the risk of an eruption. In ma ...
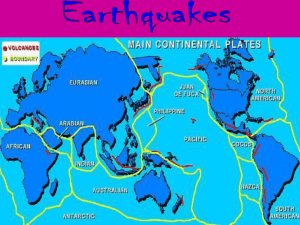
earthquake . ppt - Junction Hill C
... major earthquake before 2030. This forecast is based on years of study of the many faults in the area. The map shows the probability of a quake from each of these faults. ...
... major earthquake before 2030. This forecast is based on years of study of the many faults in the area. The map shows the probability of a quake from each of these faults. ...
Shaken Beliefs: Seismic Lessons from Japan’s Tohoku Earthquake
... same principle—the downward kick stroke requires high static friction, while the glide is possible thanks to low dynamic friction. ...
... same principle—the downward kick stroke requires high static friction, while the glide is possible thanks to low dynamic friction. ...
SUBDUCTION boundaries
... As new crust forms at the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, the Atlantic Ocean is gradually getting bigger This is called ______ ...
... As new crust forms at the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, the Atlantic Ocean is gradually getting bigger This is called ______ ...
Chapter 8: Major Elements
... The “suture zone” is marked by the mélange and become incorporated into the “mélange” in the particularly by the occurrence of ultramafic rocks accretionary wedge of deformed sediments composing the mantle portion of the ocean lithosphere ...
... The “suture zone” is marked by the mélange and become incorporated into the “mélange” in the particularly by the occurrence of ultramafic rocks accretionary wedge of deformed sediments composing the mantle portion of the ocean lithosphere ...
Earthquakes!!!!!
... The point deep within the crust where plate contact is made is called the focus. The point on the Earth’s surface (directly above the focus) is called the epicenter. ...
... The point deep within the crust where plate contact is made is called the focus. The point on the Earth’s surface (directly above the focus) is called the epicenter. ...
Plate Tectonics - West Derby School
... Study the causes and effects of a named earthquake. Bam earthquake, 2003 A large fracture in the earth’s crust, called the Bam fault, runs from north to south in the Kerman province in Iran, making earthquakes common in this area. The earthquakes in this region occur as the result of stresses at the ...
... Study the causes and effects of a named earthquake. Bam earthquake, 2003 A large fracture in the earth’s crust, called the Bam fault, runs from north to south in the Kerman province in Iran, making earthquakes common in this area. The earthquakes in this region occur as the result of stresses at the ...
Overhead: Continental Drift / Plate Tectonics
... together into one supercontinent called Pangaea • About 200 million years ago Pangaea began to break up, with each tectonic plate moving in a different direction. ...
... together into one supercontinent called Pangaea • About 200 million years ago Pangaea began to break up, with each tectonic plate moving in a different direction. ...
Pacific ring of fire and earthquake intro
... • The majority of tectonic earthquakes originate at depths not exceeding tens of kilometers. • In subduction zones, where old and cold oceanic crust descends beneath another tectonic plate, “Deep Focus Earthquakes” may occur at much greater depths (up to seven hundred kilometers!). • These earthquak ...
... • The majority of tectonic earthquakes originate at depths not exceeding tens of kilometers. • In subduction zones, where old and cold oceanic crust descends beneath another tectonic plate, “Deep Focus Earthquakes” may occur at much greater depths (up to seven hundred kilometers!). • These earthquak ...
Ch._19
... in rocks when _____. 1. stress equals the strength of the rocks involved 2. stress overcomes the strength of the rocks ...
... in rocks when _____. 1. stress equals the strength of the rocks involved 2. stress overcomes the strength of the rocks ...
Earthquakes and volcanoes
... Continent-Oceanic Crust Collision • Called SUBDUCTION and creates a volcano ...
... Continent-Oceanic Crust Collision • Called SUBDUCTION and creates a volcano ...
Frequently Asked Questions on Seismic and Volcanic Hazards in
... generates earthquakes and volcanic eruptions. Dominica will continue to experience earthquakes and its volcanoes will continue to be restless, therefore, residents should ensure that they know how to protect themselves during earthquakes. Can volcanic activity in the northern part of Dominica cause ...
... generates earthquakes and volcanic eruptions. Dominica will continue to experience earthquakes and its volcanoes will continue to be restless, therefore, residents should ensure that they know how to protect themselves during earthquakes. Can volcanic activity in the northern part of Dominica cause ...
Earthquakes
... Write down these questions and answer them in complete sentences. 1. What do you think causes an EQ? 2. EQs occur along what cracks in Earth? ...
... Write down these questions and answer them in complete sentences. 1. What do you think causes an EQ? 2. EQs occur along what cracks in Earth? ...
Plate Tectonics - Nutley Public Schools
... Ductile: describes objects that bend, stretch, or flow when a force is applied to them Fault: a fracture in bedrock, along which blocks of rock on opposite sides of the fracture move Ex. San Andreas Fault, California Plate Tectonics: Theory that lithosphere is broken into segments/plates that ...
... Ductile: describes objects that bend, stretch, or flow when a force is applied to them Fault: a fracture in bedrock, along which blocks of rock on opposite sides of the fracture move Ex. San Andreas Fault, California Plate Tectonics: Theory that lithosphere is broken into segments/plates that ...
earthquakes… - White Plains Public Schools
... the existence of this kind of wave in 1885. A Rayleigh wave rolls along the ground just like a wave rolls across a lake or an ocean. Because it rolls, it moves the ground up and down, and side-to-side in the same direction that the wave is moving. Most of the shaking felt from an earthquake is due t ...
... the existence of this kind of wave in 1885. A Rayleigh wave rolls along the ground just like a wave rolls across a lake or an ocean. Because it rolls, it moves the ground up and down, and side-to-side in the same direction that the wave is moving. Most of the shaking felt from an earthquake is due t ...
Chapter 15
... • The point where the actual movement of the plates takes place, and where the energy is released from is called the focus • The point on the Earth’s surface that is directly above the focus is called the epicenter • When an earthquake occurs, energy waves are released and move outward from the foc ...
... • The point where the actual movement of the plates takes place, and where the energy is released from is called the focus • The point on the Earth’s surface that is directly above the focus is called the epicenter • When an earthquake occurs, energy waves are released and move outward from the foc ...
Chapter 10: Earthquakes & The Earth’s Interior
... produced by the rapid release of energy Energy ...
... produced by the rapid release of energy Energy ...
Section 1.0 Practice Test
... An earthquake in Japan registers on a seismograph in Winnipeg, Manitoba. This occurs because ... seismographs anywhere will record all earthquakes the earth's crust is solid, allowing the surface waves to be recorded anywhere seismic waves travel through all the layers of the Earth the core of the e ...
... An earthquake in Japan registers on a seismograph in Winnipeg, Manitoba. This occurs because ... seismographs anywhere will record all earthquakes the earth's crust is solid, allowing the surface waves to be recorded anywhere seismic waves travel through all the layers of the Earth the core of the e ...
Document
... a. Name the 7 major (primary) plates and the minor plate with the coolest name. How do convection currents relate to the plate movements? 6. For each of the following plate boundaries, describe the characteristics of the boundary and the natural hazards / geologic processes that tend to be associate ...
... a. Name the 7 major (primary) plates and the minor plate with the coolest name. How do convection currents relate to the plate movements? 6. For each of the following plate boundaries, describe the characteristics of the boundary and the natural hazards / geologic processes that tend to be associate ...
FAMILY EARTHQUAKE DRILLS (contd.)
... INTRODUCTION • An earthquake is a series of vibrations on the earth's surface caused by the generation of elastic (seismic) waves due to sudden rupture within the earth during release of accumulated strain energy. • The earth’s different layers are in constant motion, their movement is due to many ...
... INTRODUCTION • An earthquake is a series of vibrations on the earth's surface caused by the generation of elastic (seismic) waves due to sudden rupture within the earth during release of accumulated strain energy. • The earth’s different layers are in constant motion, their movement is due to many ...
File - Sciences and Discoveries in Europe
... Earthquakes can destroy buildings and other structures. Buildings that could withstand an earthquake would cause much less injury and death in an earthquake. Engineers have to build stronger, safer buildings that could resist an earthquake. ...
... Earthquakes can destroy buildings and other structures. Buildings that could withstand an earthquake would cause much less injury and death in an earthquake. Engineers have to build stronger, safer buildings that could resist an earthquake. ...
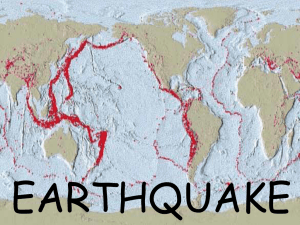
Earthquake

An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the perceptible shaking of the surface of the Earth, which can be violent enough to destroy major buildings and kill thousands of people. The severity of the shaking can range from barely felt to violent enough to toss people around. Earthquakes have destroyed whole cities. They result from the sudden release of energy in the Earth's crust that creates seismic waves. The seismicity, seismism or seismic activity of an area refers to the frequency, type and size of earthquakes experienced over a period of time.Earthquakes are measured using observations from seismometers. The moment magnitude is the most common scale on which earthquakes larger than approximately 5 are reported for the entire globe. The more numerous earthquakes smaller than magnitude 5 reported by national seismological observatories are measured mostly on the local magnitude scale, also referred to as the Richter magnitude scale. These two scales are numerically similar over their range of validity. Magnitude 3 or lower earthquakes are mostly almost imperceptible or weak and magnitude 7 and over potentially cause serious damage over larger areas, depending on their depth. The largest earthquakes in historic times have been of magnitude slightly over 9, although there is no limit to the possible magnitude. The most recent large earthquake of magnitude 9.0 or larger was a 9.0 magnitude earthquake in Japan in 2011 (as of March 2014), and it was the largest Japanese earthquake since records began. Intensity of shaking is measured on the modified Mercalli scale. The shallower an earthquake, the more damage to structures it causes, all else being equal.At the Earth's surface, earthquakes manifest themselves by shaking and sometimes displacement of the ground. When the epicenter of a large earthquake is located offshore, the seabed may be displaced sufficiently to cause a tsunami. Earthquakes can also trigger landslides, and occasionally volcanic activity.In its most general sense, the word earthquake is used to describe any seismic event — whether natural or caused by humans — that generates seismic waves. Earthquakes are caused mostly by rupture of geological faults, but also by other events such as volcanic activity, landslides, mine blasts, and nuclear tests. An earthquake's point of initial rupture is called its focus or hypocenter. The epicenter is the point at ground level directly above the hypocenter.