True motion, relative motion, and universal gravity
... we must acknowledge, then it must have a subject. For if a and b move toward one another, all the phenomena will be the same, no matter to which we attribute movement or rest, and if there were 1000 bodies, I still agree that the phenomena would not furnish us (or even the angels) with any infallibl ...
... we must acknowledge, then it must have a subject. For if a and b move toward one another, all the phenomena will be the same, no matter to which we attribute movement or rest, and if there were 1000 bodies, I still agree that the phenomena would not furnish us (or even the angels) with any infallibl ...
Advancing Physics A2
... You can use Question 80W Warm-up Exercise 'Newton’s gravitational law' to build confidence in using this equation. The Modellus model below will help you to get a feel for how gravity works. Activity 70S Software Based ''Variations in gravitational force' using File 50L Launchable File 'Newton’s gra ...
... You can use Question 80W Warm-up Exercise 'Newton’s gravitational law' to build confidence in using this equation. The Modellus model below will help you to get a feel for how gravity works. Activity 70S Software Based ''Variations in gravitational force' using File 50L Launchable File 'Newton’s gra ...
Universal Gravitational Constant - University of Tennessee Physics
... of every object to every other object, however, is anything but obvious. Despite the lack of direct evidence for any such attraction between everyday objects, Isaac Newton was able to deduce his law of universal gravitation. Newton’s law of universal gravitation: mm F G 12 2 r where m1 and m2 are t ...
... of every object to every other object, however, is anything but obvious. Despite the lack of direct evidence for any such attraction between everyday objects, Isaac Newton was able to deduce his law of universal gravitation. Newton’s law of universal gravitation: mm F G 12 2 r where m1 and m2 are t ...
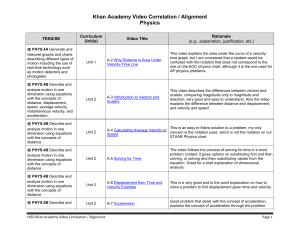
Khan Academy Video Correlation / Alignment Physics
... This video explains the acceleration due to gravity in an environment that has no air (moon). The time it would take for a heavier object to hit the ground is the same as the time it would take a lighter object given that the gravity is the same. Good explanation for review and for introduction to a ...
... This video explains the acceleration due to gravity in an environment that has no air (moon). The time it would take for a heavier object to hit the ground is the same as the time it would take a lighter object given that the gravity is the same. Good explanation for review and for introduction to a ...
A lecture on SHM-Theory
... them is an even multiple of or path difference is an even multiple of ( / 2) or time interval is an even multiple of (T / 2) because 1 time period is equivalent to 2 rad or 1 wave length () (iii) Opposite phase : When the two vibrating particles cross their respective mean positions at the same ...
... them is an even multiple of or path difference is an even multiple of ( / 2) or time interval is an even multiple of (T / 2) because 1 time period is equivalent to 2 rad or 1 wave length () (iii) Opposite phase : When the two vibrating particles cross their respective mean positions at the same ...
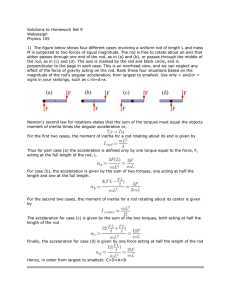
Answers to Practice Problems for Exam #1
... Consider the curve in the plane parametrized by R(t) = (t, t2 ). Find the speed, the unit tangent vector, the curvature and the principal unit normal. Find the osculating circle at the point where t = 1. Find the scalar tangential and normal components of the acceleration as the moving particle goes ...
... Consider the curve in the plane parametrized by R(t) = (t, t2 ). Find the speed, the unit tangent vector, the curvature and the principal unit normal. Find the osculating circle at the point where t = 1. Find the scalar tangential and normal components of the acceleration as the moving particle goes ...
Lecture Notes and Solved Problems
... story). This means that the fundamental differential equations of the theory are linear. This also means that a superposition principle is operative for electric fields. That is, suppose you wish to calculate the net electric field due to several point charges. The principle of superposition states ...
... story). This means that the fundamental differential equations of the theory are linear. This also means that a superposition principle is operative for electric fields. That is, suppose you wish to calculate the net electric field due to several point charges. The principle of superposition states ...
How is friction useful?
... spring stretched if it is used to drag the object across a floor at constant velocity? Assume the coefficient of kinetic friction is ...
... spring stretched if it is used to drag the object across a floor at constant velocity? Assume the coefficient of kinetic friction is ...
AP Physics 1 * Unit 2
... BIG IDEA 4: Interactions between systems can result in changes in those systems. 4.A.1.1: I can use representations of the center of mass of an isolated two-object system to analyze the motion of the system qualitatively and semi-quantitatively. [SP 1.2, 1.4, 2.3, 6.4] 4.A.2.1: I can make prediction ...
... BIG IDEA 4: Interactions between systems can result in changes in those systems. 4.A.1.1: I can use representations of the center of mass of an isolated two-object system to analyze the motion of the system qualitatively and semi-quantitatively. [SP 1.2, 1.4, 2.3, 6.4] 4.A.2.1: I can make prediction ...
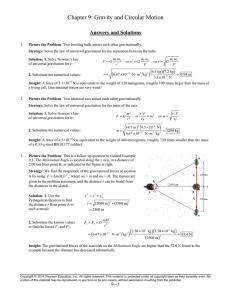
Chapter 9: Gravity and Circular Motion
... Copyright © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. This material is protected under all copyright laws as they currently exist. No portion of this material may be reproduced, in any form or by any means, without permission in writing from the publisher. ...
... Copyright © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. This material is protected under all copyright laws as they currently exist. No portion of this material may be reproduced, in any form or by any means, without permission in writing from the publisher. ...
First-Order Differential Equations
... When written this way, this sum looks sort of like the output of the product rule. If we can nd that the derivative of ...
... When written this way, this sum looks sort of like the output of the product rule. If we can nd that the derivative of ...