2002 - University of Utah Physics
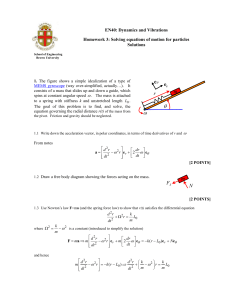
... Please note that there is a separate booklet for each numbered question (i.e., use booklet #1 for problem #1, etc.). To receive full credit, not only should the correct solutions be given, but a sufficient number of steps should be given so that a faculty grader can follow your reasoning. Define all ...
... Please note that there is a separate booklet for each numbered question (i.e., use booklet #1 for problem #1, etc.). To receive full credit, not only should the correct solutions be given, but a sufficient number of steps should be given so that a faculty grader can follow your reasoning. Define all ...
Word
... The highest point is reached at time t0 when uy = u sin – g t0 = 0, hence t0 = u sin / g. The shape of the path is parabolic. The total energy of a projectile is constant because the change of kinetic energy is equal and opposite to the change of potential energy. A projectile directed upwards a ...
... The highest point is reached at time t0 when uy = u sin – g t0 = 0, hence t0 = u sin / g. The shape of the path is parabolic. The total energy of a projectile is constant because the change of kinetic energy is equal and opposite to the change of potential energy. A projectile directed upwards a ...
Ch 13 Equilibrium
... turn out to be negative. Thus we do not have to know ahead of time whether the beam is under tension or compression. Solution: When you have a statics problem involving an object with a lot of pieces, and you want to calculate the force in one of the pieces, the first step is to isolate part of the ...
... turn out to be negative. Thus we do not have to know ahead of time whether the beam is under tension or compression. Solution: When you have a statics problem involving an object with a lot of pieces, and you want to calculate the force in one of the pieces, the first step is to isolate part of the ...
On the Problem of van der Waals Forces in
... (2.3) is divergent at small l. However, this infinite contribution does not depend on d and can be omitted altogether with a d-independent constant. We discussed the idea with Landau and he agreed with the argumentation. We immediately began calculations of the force F for the three-boundary configu ...
... (2.3) is divergent at small l. However, this infinite contribution does not depend on d and can be omitted altogether with a d-independent constant. We discussed the idea with Landau and he agreed with the argumentation. We immediately began calculations of the force F for the three-boundary configu ...
Physics 206a
... insist on sticking numbers in there early on, you have to do the same problem three times. Me, I’m lazy. I’d rather do it once. Once again, we start by stating everything we know: We know the masses of the balls. We know the initial speeds. We also know that the collision will be head-on, so this is ...
... insist on sticking numbers in there early on, you have to do the same problem three times. Me, I’m lazy. I’d rather do it once. Once again, we start by stating everything we know: We know the masses of the balls. We know the initial speeds. We also know that the collision will be head-on, so this is ...
12.2 Newton`s First and Second Laws of Motion
... Newton’s Second Law of Motion 3. An automobile with a mass of 1200 kg accelerates at a rate of 3.0 m/s2 in the forward direction. What is the net force acting on the automobile? (Hint: Solve the acceleration formula for force.) ...
... Newton’s Second Law of Motion 3. An automobile with a mass of 1200 kg accelerates at a rate of 3.0 m/s2 in the forward direction. What is the net force acting on the automobile? (Hint: Solve the acceleration formula for force.) ...
Two Cars on a Curving Road
... To solve this problem use proportional reasoning. Find the simplest equation that contains the variables and other known quantities from the problem. Write this equation twice: once for the car of mass m and speed v S and again for the car of mass 4m and speed v L . Write each equation so that al ...
... To solve this problem use proportional reasoning. Find the simplest equation that contains the variables and other known quantities from the problem. Write this equation twice: once for the car of mass m and speed v S and again for the car of mass 4m and speed v L . Write each equation so that al ...
Circular Motion and Gravitation Newton*s Law of Gravitation
... Circular Motion and Gravitation Newton’s Law of Gravitation Newton’s law of gravitation In 1687 Isaac Newton published what has been called by some the greatest scientific discovery of all time – his universal law of gravitation. The law states that the gravitational force between two point masse ...
... Circular Motion and Gravitation Newton’s Law of Gravitation Newton’s law of gravitation In 1687 Isaac Newton published what has been called by some the greatest scientific discovery of all time – his universal law of gravitation. The law states that the gravitational force between two point masse ...
Unit 1 - Teacher Notes
... Under what conditions will a satellite stay in the same position in the sky? What is the difference between centripetal force and centrifugal force? ...
... Under what conditions will a satellite stay in the same position in the sky? What is the difference between centripetal force and centrifugal force? ...