Mitochondrial - Reversible infantile respiratory chain deficiency
... heterogeneous. A rare subset of these disorders is associated with reversible/transient myopathy and/or hepatopathy. This is known as reversible/transient infantile respiratory chain deficiency, or reversible/benign cytochrome c oxidase (COX) deficiency. To date this disorder has been associated wit ...
... heterogeneous. A rare subset of these disorders is associated with reversible/transient myopathy and/or hepatopathy. This is known as reversible/transient infantile respiratory chain deficiency, or reversible/benign cytochrome c oxidase (COX) deficiency. To date this disorder has been associated wit ...
1) Genetics Vocabulary
... Asexual Reproduction – type of reproduction, such as budding or regeneration, in which a new organism is produced from a part of another organism by mitosis Cloning – making copies of organisms, each of which is a clone that receives DNA from only one parent. DNA – a chemical inside cells that conta ...
... Asexual Reproduction – type of reproduction, such as budding or regeneration, in which a new organism is produced from a part of another organism by mitosis Cloning – making copies of organisms, each of which is a clone that receives DNA from only one parent. DNA – a chemical inside cells that conta ...
Our new understanding of genetic mechanisms is leading to
... – Replace defective gene with healthy gene – In vivo – In vitro ...
... – Replace defective gene with healthy gene – In vivo – In vitro ...
DNA in classifying species
... The DNA used to identify differences and similarities between organisms must be ...
... The DNA used to identify differences and similarities between organisms must be ...
PowerPoint Genetic Technology Notes
... Personal Identification No individual is exactly like any other genetically—except for ___________ twins, who share the same genome. Chromosomes contain many regions with ___________ DNA sequences that do not code for proteins. These vary from person to person. DNA fingerprinting can be used to ____ ...
... Personal Identification No individual is exactly like any other genetically—except for ___________ twins, who share the same genome. Chromosomes contain many regions with ___________ DNA sequences that do not code for proteins. These vary from person to person. DNA fingerprinting can be used to ____ ...
Chapter 12 DNA Analysis Checkpoint Answers In the nucleus of the
... packed into the nucleus. 4. The Human Genome Project is a unified effort to identify and determine the sequence of all genes found on the human chromosome. 5. The nucleus 6. Adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine 7. The phosphate groups give DNA its acidic properties. 8. Blood, semen, saliva, hair foll ...
... packed into the nucleus. 4. The Human Genome Project is a unified effort to identify and determine the sequence of all genes found on the human chromosome. 5. The nucleus 6. Adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine 7. The phosphate groups give DNA its acidic properties. 8. Blood, semen, saliva, hair foll ...
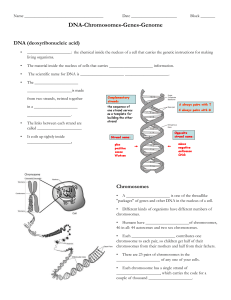
DNA-Chromosomes-Genes-Genome student notesheet
... chromosomes from their mothers and half from their fathers. • There are 23 pairs of chromosomes in the _____________________ of any one of your cells. • Each chromosome has a single strand of _____________________, which carries the code for a couple of thousand _____________________. ...
... chromosomes from their mothers and half from their fathers. • There are 23 pairs of chromosomes in the _____________________ of any one of your cells. • Each chromosome has a single strand of _____________________, which carries the code for a couple of thousand _____________________. ...
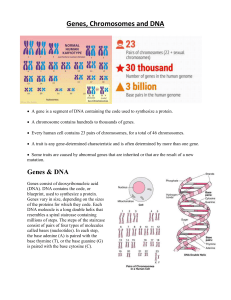
Genes Chromosomes and DNA
... A chromosome contains hundreds to thousands of genes. Every human cell contains 23 pairs of chromosomes, for a total of 46 chromosomes. A trait is any gene-determined characteristic and is often determined by more than one gene. Some traits are caused by abnormal genes that are inherited or ...
... A chromosome contains hundreds to thousands of genes. Every human cell contains 23 pairs of chromosomes, for a total of 46 chromosomes. A trait is any gene-determined characteristic and is often determined by more than one gene. Some traits are caused by abnormal genes that are inherited or ...
Document
... Mitochondrial Inheritance Mitochondrial inheritance from yeast is biparental, and both parent cells contribute to the daughter cells when the haploid cells fuse. After meiosis and mitosis, there is random distribution of mitochondria to daughter cells. If the fusion is with yeast that are petite an ...
... Mitochondrial Inheritance Mitochondrial inheritance from yeast is biparental, and both parent cells contribute to the daughter cells when the haploid cells fuse. After meiosis and mitosis, there is random distribution of mitochondria to daughter cells. If the fusion is with yeast that are petite an ...
Biology 3 Study Guide – Exam #3
... the concepts of evolution and natural selection various types of evidence for evolution various types of fossils and radiometric dating gene pools and allele frequencies Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium and using the Hardy-Weinberg equation the role of mutations in evolution genetic drift and artificial s ...
... the concepts of evolution and natural selection various types of evidence for evolution various types of fossils and radiometric dating gene pools and allele frequencies Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium and using the Hardy-Weinberg equation the role of mutations in evolution genetic drift and artificial s ...
Data visualization in the post
... Almost every human gene has a counterpart in the mouse and some blocks of DNA are proving impossible to tell apart ...
... Almost every human gene has a counterpart in the mouse and some blocks of DNA are proving impossible to tell apart ...
Mitochondrial Function
... Mitochondrial diseases are the result of either inherited遗传的 or spontaneous自发的 mutations in mtDNA or nDNA which lead to altered functions of the proteins or RNA molecules in mitochondria. mtDNA and/or nuclear DNA mutation ...
... Mitochondrial diseases are the result of either inherited遗传的 or spontaneous自发的 mutations in mtDNA or nDNA which lead to altered functions of the proteins or RNA molecules in mitochondria. mtDNA and/or nuclear DNA mutation ...
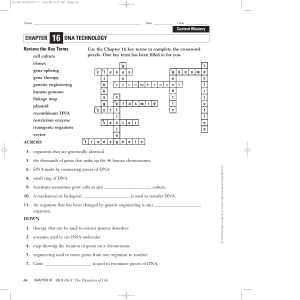
chapter dna technology - Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
... 8. small ring of DNA 9. Scientists sometimes grow cells in a(n) ______________________ culture. 10. A mechanical or biological ______________________ is used to transfer DNA. 11. An organism that has been changed by genetic engineering is a(n) ______________________ organism. DOWN 1. therapy that ca ...
... 8. small ring of DNA 9. Scientists sometimes grow cells in a(n) ______________________ culture. 10. A mechanical or biological ______________________ is used to transfer DNA. 11. An organism that has been changed by genetic engineering is a(n) ______________________ organism. DOWN 1. therapy that ca ...
Game 2
... of a reaction rate (product in moles vs. time) and indicate the initial reaction rate & explain why the asymptote that is approached as the reaction finishes is present ...
... of a reaction rate (product in moles vs. time) and indicate the initial reaction rate & explain why the asymptote that is approached as the reaction finishes is present ...
Genetics - Bill Nye ANSWERS
... RNA is similar to DNA, but its different. What’s different? RNA only has one strand. There are 20 amino acids that make up proteins. Name the 2 scientists that discovered the double helix. Watson and Crick How many bases align in a sequence to code for a specific amino acid? 3 Bacteria resistant to ...
... RNA is similar to DNA, but its different. What’s different? RNA only has one strand. There are 20 amino acids that make up proteins. Name the 2 scientists that discovered the double helix. Watson and Crick How many bases align in a sequence to code for a specific amino acid? 3 Bacteria resistant to ...
Journey Into dna
... How many cells does the human body contain? What is the only type of cell in the human body that contains no nucleus and therefore no nuclear DNA? ...
... How many cells does the human body contain? What is the only type of cell in the human body that contains no nucleus and therefore no nuclear DNA? ...
Greatest Discoveries with Bill Nye: Genetics
... ______________________________. 21. With restriction enzymes, scientists had a pair of molecular ______________ to ________ DNA molecules. #10- RNA Alternative Splicing ...
... ______________________________. 21. With restriction enzymes, scientists had a pair of molecular ______________ to ________ DNA molecules. #10- RNA Alternative Splicing ...
Greatest Discoveries with Bill Nye: Genetics
... 3. Dropsphila melanogaster is known as the common _____________ _____________. 4. Human females have 2 _____ chromosomes, while human males have 1 _____ and 1 _____ chromosome. 5. Morgan was awarded the Nobel Prize for Medicine in the year _________. #3- Genes Control Biochemical Events ...
... 3. Dropsphila melanogaster is known as the common _____________ _____________. 4. Human females have 2 _____ chromosomes, while human males have 1 _____ and 1 _____ chromosome. 5. Morgan was awarded the Nobel Prize for Medicine in the year _________. #3- Genes Control Biochemical Events ...
Document
... Major Patterns of Monogenic Inheritance – Patterns of autosomal dominant inheritance (AD) 常染色体显性 – Patterns of autosomal recessive inheritance (AR) 常染色体隐性 – Patterns of X-linked recessive inheritance (XD) X-连锁显性 – Patterns of X-linked dominant inheritance (XR) X-连锁隐性 – Patterns of Y-linked inherita ...
... Major Patterns of Monogenic Inheritance – Patterns of autosomal dominant inheritance (AD) 常染色体显性 – Patterns of autosomal recessive inheritance (AR) 常染色体隐性 – Patterns of X-linked recessive inheritance (XD) X-连锁显性 – Patterns of X-linked dominant inheritance (XR) X-连锁隐性 – Patterns of Y-linked inherita ...
Genetic Engineering - Duplin County Schools
... • Continued breeding of individuals with similar characteristics • Useful in retaining a certain set of characteristics • Can produce some serious genetic defects ...
... • Continued breeding of individuals with similar characteristics • Useful in retaining a certain set of characteristics • Can produce some serious genetic defects ...
Epigenetics
... ways, both which may turn genes off or on. • The first type of mark, called DNA methylation, directly affects the DNA in your genome. This can also occur with acetylation. • In this process, chemical tags called methyl groups attach to the backbone of the DNA molecule in specific places. • The methy ...
... ways, both which may turn genes off or on. • The first type of mark, called DNA methylation, directly affects the DNA in your genome. This can also occur with acetylation. • In this process, chemical tags called methyl groups attach to the backbone of the DNA molecule in specific places. • The methy ...
Bill Nye: Genes - stephaniemcoggins
... 5. How many times longer is DNA than it is wide? 6. How does Bill define a Gene? 7. Why is the white blood cell dark on the computer screen? 8. What does the nucleus of the cell contain? 9. What can you do with DNA after you take it out of an organism? a. b. 10. What do genes do?. 11. What analogy d ...
... 5. How many times longer is DNA than it is wide? 6. How does Bill define a Gene? 7. Why is the white blood cell dark on the computer screen? 8. What does the nucleus of the cell contain? 9. What can you do with DNA after you take it out of an organism? a. b. 10. What do genes do?. 11. What analogy d ...
BSCS
... 21. Be able to discuss genomic imprinting and its effects when inherited from mom or dad. (To help you understand this phenomenon, study Figure 14.9) 22. What is methylation? How does it contribute to our understanding of genomic imprinting and X-inactivation? 23. Remember from the chemistry section ...
... 21. Be able to discuss genomic imprinting and its effects when inherited from mom or dad. (To help you understand this phenomenon, study Figure 14.9) 22. What is methylation? How does it contribute to our understanding of genomic imprinting and X-inactivation? 23. Remember from the chemistry section ...
Mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA or mDNA) is the DNA located in mitochondria, cellular organelles within eukaryotic cells that convert chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use, adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial DNA is only a small portion of the DNA in a eukaryotic cell; most of the DNA can be found in the cell nucleus and, in plants, in the chloroplast.In humans, mitochondrial DNA can be assessed as the smallest chromosome coding for 37 genes and containing approximately 16,600 base pairs. Human mitochondrial DNA was the first significant part of the human genome to be sequenced. In most species, including humans, mtDNA is inherited solely from the mother.The DNA sequence of mtDNA has been determined from a large number of organisms and individuals (including some organisms that are extinct), and the comparison of those DNA sequences represents a mainstay of phylogenetics, in that it allows biologists to elucidate the evolutionary relationships among species. It also permits an examination of the relatedness of populations, and so has become important in anthropology and field biology.