Geosphere
... Ash clouds from major eruptions can block sunlight & change drop the average global temp. ...
... Ash clouds from major eruptions can block sunlight & change drop the average global temp. ...
True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false
... intermediate/medium 46. rhyolitic ...
... intermediate/medium 46. rhyolitic ...
Stress Transfer Eart..
... ΔCFS and “Stress Shadows” • After an earthquake event, the entire surrounding stress field is subjected to changes which can be approximated using ΔCFS as detailed above • ΔCFS is resolved onto the fault plane and in the slip direction of the subsequent earthquake • ΔCFS > 0: the fault plane is loa ...
... ΔCFS and “Stress Shadows” • After an earthquake event, the entire surrounding stress field is subjected to changes which can be approximated using ΔCFS as detailed above • ΔCFS is resolved onto the fault plane and in the slip direction of the subsequent earthquake • ΔCFS > 0: the fault plane is loa ...
Inside the Restless Earth
... 12. For each of the boundaries diagramed above, explain what happens at each of these boundaries and give a real-world example of each one. a. Convergent boundaries occur when two tectonic boundaries are pushing together. At oceanic/oceanic and oceanic/continental boundaries the more dense oceanic p ...
... 12. For each of the boundaries diagramed above, explain what happens at each of these boundaries and give a real-world example of each one. a. Convergent boundaries occur when two tectonic boundaries are pushing together. At oceanic/oceanic and oceanic/continental boundaries the more dense oceanic p ...
SEISMOTECTONIC ANALYSIS OF ZIARAT, BALOCHISTAN
... A severe shock of magnitude 6.5 Mb on Richter scale occurred on 29 October 2008 in Chiltan hills Balochistan at 05:10 PST having Epicentral coordinates 30.612oN and 67.436oE, at depth of 15 km. Foreshock of Magnitude 5.0 Mb originated at 04:33 PST having Epicentral coordinates 30.51oN and 67.48oE an ...
... A severe shock of magnitude 6.5 Mb on Richter scale occurred on 29 October 2008 in Chiltan hills Balochistan at 05:10 PST having Epicentral coordinates 30.612oN and 67.436oE, at depth of 15 km. Foreshock of Magnitude 5.0 Mb originated at 04:33 PST having Epicentral coordinates 30.51oN and 67.48oE an ...
Christchurch shakes : 4 September 2010
... Christchurch and the depth of the quake was at 10 km. It is the most damaging earthquake since the Hawkes Bay earthquake in 1931. For many people the earthquake came as a complete surprise, as there have been just 3 moderate earthquakes in the area in the past 40 years and any faultlines were not de ...
... Christchurch and the depth of the quake was at 10 km. It is the most damaging earthquake since the Hawkes Bay earthquake in 1931. For many people the earthquake came as a complete surprise, as there have been just 3 moderate earthquakes in the area in the past 40 years and any faultlines were not de ...
Earthquakes and the Earth`s Interior
... deformed slowly. Thus, when they are acted upon by differential stress, they tend to fracture. Faults Most natural earthquakes are caused by sudden slippage along a fault. Faults occur when brittle rocks fracture and there is displacement of one side of the fracture relative to the other side. The a ...
... deformed slowly. Thus, when they are acted upon by differential stress, they tend to fracture. Faults Most natural earthquakes are caused by sudden slippage along a fault. Faults occur when brittle rocks fracture and there is displacement of one side of the fracture relative to the other side. The a ...
1 Earthquake Hazard Information – Hazard, Risk, Magnitude
... about 6.5 - 6.8. In fact, the surface-wave magnitudes underestimate the size of very large earthquakes; the maximum observed values are about 8.3 - 8.7. Some investigators have suggested that the 100 s mantle Love waves (a type of surface wave) should be used to estimate magnitude of great earthquak ...
... about 6.5 - 6.8. In fact, the surface-wave magnitudes underestimate the size of very large earthquakes; the maximum observed values are about 8.3 - 8.7. Some investigators have suggested that the 100 s mantle Love waves (a type of surface wave) should be used to estimate magnitude of great earthquak ...
Restless World - ARK Elvin Academy
... Latest earthquakes in the world - past 7 days. Earthquakes occur at plate boundaries because of the build up of friction that occurs are plates try to move past each other and get stuck. Plate boundary ...
... Latest earthquakes in the world - past 7 days. Earthquakes occur at plate boundaries because of the build up of friction that occurs are plates try to move past each other and get stuck. Plate boundary ...
EARTHQUAKES.2
... vibrate back and forth perpendicular to the direction the wave is moving Slower than P waves (4-5 kms./s) TRAVEL THROUGH SOLIDS ONLY ...
... vibrate back and forth perpendicular to the direction the wave is moving Slower than P waves (4-5 kms./s) TRAVEL THROUGH SOLIDS ONLY ...
Earthquakes
... vibrate back and forth perpendicular to the direction the wave is moving Slower than P waves (4-5 kms./s) TRAVEL THROUGH SOLIDS ONLY ...
... vibrate back and forth perpendicular to the direction the wave is moving Slower than P waves (4-5 kms./s) TRAVEL THROUGH SOLIDS ONLY ...
Earthquakes and Volcanoes
... Rainier in Washington state are example of dormant volcanoes in the United States. ...
... Rainier in Washington state are example of dormant volcanoes in the United States. ...
Earthquake Notes
... Volcanoes are the result of hot spots within the crust or mantle of the earth. The hot, liquid rock will break through weak spots in the surface and form volcanoes or flood basalts. Many volcanoes do not release lava, instead they spit ash and small bits of lava called lapilli. Some eruptions are qu ...
... Volcanoes are the result of hot spots within the crust or mantle of the earth. The hot, liquid rock will break through weak spots in the surface and form volcanoes or flood basalts. Many volcanoes do not release lava, instead they spit ash and small bits of lava called lapilli. Some eruptions are qu ...
Earthquakes, Volcanoes, and Plate Tectonics
... forced upward through Earth’s mantle and crust. Scientists think that this is what is occurring at a hot spot that exists under the present location of Hawaii. ...
... forced upward through Earth’s mantle and crust. Scientists think that this is what is occurring at a hot spot that exists under the present location of Hawaii. ...
Forces Within Earth
... • Normal faults are fractures caused by horizontal tension. • Strike-slip faults are fractures caused by horizontal shear. ...
... • Normal faults are fractures caused by horizontal tension. • Strike-slip faults are fractures caused by horizontal shear. ...
Plate boundaries - MrD-Home
... • Knowing this, scientists can learn much about both earthquakes and the ________ interior of Earth. ...
... • Knowing this, scientists can learn much about both earthquakes and the ________ interior of Earth. ...
4 Tectonics and Geologic Processes
... 15. What forms along divergent plate boundaries… • When they occur in the ocean? • When they occur on continents? 16. While earthquakes can occur along any type of tectonic boundary, they are most common along… 17. What forms many times when earthquakes occur near to or beneath the ocean? 18. What i ...
... 15. What forms along divergent plate boundaries… • When they occur in the ocean? • When they occur on continents? 16. While earthquakes can occur along any type of tectonic boundary, they are most common along… 17. What forms many times when earthquakes occur near to or beneath the ocean? 18. What i ...
AQA A2 Unit 3: Contemporary Geographical Issues Plate tectonics
... rub and stick against each other.When the plates stick the pressure builds up because the two plates are still trying to move past each other Until eventually the pressure gets too much and the plates suddenly move. This sudden movement is a shallow focus earthquake. An example of this type of bound ...
... rub and stick against each other.When the plates stick the pressure builds up because the two plates are still trying to move past each other Until eventually the pressure gets too much and the plates suddenly move. This sudden movement is a shallow focus earthquake. An example of this type of bound ...
The Modified Mercalli Intensity Scale
... 4. Sendai, Japan 11 March 2011 (magnitude 9.0) So far the official death toll stands at several thousand from the combined effect of the powerful earthquake, aftershocks and the tsunami. However, the total is expected to rise, with some estimates of a final toll of over 10,000. Economic impacts are ...
... 4. Sendai, Japan 11 March 2011 (magnitude 9.0) So far the official death toll stands at several thousand from the combined effect of the powerful earthquake, aftershocks and the tsunami. However, the total is expected to rise, with some estimates of a final toll of over 10,000. Economic impacts are ...
File - Mr. Medler, Science
... gas). Convection currents are circular currents or movement within a liquid (or gas) due to different densities of the hotter and cooler parts. Hot liquids will rise because they are less dense than cold liquids. In the earth’s deep mantle and outer core, the magma is extremely hot and rises because ...
... gas). Convection currents are circular currents or movement within a liquid (or gas) due to different densities of the hotter and cooler parts. Hot liquids will rise because they are less dense than cold liquids. In the earth’s deep mantle and outer core, the magma is extremely hot and rises because ...
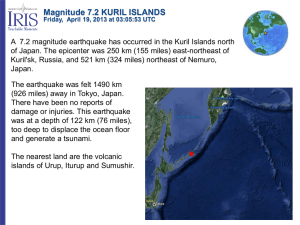
Magnitude 7.2 KURIL ISLANDS
... The Kuril-Kamchatka arc is considered one of the most seismically active regions in the world. Deformation of the overriding North America Plate generates shallow crustal earthquakes, whereas slip at the subduction zone interface between the Pacific and North America plates generates interplate eart ...
... The Kuril-Kamchatka arc is considered one of the most seismically active regions in the world. Deformation of the overriding North America Plate generates shallow crustal earthquakes, whereas slip at the subduction zone interface between the Pacific and North America plates generates interplate eart ...
PRACTICE Test: Earth Science INSTRUCTIONS - Ms
... b. The Farallon Plate collided with the Pacific Plate, forming a larger oceanic plate. c. The Farallon Plate subducted beneath the Pacific Plate and parts of it were renamed. d. The Farallon Plate subducted beneath the North American Plate and parts of it were ...
... b. The Farallon Plate collided with the Pacific Plate, forming a larger oceanic plate. c. The Farallon Plate subducted beneath the Pacific Plate and parts of it were renamed. d. The Farallon Plate subducted beneath the North American Plate and parts of it were ...
Powerpoint Presentation Physical Geology, 10/e
... gets older and farther from the ridge where it formed – Eventually oceanic lithosphere collides with another plate; whichever is colder and denser will be forced underneath and pulled back down into the mantle ...
... gets older and farther from the ridge where it formed – Eventually oceanic lithosphere collides with another plate; whichever is colder and denser will be forced underneath and pulled back down into the mantle ...
Episodic Tremor and Slip
... Episodic tremor and slip (ETS) represents a newly discovered mode of fault behavior occurring just below the locked zone that generates great earthquakes. Initially discovered in subduction zones, this new slip mechanism can release energy equivalent to at least a magnitude 7 earthquake! While this ...
... Episodic tremor and slip (ETS) represents a newly discovered mode of fault behavior occurring just below the locked zone that generates great earthquakes. Initially discovered in subduction zones, this new slip mechanism can release energy equivalent to at least a magnitude 7 earthquake! While this ...
Earthquake

An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the perceptible shaking of the surface of the Earth, which can be violent enough to destroy major buildings and kill thousands of people. The severity of the shaking can range from barely felt to violent enough to toss people around. Earthquakes have destroyed whole cities. They result from the sudden release of energy in the Earth's crust that creates seismic waves. The seismicity, seismism or seismic activity of an area refers to the frequency, type and size of earthquakes experienced over a period of time.Earthquakes are measured using observations from seismometers. The moment magnitude is the most common scale on which earthquakes larger than approximately 5 are reported for the entire globe. The more numerous earthquakes smaller than magnitude 5 reported by national seismological observatories are measured mostly on the local magnitude scale, also referred to as the Richter magnitude scale. These two scales are numerically similar over their range of validity. Magnitude 3 or lower earthquakes are mostly almost imperceptible or weak and magnitude 7 and over potentially cause serious damage over larger areas, depending on their depth. The largest earthquakes in historic times have been of magnitude slightly over 9, although there is no limit to the possible magnitude. The most recent large earthquake of magnitude 9.0 or larger was a 9.0 magnitude earthquake in Japan in 2011 (as of March 2014), and it was the largest Japanese earthquake since records began. Intensity of shaking is measured on the modified Mercalli scale. The shallower an earthquake, the more damage to structures it causes, all else being equal.At the Earth's surface, earthquakes manifest themselves by shaking and sometimes displacement of the ground. When the epicenter of a large earthquake is located offshore, the seabed may be displaced sufficiently to cause a tsunami. Earthquakes can also trigger landslides, and occasionally volcanic activity.In its most general sense, the word earthquake is used to describe any seismic event — whether natural or caused by humans — that generates seismic waves. Earthquakes are caused mostly by rupture of geological faults, but also by other events such as volcanic activity, landslides, mine blasts, and nuclear tests. An earthquake's point of initial rupture is called its focus or hypocenter. The epicenter is the point at ground level directly above the hypocenter.