Electricity and Magnetism I (PHY 321) Gauss`s Law problems
... Problem 3 (Fleisch Problem 1.4) What is the flux through any closed surface surrounding a charged sphere of radius a0 with volume charge density of ρ = ρ0 (r/a0 ), where r is the distance from the center of the sphere? Problem 4 (Fleisch Problem 1.5) A circular disk with surface charge density 2 × 1 ...
... Problem 3 (Fleisch Problem 1.4) What is the flux through any closed surface surrounding a charged sphere of radius a0 with volume charge density of ρ = ρ0 (r/a0 ), where r is the distance from the center of the sphere? Problem 4 (Fleisch Problem 1.5) A circular disk with surface charge density 2 × 1 ...
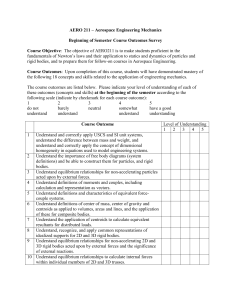
Outcomes Survey Begi.. - Aerospace Engineering Courses page
... Understand and correctly apply USCS and SI unit systems, understand the difference between mass and weight, and understand and correctly apply the concept of dimensional homogeneity in equations used to model engineering systems. 2 Understand the importance of free body diagrams (system definitions) ...
... Understand and correctly apply USCS and SI unit systems, understand the difference between mass and weight, and understand and correctly apply the concept of dimensional homogeneity in equations used to model engineering systems. 2 Understand the importance of free body diagrams (system definitions) ...
Derived copy of Further Applications of Newton`s
... A ea jumps by exerting a force of 1.20 × 10 N straight down on the ground. A breeze blowing on the ea parallel to the ground exerts a force of 0.500 × 10 N on the ea. Find the direction and magnitude of the acceleration of the ea if its mass is 6.00 × 10 kg. Do not neglect the gravitational forc ...
... A ea jumps by exerting a force of 1.20 × 10 N straight down on the ground. A breeze blowing on the ea parallel to the ground exerts a force of 0.500 × 10 N on the ea. Find the direction and magnitude of the acceleration of the ea if its mass is 6.00 × 10 kg. Do not neglect the gravitational forc ...
Problems
... We will estimate the electrical field between an ionized donor atom and a negatively charged vacancy, and its effect upon diffusion. Assume a Si crystal at 1000 °C. The donor atom and vacancy will interact by Coulomb forces. We will calculate the corresponding electrical field for different separati ...
... We will estimate the electrical field between an ionized donor atom and a negatively charged vacancy, and its effect upon diffusion. Assume a Si crystal at 1000 °C. The donor atom and vacancy will interact by Coulomb forces. We will calculate the corresponding electrical field for different separati ...
Unit 3 Powerpoint
... to solve any problem involving onedimensional motion with a constant acceleration You may need to use two of the equations to solve one problem Many times there is more than one way to solve a problem ...
... to solve any problem involving onedimensional motion with a constant acceleration You may need to use two of the equations to solve one problem Many times there is more than one way to solve a problem ...
Physical Meaning of Hydrostatic Equilibrium of Celestial
... force which decreases the water weight in the last branch by the unit. He found by calculation that if the Earth has a uniform mass of matter and has no any motion and the ratio of its axis PQ to the diameter £¥ is 100:101, then the gravity force of the Earth at the point Q relates to the gravity fo ...
... force which decreases the water weight in the last branch by the unit. He found by calculation that if the Earth has a uniform mass of matter and has no any motion and the ratio of its axis PQ to the diameter £¥ is 100:101, then the gravity force of the Earth at the point Q relates to the gravity fo ...