mutation - ahsbognasbi4u
... change bases in DNA to unrecognizable (by DNA polymerase) forms It can also break the sugar–phosphate backbone of DNA, causing ...
... change bases in DNA to unrecognizable (by DNA polymerase) forms It can also break the sugar–phosphate backbone of DNA, causing ...
Test Review Questions
... original. The immediate is a decrease genetic diversity. 15.Write the Hardy-Weinberg principle as a mathematics equation. ...
... original. The immediate is a decrease genetic diversity. 15.Write the Hardy-Weinberg principle as a mathematics equation. ...
the element makes na RNA copy of itself which is reversed
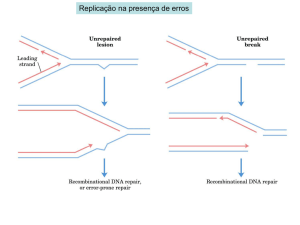
... • Breakage and joining also directed by enzymes. • Homologous recombination occurs during synapsis in meiosis I, general recombination in bacteria, and viral genetic exchange. • Molecular mechanism proposed by Holliday and Whitehouse (1964). • Depends on complementary base pairing. ...
... • Breakage and joining also directed by enzymes. • Homologous recombination occurs during synapsis in meiosis I, general recombination in bacteria, and viral genetic exchange. • Molecular mechanism proposed by Holliday and Whitehouse (1964). • Depends on complementary base pairing. ...
DNA Worksheet
... 22. Where are proteins made in the cell? _____________________________ 23. Use the amino acid chart in your notes to translate the sequence of codons (from #16) and write the ...
... 22. Where are proteins made in the cell? _____________________________ 23. Use the amino acid chart in your notes to translate the sequence of codons (from #16) and write the ...
DNA, RNA, PROTEINS STARTS WITH
... 2. The group of 3 nitrogen bases in the mRNA message that is read together is called a _C_ __ __ __ __. 3. In dividing cells, the DNA is scrunched into _C_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ so it can be moved. 4. The mRNA message tells the ribosomes which _A_ __ __ __ __ _A_ __ __ __ to put in next when ...
... 2. The group of 3 nitrogen bases in the mRNA message that is read together is called a _C_ __ __ __ __. 3. In dividing cells, the DNA is scrunched into _C_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ so it can be moved. 4. The mRNA message tells the ribosomes which _A_ __ __ __ __ _A_ __ __ __ to put in next when ...
DNA - eduBuzz.org
... Every living organism has a characteristic number of chromosomes and each one of their cells contains an identical copy of these chromosomes. This is important to ensure that every cell has all of the characteristics of the organism. This characteristic number is known as the chromosome complement a ...
... Every living organism has a characteristic number of chromosomes and each one of their cells contains an identical copy of these chromosomes. This is important to ensure that every cell has all of the characteristics of the organism. This characteristic number is known as the chromosome complement a ...
Iron-sulfur proteins
... defective mitochondrial genes that are involved in electron transfer. • Vision loss usually occurs between the ages of 15 and 35. ...
... defective mitochondrial genes that are involved in electron transfer. • Vision loss usually occurs between the ages of 15 and 35. ...
Fertilisation, development and DNA
... I can describe how some viruses can cause damage to a developing embryo e.g. german measles. I can state that DNA contains the instructions for life and reproduction. I can state that DNA is found in the nucleus of every cell. ...
... I can describe how some viruses can cause damage to a developing embryo e.g. german measles. I can state that DNA contains the instructions for life and reproduction. I can state that DNA is found in the nucleus of every cell. ...
Sc9 - a 3.1(teacher notes)
... DNA video - http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8kK2zwjRV0M Characteristics are passed on from one generation to another within a species through the genetic code of the parents. This genetic code is called DNA ...
... DNA video - http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8kK2zwjRV0M Characteristics are passed on from one generation to another within a species through the genetic code of the parents. This genetic code is called DNA ...
Table 3.
... and flank melt domains. Low PCR yield Optimize PCR to enhance product yield. Optimize PCR conditions to obtain clean product or design new primers without secondary structures. ...
... and flank melt domains. Low PCR yield Optimize PCR to enhance product yield. Optimize PCR conditions to obtain clean product or design new primers without secondary structures. ...
Midterm Key - Berkeley MCB
... correct or there is something wrong with them. Pick four of the statements and briefly describe what is wrong with them. (5 points each) One of the Eugenic approaches in this country was to sterilize cattle that displayed negative traits. Humans, not cattle were sterilized. Fruitless is transcribed ...
... correct or there is something wrong with them. Pick four of the statements and briefly describe what is wrong with them. (5 points each) One of the Eugenic approaches in this country was to sterilize cattle that displayed negative traits. Humans, not cattle were sterilized. Fruitless is transcribed ...
DNA Unit Study Guide 2017 - Liberty Union High School District
... 23. Transcription and Translation for the following Strand of DNA. DNA T A C T A T T C C T C G T C T C G G C G T A T T mRNA_______________________________________________________________________ tRNA________________________________________________________________________ rRNA/aa_____________________ ...
... 23. Transcription and Translation for the following Strand of DNA. DNA T A C T A T T C C T C G T C T C G G C G T A T T mRNA_______________________________________________________________________ tRNA________________________________________________________________________ rRNA/aa_____________________ ...
genome433
... region of DNA whose sequence is known, so that it can be amplified by PCR; may contain sequence polymorphisms. One particularly useful type of STS is the microsatellite marker. A microsatellite is an STS which contains a tandem repeat of a very simple DNA sequence, e.g., (CA)n. Because errors are ma ...
... region of DNA whose sequence is known, so that it can be amplified by PCR; may contain sequence polymorphisms. One particularly useful type of STS is the microsatellite marker. A microsatellite is an STS which contains a tandem repeat of a very simple DNA sequence, e.g., (CA)n. Because errors are ma ...
12.2 DNA Replication ppt
... Action: Adds new nucleotides to the exposed bases using the base-pair rule; also proofreads every connection at this time (avg. 1 error per 2 billion nucleotides) Result: 2 new double DNA strands are created (but still attached) ...
... Action: Adds new nucleotides to the exposed bases using the base-pair rule; also proofreads every connection at this time (avg. 1 error per 2 billion nucleotides) Result: 2 new double DNA strands are created (but still attached) ...
29 - Karmayog .org
... Humans have 46 chromosomes in every cell except the sperm and the egg, these have 23 chromosomes, the 23rd chromosome is sex chromosome. The females carry XX chromosome while the male carries an XY chromosome. The female egg will thus always have an X chromosome while the male sperm may have an X or ...
... Humans have 46 chromosomes in every cell except the sperm and the egg, these have 23 chromosomes, the 23rd chromosome is sex chromosome. The females carry XX chromosome while the male carries an XY chromosome. The female egg will thus always have an X chromosome while the male sperm may have an X or ...
Dangerous Ideas and Forbidden Knowledge: Quiz 2 Review Outline
... a) Individuals 2 and 3 share a more recent common ancestor that individuals 1 and 2 b) There are fewer differences between the DNA sequences of individual 1 and individual 4 than there are between individual 1 and individual 2. c) Individual 1 is more highly evolved than individual 3. d) All of thes ...
... a) Individuals 2 and 3 share a more recent common ancestor that individuals 1 and 2 b) There are fewer differences between the DNA sequences of individual 1 and individual 4 than there are between individual 1 and individual 2. c) Individual 1 is more highly evolved than individual 3. d) All of thes ...
The Human Genome
... • Western white butterfly wing coloration is affected by temp. • Japanese goby fish can change its sex back and forth in response to changes in its social environment. ...
... • Western white butterfly wing coloration is affected by temp. • Japanese goby fish can change its sex back and forth in response to changes in its social environment. ...
Mutations are heritable alteration in DNA sequence Most common
... proteins) must discriminate between the correct strand and the strand with the mismatch. Discrimination is based on the degree of methylation. GATC sequences are methylated on the adenine residues. The newly synthesized DNA is not immediately methylated The methylated template strand is cons ...
... proteins) must discriminate between the correct strand and the strand with the mismatch. Discrimination is based on the degree of methylation. GATC sequences are methylated on the adenine residues. The newly synthesized DNA is not immediately methylated The methylated template strand is cons ...
Mutations
... Risks: Food allergies, other negative health effects; introduced species or “superweeds” ...
... Risks: Food allergies, other negative health effects; introduced species or “superweeds” ...
Acc_Bio_Biotechnology_12
... DNA of both bacteria and yeasts. Pure chymosin can now be made. The enzyme is identical to that produced in the calf and the process itself adds no contaminants. The FDA evaluated the safety of the process and the product itself in 1990 and ruled that the enzyme preparation was safe for human consum ...
... DNA of both bacteria and yeasts. Pure chymosin can now be made. The enzyme is identical to that produced in the calf and the process itself adds no contaminants. The FDA evaluated the safety of the process and the product itself in 1990 and ruled that the enzyme preparation was safe for human consum ...
Worksheet for 4/16
... gel electrophoresis. Diagram a gel including electric charge, and labeled fragments. ...
... gel electrophoresis. Diagram a gel including electric charge, and labeled fragments. ...
Genetics Webquest Name: What is DNA? http://learn.genetics.utah
... 12) If you stretched the DNA from a cell out, how long would it be? 13) How many chromosomes are in a human cell? In a mosquito? In a carp? What is a Protein? 14) How is a protein like a car engine? 15) Receptor proteins are responsible for picking up _______________. ...
... 12) If you stretched the DNA from a cell out, how long would it be? 13) How many chromosomes are in a human cell? In a mosquito? In a carp? What is a Protein? 14) How is a protein like a car engine? 15) Receptor proteins are responsible for picking up _______________. ...
Genetics Syllabus
... 10-12th Grade Genetics Course Syllabus Unit #1: Structure and Function of Nucleic Acids Objectives: Know how DNA was identified as the molecule of heredity. Know the chemical structure of DNA and RNA. Model the replication of a DNA molecule. Understand the process of protein synthesis. Know the rela ...
... 10-12th Grade Genetics Course Syllabus Unit #1: Structure and Function of Nucleic Acids Objectives: Know how DNA was identified as the molecule of heredity. Know the chemical structure of DNA and RNA. Model the replication of a DNA molecule. Understand the process of protein synthesis. Know the rela ...
Mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA or mDNA) is the DNA located in mitochondria, cellular organelles within eukaryotic cells that convert chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use, adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial DNA is only a small portion of the DNA in a eukaryotic cell; most of the DNA can be found in the cell nucleus and, in plants, in the chloroplast.In humans, mitochondrial DNA can be assessed as the smallest chromosome coding for 37 genes and containing approximately 16,600 base pairs. Human mitochondrial DNA was the first significant part of the human genome to be sequenced. In most species, including humans, mtDNA is inherited solely from the mother.The DNA sequence of mtDNA has been determined from a large number of organisms and individuals (including some organisms that are extinct), and the comparison of those DNA sequences represents a mainstay of phylogenetics, in that it allows biologists to elucidate the evolutionary relationships among species. It also permits an examination of the relatedness of populations, and so has become important in anthropology and field biology.