Plate Boundaries
... As the sea floor spreads away from a mid-ocean ridge, it carries with it a record of magnetic reversals. ...
... As the sea floor spreads away from a mid-ocean ridge, it carries with it a record of magnetic reversals. ...
Location of earthquakes around the world.
... plates stick together and then energy builds up. When the plates finally break apart an earthquake is caused. ...
... plates stick together and then energy builds up. When the plates finally break apart an earthquake is caused. ...
EARTH: natural disasters
... the United States Geological Survey. It was the largest ever to rock Japan. Japan’s tremor was nearly 8,000 times as strong as the one that devastated Christchurch, New Zealand, one month earlier. Japan has experienced many earthquakes in the past, so the country was better prepared than most for su ...
... the United States Geological Survey. It was the largest ever to rock Japan. Japan’s tremor was nearly 8,000 times as strong as the one that devastated Christchurch, New Zealand, one month earlier. Japan has experienced many earthquakes in the past, so the country was better prepared than most for su ...
Deep Focus Earthquake
... Mercalli Scale- Scale that expresses the intensity of an earthquake Intensity- the amount of damage caused •Any given earthquake can be described by only one magnitude, but many intensities: •the earthquake effects vary with circumstances such as distance from the epicenter, quality of buildings an ...
... Mercalli Scale- Scale that expresses the intensity of an earthquake Intensity- the amount of damage caused •Any given earthquake can be described by only one magnitude, but many intensities: •the earthquake effects vary with circumstances such as distance from the epicenter, quality of buildings an ...
subduction zone
... causes them to stick together. When built up energy causes them to break, earthquakes ...
... causes them to stick together. When built up energy causes them to break, earthquakes ...
Video Script: Volcanoes and Earthquakes
... 19. Strong forces within the earthʼs crust may cause rocks to bend and to build up stress and tension over time. 20. When stress exceeds the strength of the rock, the rock breaks or moves along planes called faults. 21. This sudden movement in the earthʼs crust generates waves of energy, which trave ...
... 19. Strong forces within the earthʼs crust may cause rocks to bend and to build up stress and tension over time. 20. When stress exceeds the strength of the rock, the rock breaks or moves along planes called faults. 21. This sudden movement in the earthʼs crust generates waves of energy, which trave ...
12.2 PPT - gessramsey
... Since rock slides past rock, no mountains or Transform boundary volcanoes form. Earthquakes and faults are very common. ...
... Since rock slides past rock, no mountains or Transform boundary volcanoes form. Earthquakes and faults are very common. ...
12.2 PPT
... Since rock slides past rock, no mountains or Transform boundary volcanoes form. Earthquakes and faults are very common. ...
... Since rock slides past rock, no mountains or Transform boundary volcanoes form. Earthquakes and faults are very common. ...
Richter scale - Plain Local Schools
... the energy released by the earthquake Richter scale=measurement of energy released based upon wave amplitude (size of vibration) ...
... the energy released by the earthquake Richter scale=measurement of energy released based upon wave amplitude (size of vibration) ...
chapter 8 - Team Strength
... 41. A chain of small volcanic islands that forms when two oceanic plates converge, one descending beneath the other, is called a(n) ____________________. 42. Earthquakes associated with divergent boundaries have ____________________ foci. 43. The primary forces that cause plate motion are made possi ...
... 41. A chain of small volcanic islands that forms when two oceanic plates converge, one descending beneath the other, is called a(n) ____________________. 42. Earthquakes associated with divergent boundaries have ____________________ foci. 43. The primary forces that cause plate motion are made possi ...
AICE Env Day 1 Types of Faults Foldable Booklet
... turn, pushes up against the hanging wall. These faults occur where the crust is being pulled apart, at a divergent plate boundary. Reverse Fault The fault plane in a reverse fault is also nearly vertical, but the hanging wall pushes up, and the footwall pushes down. This sort of fault forms where a ...
... turn, pushes up against the hanging wall. These faults occur where the crust is being pulled apart, at a divergent plate boundary. Reverse Fault The fault plane in a reverse fault is also nearly vertical, but the hanging wall pushes up, and the footwall pushes down. This sort of fault forms where a ...
Chapter 2 PPT
... Accurate measurements for small, nearby earthquakes not large, distant earthquakes ...
... Accurate measurements for small, nearby earthquakes not large, distant earthquakes ...
We used results of other geophysical surveys (shallow seismic
... Shallow seismic activity with magnitudes up to 2.9 and intensities V MM has been observed in the Bebedouro rural area, Northeast of São Paulo State, Brazil, since 2004, near deep wells (120–200 m) that were drilled in early 2003. The wells were drilled for irrigation purposes, cross a sandstone laye ...
... Shallow seismic activity with magnitudes up to 2.9 and intensities V MM has been observed in the Bebedouro rural area, Northeast of São Paulo State, Brazil, since 2004, near deep wells (120–200 m) that were drilled in early 2003. The wells were drilled for irrigation purposes, cross a sandstone laye ...
Part A
... d) time at which waves arrive at the device 25. The minimum number of seismograph stations usually required to give the location for an epicentre is a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 4 26. A seismograph cannot be used to a) predict earthquakes b) record time of wave arrivals c) calculate distance to the epicentre d ...
... d) time at which waves arrive at the device 25. The minimum number of seismograph stations usually required to give the location for an epicentre is a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 4 26. A seismograph cannot be used to a) predict earthquakes b) record time of wave arrivals c) calculate distance to the epicentre d ...
Activity 47: Spreading Plates
... changes, such as a wider valley and the formation of the first volcano. 3. a. In 1,000 years there will still be 7 continents because plates don’t move that far in 1,000 years. ...
... changes, such as a wider valley and the formation of the first volcano. 3. a. In 1,000 years there will still be 7 continents because plates don’t move that far in 1,000 years. ...
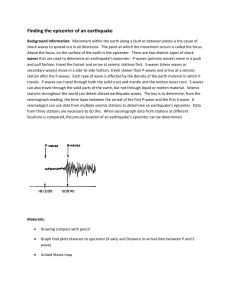
Finding the epicenter of an earthquake Background Information
... Background Information: Movement within the earth along a fault or between plates is the cause of shock waves to spread out in all directions. The point at which the movement occurs is called the focus. Above the focus, on the surface of the earth is the epicenter. There are two distinct types of sh ...
... Background Information: Movement within the earth along a fault or between plates is the cause of shock waves to spread out in all directions. The point at which the movement occurs is called the focus. Above the focus, on the surface of the earth is the epicenter. There are two distinct types of sh ...
Plate Tectonics 10.2
... What lies beneath the tectonic plates? • Below the lithosphere (which makes up the tectonic plates) is the asthenosphere. – Lower part of mantel – Mantel has molten rock (magma) ...
... What lies beneath the tectonic plates? • Below the lithosphere (which makes up the tectonic plates) is the asthenosphere. – Lower part of mantel – Mantel has molten rock (magma) ...
DEEP ELECTRICAL STRUCTURE ACROSS BHUJ EARTHQUAKE
... Caldarusani-Tulnici, in the nearness of the Intramoesian active fault and at about 140 km far from the seismogenic slab. In this paper, the seismicity of the Vrancea area, the high sensitive (magnetotelluric and magnetovariation) equipment and a specific electromagnetic (EM) methodology are presente ...
... Caldarusani-Tulnici, in the nearness of the Intramoesian active fault and at about 140 km far from the seismogenic slab. In this paper, the seismicity of the Vrancea area, the high sensitive (magnetotelluric and magnetovariation) equipment and a specific electromagnetic (EM) methodology are presente ...
Invited speaker Topic 2 Professor Shuichi Hasegawa Georisks
... Georisks along active faults of Median Tectonic Line in Shikoku, Southwest Japan The Median Tectonic Line (MTL) is one of the most predominant and active faults in Japan. The MTL marks striking contrast in topography between the mountains and alluvial plains in Shikoku, Southwest Japan. The active f ...
... Georisks along active faults of Median Tectonic Line in Shikoku, Southwest Japan The Median Tectonic Line (MTL) is one of the most predominant and active faults in Japan. The MTL marks striking contrast in topography between the mountains and alluvial plains in Shikoku, Southwest Japan. The active f ...
Earthquake

An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the perceptible shaking of the surface of the Earth, which can be violent enough to destroy major buildings and kill thousands of people. The severity of the shaking can range from barely felt to violent enough to toss people around. Earthquakes have destroyed whole cities. They result from the sudden release of energy in the Earth's crust that creates seismic waves. The seismicity, seismism or seismic activity of an area refers to the frequency, type and size of earthquakes experienced over a period of time.Earthquakes are measured using observations from seismometers. The moment magnitude is the most common scale on which earthquakes larger than approximately 5 are reported for the entire globe. The more numerous earthquakes smaller than magnitude 5 reported by national seismological observatories are measured mostly on the local magnitude scale, also referred to as the Richter magnitude scale. These two scales are numerically similar over their range of validity. Magnitude 3 or lower earthquakes are mostly almost imperceptible or weak and magnitude 7 and over potentially cause serious damage over larger areas, depending on their depth. The largest earthquakes in historic times have been of magnitude slightly over 9, although there is no limit to the possible magnitude. The most recent large earthquake of magnitude 9.0 or larger was a 9.0 magnitude earthquake in Japan in 2011 (as of March 2014), and it was the largest Japanese earthquake since records began. Intensity of shaking is measured on the modified Mercalli scale. The shallower an earthquake, the more damage to structures it causes, all else being equal.At the Earth's surface, earthquakes manifest themselves by shaking and sometimes displacement of the ground. When the epicenter of a large earthquake is located offshore, the seabed may be displaced sufficiently to cause a tsunami. Earthquakes can also trigger landslides, and occasionally volcanic activity.In its most general sense, the word earthquake is used to describe any seismic event — whether natural or caused by humans — that generates seismic waves. Earthquakes are caused mostly by rupture of geological faults, but also by other events such as volcanic activity, landslides, mine blasts, and nuclear tests. An earthquake's point of initial rupture is called its focus or hypocenter. The epicenter is the point at ground level directly above the hypocenter.