Lecture8-Chap5 Sept26
... whose sequences are present in multiple organisms. • zoo blot – The use of Southern blotting to test the ability of a DNA probe from one species to hybridize with the DNA from the genomes of a variety of other species. • Human disease genes are identified by mapping and sequencing DNA of patients to ...
... whose sequences are present in multiple organisms. • zoo blot – The use of Southern blotting to test the ability of a DNA probe from one species to hybridize with the DNA from the genomes of a variety of other species. • Human disease genes are identified by mapping and sequencing DNA of patients to ...
13.3- The Human Genome
... learned that there were fewer genes than originally believed that make up the human genome.They were able to learn that all genes do not have one specific role, as was previously believed, but can actually make up to three proteins” (Discovery Channel). ...
... learned that there were fewer genes than originally believed that make up the human genome.They were able to learn that all genes do not have one specific role, as was previously believed, but can actually make up to three proteins” (Discovery Channel). ...
A genome is the full set of genetic information that an organism
... 23. Breeders can increase the mutation rate of an organism by using radiation or chemicals. 24. Polyploidy can quickly produce new species of plants that are larger and stronger than their diploid relatives ...
... 23. Breeders can increase the mutation rate of an organism by using radiation or chemicals. 24. Polyploidy can quickly produce new species of plants that are larger and stronger than their diploid relatives ...
Ch. 13 Genetic Engineering, Chapter Summary Date
... 6. a techniques scientist used to make many copies of a certain gene. 8. produced by combining DNA from different species or different sources. 14. a technique that breed specific animals and plants with desired traits. This technique takes advantage of naturally occurring genetic variation in a gro ...
... 6. a techniques scientist used to make many copies of a certain gene. 8. produced by combining DNA from different species or different sources. 14. a technique that breed specific animals and plants with desired traits. This technique takes advantage of naturally occurring genetic variation in a gro ...
UNIVERSITETET I OSLO Det matematisk
... 13. How does DNA hypermethylation of the SUPERMAN locus affect floral organ development? Explain using the ABC model. What happens if additionally the HMTase KRYPTONITE is mutated? 14. How is flowering time in Arabidopsis controlled? Which genes and mechanisms are important for the transition to flo ...
... 13. How does DNA hypermethylation of the SUPERMAN locus affect floral organ development? Explain using the ABC model. What happens if additionally the HMTase KRYPTONITE is mutated? 14. How is flowering time in Arabidopsis controlled? Which genes and mechanisms are important for the transition to flo ...
Advances in genetics
... Researchers have cloned pigs and sheep. This method is complex. Involves taking the nucleus of an animal’s body cell and using that to produce a new-animal. ...
... Researchers have cloned pigs and sheep. This method is complex. Involves taking the nucleus of an animal’s body cell and using that to produce a new-animal. ...
Power, Sex, Suicide. Mitochondria and the Meaning
... electron acceptor - occur at fixed frequency. ...
... electron acceptor - occur at fixed frequency. ...
Chapter 4
... • Polypeptides are generally coded by sequences in nonrepetitive DNA. • Larger genomes within a taxon do not contain more genes, but have large amounts of repetitive DNA. • A large part of moderately repetitive DNA may be made up of transposons. ...
... • Polypeptides are generally coded by sequences in nonrepetitive DNA. • Larger genomes within a taxon do not contain more genes, but have large amounts of repetitive DNA. • A large part of moderately repetitive DNA may be made up of transposons. ...
Goal 3.05 Examine the Theory of Evolution by Natural
... 2. Selective breeding: 2 types are HYBRIDIZATION, INBREEDING and they produce desired TRAITS/CHARACTERSTICS. 3. Two sources of genetic variation are MUTATIONS, and SEXUAL reproduction. In sexual reproduction(meiosis), these two processes:_TETRAD FORMATION and CROSSING OVER, guarantee variation. Indu ...
... 2. Selective breeding: 2 types are HYBRIDIZATION, INBREEDING and they produce desired TRAITS/CHARACTERSTICS. 3. Two sources of genetic variation are MUTATIONS, and SEXUAL reproduction. In sexual reproduction(meiosis), these two processes:_TETRAD FORMATION and CROSSING OVER, guarantee variation. Indu ...
5th and 6th grade Ch 4 test Notes:
... A) Dominant trumps one recessive gene B) Recessive needs two genes to dominant C) You need to read a Punnett Square D) One Dominant and one recessive gene equals a hybrid trait. Part B Short Answer 1. Answer questions based on a chart of Body Cell Chromosomes number. Remember that sex cells have ½ o ...
... A) Dominant trumps one recessive gene B) Recessive needs two genes to dominant C) You need to read a Punnett Square D) One Dominant and one recessive gene equals a hybrid trait. Part B Short Answer 1. Answer questions based on a chart of Body Cell Chromosomes number. Remember that sex cells have ½ o ...
江 苏 大 学 试 题 (A)卷
... 2.17. Which of the following statements is true? A) Traits showing non-Mendelian extranuclear inheritance are almost inherited from the mother. B) The molecules used to carry out photosynthesis are encoded in nuclear DNA and mitochondrial DNA. C) cpDNA is found in the chloroplasts. D) Molecular evid ...
... 2.17. Which of the following statements is true? A) Traits showing non-Mendelian extranuclear inheritance are almost inherited from the mother. B) The molecules used to carry out photosynthesis are encoded in nuclear DNA and mitochondrial DNA. C) cpDNA is found in the chloroplasts. D) Molecular evid ...
4.1 Le Noyau
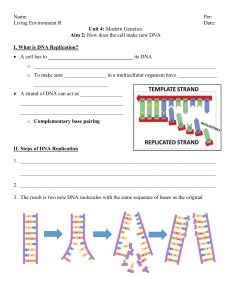
... • Everything that occurs within a cell is the result of how the bases on the DNA molecule are arranged. • A joins with T • G joins with C • But the order and number of these bases can vary greatly within the DNA molecule ...
... • Everything that occurs within a cell is the result of how the bases on the DNA molecule are arranged. • A joins with T • G joins with C • But the order and number of these bases can vary greatly within the DNA molecule ...
Introduction to DNA webquest: Name http://learn.genetics.utah.
... 1. What are genes needed for? ...
... 1. What are genes needed for? ...
Mitochondrial Eve
... In the field of human genetics, the name Mitochondrial Eve refers to the matrilineal most recent common ancestor (MRCA) of all currently living anatomically modern humans, who is estimated to have lived approximately 100,000–200,000 years ago. This is the most recent woman from whom all living human ...
... In the field of human genetics, the name Mitochondrial Eve refers to the matrilineal most recent common ancestor (MRCA) of all currently living anatomically modern humans, who is estimated to have lived approximately 100,000–200,000 years ago. This is the most recent woman from whom all living human ...
2D Barcode Quiz
... A primer is the first bit of DNA of a gene to be copied in a cell Most PCR reactions utilise a polymerase which works best at room temperature The Taq polymerase used in PCR was originally isolated from a bacterium called Thermus aquaticus The replication of template DNA during PCR occurs in an expo ...
... A primer is the first bit of DNA of a gene to be copied in a cell Most PCR reactions utilise a polymerase which works best at room temperature The Taq polymerase used in PCR was originally isolated from a bacterium called Thermus aquaticus The replication of template DNA during PCR occurs in an expo ...
The relationship between genes and traits is often complex
... Next week for our final lecture of the semester, we will look at what DNA can tell us about the origins of Homo sapiens. ...
... Next week for our final lecture of the semester, we will look at what DNA can tell us about the origins of Homo sapiens. ...
Introduction to DNA - University of Dayton
... Intro to DNA • Chromosomes exist in “matching pairs” in the nucleus of a cell • Scientists call the matching pairs “homologous pairs”. • In every human body cell, there are 23 homologous pairs of chromosomes. ...
... Intro to DNA • Chromosomes exist in “matching pairs” in the nucleus of a cell • Scientists call the matching pairs “homologous pairs”. • In every human body cell, there are 23 homologous pairs of chromosomes. ...
5. Protein Synthesis
... 4. What part of the nucleotide is different about the 4 nucleotides of DNA? 5. Information flows from DNA to ________ to proteins. 6. What holds base pairs together? 7. What is the process of a cells making an exact copy of its DNA called? 8. What is a codon? 9. What is an anticodon and where is it ...
... 4. What part of the nucleotide is different about the 4 nucleotides of DNA? 5. Information flows from DNA to ________ to proteins. 6. What holds base pairs together? 7. What is the process of a cells making an exact copy of its DNA called? 8. What is a codon? 9. What is an anticodon and where is it ...
Biological ideas relating to genetic modification
... A molecule containing a sugar, a phosphate, and a base. ...
... A molecule containing a sugar, a phosphate, and a base. ...
Ans. Our cell contains 23 pairs of chromosome and it is inherited as
... Ans. Our cell contains 23 pairs of chromosome and it is inherited as one pair from each of our parents, which means that the sperm and egg receive 23 chromosomes through a complex process of cell division called as the meiosis. 2. Where is DNA found? Ans. Most of the DNA in a human cell is found in ...
... Ans. Our cell contains 23 pairs of chromosome and it is inherited as one pair from each of our parents, which means that the sperm and egg receive 23 chromosomes through a complex process of cell division called as the meiosis. 2. Where is DNA found? Ans. Most of the DNA in a human cell is found in ...
pdf format publicity flyer for the proceedings
... mitochondria and their bacterial homologues: New perspectives on symbiosis in cell evolution Compiled and edited by John Raven and John Allen To be published January 2003: Special offer price: £45 (usual price: £85) Chloroplasts and mitochondria are energy-converting organelles of eukaryotic cells. ...
... mitochondria and their bacterial homologues: New perspectives on symbiosis in cell evolution Compiled and edited by John Raven and John Allen To be published January 2003: Special offer price: £45 (usual price: £85) Chloroplasts and mitochondria are energy-converting organelles of eukaryotic cells. ...
Virtual DNA Lab
... 4. Examine the picture. Which type of bonds hold the DNA bases together? ____________________ 5. What molecule do genes create? ____________________________________________________ What is a Gene? 6. Why are genes called the instruction manual for our body? _______________________________ __________ ...
... 4. Examine the picture. Which type of bonds hold the DNA bases together? ____________________ 5. What molecule do genes create? ____________________________________________________ What is a Gene? 6. Why are genes called the instruction manual for our body? _______________________________ __________ ...
ch 14 RTC - WordPress.com
... the detecIon of a viral infecIon, geneIc disorder, or cancer, the convicIon of criminals, comparing fossils with known animals, the idenIficaIon of vicIms of terrorist aUacks, the establishment of paternity, ...
... the detecIon of a viral infecIon, geneIc disorder, or cancer, the convicIon of criminals, comparing fossils with known animals, the idenIficaIon of vicIms of terrorist aUacks, the establishment of paternity, ...
Mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA or mDNA) is the DNA located in mitochondria, cellular organelles within eukaryotic cells that convert chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use, adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial DNA is only a small portion of the DNA in a eukaryotic cell; most of the DNA can be found in the cell nucleus and, in plants, in the chloroplast.In humans, mitochondrial DNA can be assessed as the smallest chromosome coding for 37 genes and containing approximately 16,600 base pairs. Human mitochondrial DNA was the first significant part of the human genome to be sequenced. In most species, including humans, mtDNA is inherited solely from the mother.The DNA sequence of mtDNA has been determined from a large number of organisms and individuals (including some organisms that are extinct), and the comparison of those DNA sequences represents a mainstay of phylogenetics, in that it allows biologists to elucidate the evolutionary relationships among species. It also permits an examination of the relatedness of populations, and so has become important in anthropology and field biology.