Cells to Body Systems
... • Size and Shape depend upon its function. • Red blood cells are small and disc shaped to fit through the smallest blood vessel. • Muscle cells are long and thin. When they contract they produce movement. • Nerve cells which carry signals to the brain are very long. ...
... • Size and Shape depend upon its function. • Red blood cells are small and disc shaped to fit through the smallest blood vessel. • Muscle cells are long and thin. When they contract they produce movement. • Nerve cells which carry signals to the brain are very long. ...
Cells - Livingstone High School
... • Size and Shape depend upon its function. • Red blood cells are small and disc shaped to fit through the smallest blood vessel. • Muscle cells are long and thin. When they contract they produce movement. • Nerve cells which carry signals to the brain are very long. ...
... • Size and Shape depend upon its function. • Red blood cells are small and disc shaped to fit through the smallest blood vessel. • Muscle cells are long and thin. When they contract they produce movement. • Nerve cells which carry signals to the brain are very long. ...
Unit 1 Test Review Guide
... 2. Clearly and neatly draw an animal cell and add the following organelles: Nucleus, Nucleolus, Smooth ER, Rough ER, Golgi Body, Mitochondria, Ribosomes, Cell membrane, Centrioles (always a pair!), Lysosomes, Cytoplasm. Label each part! ...
... 2. Clearly and neatly draw an animal cell and add the following organelles: Nucleus, Nucleolus, Smooth ER, Rough ER, Golgi Body, Mitochondria, Ribosomes, Cell membrane, Centrioles (always a pair!), Lysosomes, Cytoplasm. Label each part! ...
Biology Final Review Sheet
... What is photosynthesis? In what organelle does photosynthesis occur? What is an organism that is able to produce its own food called? Why do leaves of a plant appear green? What is the chemical f ...
... What is photosynthesis? In what organelle does photosynthesis occur? What is an organism that is able to produce its own food called? Why do leaves of a plant appear green? What is the chemical f ...
Summer Review Package: `16-`17 1. Vocabulary
... 5. Robert Hooke is credited with discovering cells while observing a piece of cork under a microscope. In his book Micrographia, which he published in 1665, Hooke describes the small structures that he observed under the microscope. Which part of the cell theory is best supported by this discovery? ...
... 5. Robert Hooke is credited with discovering cells while observing a piece of cork under a microscope. In his book Micrographia, which he published in 1665, Hooke describes the small structures that he observed under the microscope. Which part of the cell theory is best supported by this discovery? ...
HIGHLIGHTS FOR 7TH GRADE SCIENCE CURRICULUM Cells
... Ribosomes- proteins are made/held here. Determine processes/traits of the cell. ER- endoplasmic reticulum. Moves materials from one place to another within the cell. Like a train. Two types - rough (carries ribosomes) and smooth. It regulates processes in the cells. Like muscles contractions or brea ...
... Ribosomes- proteins are made/held here. Determine processes/traits of the cell. ER- endoplasmic reticulum. Moves materials from one place to another within the cell. Like a train. Two types - rough (carries ribosomes) and smooth. It regulates processes in the cells. Like muscles contractions or brea ...
Summer Review Package: `14 -`15 PART I 1. Vocabulary – Please b
... 5. Robert Hooke is credited with discovering cells while observing a piece of cork under a microscope. In his book Micrographia, which he published in 1665, Hooke describes the small structures that he observed under the microscope. Which part of the cell theory is best supported by this discovery? ...
... 5. Robert Hooke is credited with discovering cells while observing a piece of cork under a microscope. In his book Micrographia, which he published in 1665, Hooke describes the small structures that he observed under the microscope. Which part of the cell theory is best supported by this discovery? ...
7.2 Many organisms, including humans, have specialized organ
... the organism alive. Many organisms (for example yeast, algae) are single-celled and many organisms (for example plants, fungi and animals) are made of millions of cells that work in coordination. 3. All cells come from other cells and they hold the genetic information needed for cell division and gr ...
... the organism alive. Many organisms (for example yeast, algae) are single-celled and many organisms (for example plants, fungi and animals) are made of millions of cells that work in coordination. 3. All cells come from other cells and they hold the genetic information needed for cell division and gr ...
Cell Intro - PPT - Brookville Local Schools
... Von Ebner's gland cell in tongue (washes taste buds) Mammary gland cell (milk secretion) Lacrimal gland cell (tear secretion) Ceruminous gland cell in ear (earwax secretion) Eccrine sweat gland dark cell (glycoprotein secretion) Eccrine sweat gland clear cell (small molecule secretion) Apocrine swea ...
... Von Ebner's gland cell in tongue (washes taste buds) Mammary gland cell (milk secretion) Lacrimal gland cell (tear secretion) Ceruminous gland cell in ear (earwax secretion) Eccrine sweat gland dark cell (glycoprotein secretion) Eccrine sweat gland clear cell (small molecule secretion) Apocrine swea ...
Science - B3 Revision
... ◦ Allows for cell differentiation ◦ organism can be more complex Becoming multi-cellular requires the development of specialised organ systems: ◦ communication between cells (nervous system) ◦ supplying the cells with nutrients (digestive system) ◦ controlling exchanges with the environment (respira ...
... ◦ Allows for cell differentiation ◦ organism can be more complex Becoming multi-cellular requires the development of specialised organ systems: ◦ communication between cells (nervous system) ◦ supplying the cells with nutrients (digestive system) ◦ controlling exchanges with the environment (respira ...
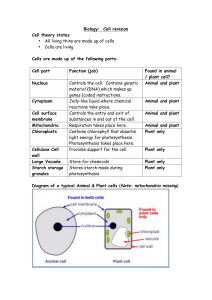
Biology Cell revision
... Biology: Cell revision Cell theory states • All living thins are made up of cells • Cells are living Cells are made up of the following parts: Cell part ...
... Biology: Cell revision Cell theory states • All living thins are made up of cells • Cells are living Cells are made up of the following parts: Cell part ...
CELLS
... 2. What are animal structures? How do they help animals in growth and survival? 3. What are some of the similarities in plants and animals? How are they different? ...
... 2. What are animal structures? How do they help animals in growth and survival? 3. What are some of the similarities in plants and animals? How are they different? ...
Review Sheet
... 4. For each "Great Moment in Cell Biology": what was the main question or problem being addressed? What were the methods used? What were the key results? What was the conclusion? (You should be able to answer each question with at least a couple sentences of information.) 5. What is the "cell theory ...
... 4. For each "Great Moment in Cell Biology": what was the main question or problem being addressed? What were the methods used? What were the key results? What was the conclusion? (You should be able to answer each question with at least a couple sentences of information.) 5. What is the "cell theory ...
Semester Review
... c. Cells are the basic unit of life d. Cells in multicellular organisms have specific jobs List the functions that are performed by every cell. a. Receive nutrients b. Exchange carbon dioxide and c. Have waste products taken away The process that converts light energy from the sun into chemical ener ...
... c. Cells are the basic unit of life d. Cells in multicellular organisms have specific jobs List the functions that are performed by every cell. a. Receive nutrients b. Exchange carbon dioxide and c. Have waste products taken away The process that converts light energy from the sun into chemical ener ...
Biology Second Semester Exam Review Answers Bacteria and
... 2. Describe the function of each bacteria part: a. Flagella 473 Whip-like tail used for movement b. Ribosome-177 Small organelle on which proteins are assembled c. Cell Wall-183 For protection & support 3. Describe Gram staining and what the results mean. 473 Gram Staining identifies bacteria with l ...
... 2. Describe the function of each bacteria part: a. Flagella 473 Whip-like tail used for movement b. Ribosome-177 Small organelle on which proteins are assembled c. Cell Wall-183 For protection & support 3. Describe Gram staining and what the results mean. 473 Gram Staining identifies bacteria with l ...
Content Domain 2: Organisms
... 16. Bulk transport into the cell is known as _________________________, and bulk transport out of the cell is known as ___________________________. 17. ______________________ are special proteins that speed up the rate of chemical reactions. 18. The ___________________ is the substance an enzyme act ...
... 16. Bulk transport into the cell is known as _________________________, and bulk transport out of the cell is known as ___________________________. 17. ______________________ are special proteins that speed up the rate of chemical reactions. 18. The ___________________ is the substance an enzyme act ...
Human Anatomy
... Organs – different tissues working together to do a special function Organ Systems – several organs working together ...
... Organs – different tissues working together to do a special function Organ Systems – several organs working together ...
Science Chapter 1 Unit A
... Vacuoles- sacs that store water, food, & waste Golgi apparatus- helps cell from breaking Chloroplast (only in plant cells)- absorbs sunlight & uses energy to make food ...
... Vacuoles- sacs that store water, food, & waste Golgi apparatus- helps cell from breaking Chloroplast (only in plant cells)- absorbs sunlight & uses energy to make food ...
Advanced Cell Biology BI735
... Advanced Cell Biology BI735 Syllabus Fall 2008 Overview Complex organisms are comprised of hundreds of distinct cell types that carry out different functions required to keep the organism alive. To investigate and understand these functions, cell biologists have developed fascinating experimental ap ...
... Advanced Cell Biology BI735 Syllabus Fall 2008 Overview Complex organisms are comprised of hundreds of distinct cell types that carry out different functions required to keep the organism alive. To investigate and understand these functions, cell biologists have developed fascinating experimental ap ...
Hello!!! - Elida Local Schools
... Organization in Multicellular Organisms From simplest to most complex, the proper levels of organization in multicellular organisms are: ...
... Organization in Multicellular Organisms From simplest to most complex, the proper levels of organization in multicellular organisms are: ...
Biology Facts
... o Examples are – point mutation, frameshift mutation (more harmful), chromosomal mutation A clone has exact copy of DNA – like an identical twin Genetic engineering – method of altering a gene to add change or delete a trait. Errors in chromosome number can result in genetic disorders. o Ex- trisomy ...
... o Examples are – point mutation, frameshift mutation (more harmful), chromosomal mutation A clone has exact copy of DNA – like an identical twin Genetic engineering – method of altering a gene to add change or delete a trait. Errors in chromosome number can result in genetic disorders. o Ex- trisomy ...
Chapter 1 (Sections 1-3) Study Guide: Cell Structure and Function
... daughter cell two cells that form when the cytoplasm and its components divide cell plate a disk formed between the two new nuclei of a plant cell that is dividing homologous chromosome a pair of similar chromosomes sister chromatid copy of a chromosome made during S-phase of cell cycle cell differe ...
... daughter cell two cells that form when the cytoplasm and its components divide cell plate a disk formed between the two new nuclei of a plant cell that is dividing homologous chromosome a pair of similar chromosomes sister chromatid copy of a chromosome made during S-phase of cell cycle cell differe ...
Chapter 1 (Sections 1-3) Study Guide: Cell Structure and Function
... daughter cell two cells that form when the cytoplasm and its components divide cell plate a disk formed between the two new nuclei of a plant cell that is dividing homologous chromosome a pair of similar chromosomes sister chromatid copy of a chromosome made during S-phase of cell cycle cell differe ...
... daughter cell two cells that form when the cytoplasm and its components divide cell plate a disk formed between the two new nuclei of a plant cell that is dividing homologous chromosome a pair of similar chromosomes sister chromatid copy of a chromosome made during S-phase of cell cycle cell differe ...
Cell (biology)

The cell (from Latin cella, meaning ""small room"") is the basic structural, functional, and biological unit of all known living organisms. Cells are the smallest unit of life that can replicate independently, and are often called the ""building blocks of life"". The study of cells is called cell biology.Cells consist of cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, which contains many biomolecules such as proteins and nucleic acids. Organisms can be classified as unicellular (consisting of a single cell; including bacteria) or multicellular (including plants and animals). While the number of cells in plants and animals varies from species to species, humans contain more than 10 trillion (1013) cells. Most plant and animal cells are visible only under the microscope, with dimensions between 1 and 100 micrometres.The cell was discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665, who named the biological unit for its resemblance to cells inhabited by Christian monks in a monastery. Cell theory, first developed in 1839 by Matthias Jakob Schleiden and Theodor Schwann, states that all organisms are composed of one or more cells, that cells are the fundamental unit of structure and function in all living organisms, that all cells come from preexisting cells, and that all cells contain the hereditary information necessary for regulating cell functions and for transmitting information to the next generation of cells. Cells emerged on Earth at least 3.5 billion years ago.