Descriptor PDF
... 10 semester units – 6 units lecture, 4 units lab E. Course Topics 1. Atoms and molecules important for life 2. Protein structure and function 3. Nucleic acids and the RNA world 4. Carbohydrates 5. Lipids, membranes and the first cells 6. Cell structure – prokaryotic and eukaryotic 7. Cell-cell inter ...
... 10 semester units – 6 units lecture, 4 units lab E. Course Topics 1. Atoms and molecules important for life 2. Protein structure and function 3. Nucleic acids and the RNA world 4. Carbohydrates 5. Lipids, membranes and the first cells 6. Cell structure – prokaryotic and eukaryotic 7. Cell-cell inter ...
Chapter 1: What is Biology
... Light-independent (dark reactions or Calvin Cycle) White light: ROYGBIV o Most light for photosynthesis is from red, blue, and violet part of spectrum Chemosynthesis: makes food using chemicals (no light) Autotrophs: _____________________________ Heterotrophs: ___________________________ ...
... Light-independent (dark reactions or Calvin Cycle) White light: ROYGBIV o Most light for photosynthesis is from red, blue, and violet part of spectrum Chemosynthesis: makes food using chemicals (no light) Autotrophs: _____________________________ Heterotrophs: ___________________________ ...
Ch_2
... - 2 types: DNA (genetic material) and RNA (helps in protein synthesis) • inorganic compound: doesn’t come from living things Water is used for - carrying substances in the body - controlling body temperature - keeping the size/shape of cells - helping processes like digestion ...
... - 2 types: DNA (genetic material) and RNA (helps in protein synthesis) • inorganic compound: doesn’t come from living things Water is used for - carrying substances in the body - controlling body temperature - keeping the size/shape of cells - helping processes like digestion ...
Bio2201Unit1SG File
... 12. Explain osmosis. Under which condition does water move into the cell? Out of the cell? Under which condition do equal amounts of water enter and exit the cell? 13. How does osmosis affect plant and animal cells differently? 14. Explain facilitated diffusion. Name a molecule that moves across th ...
... 12. Explain osmosis. Under which condition does water move into the cell? Out of the cell? Under which condition do equal amounts of water enter and exit the cell? 13. How does osmosis affect plant and animal cells differently? 14. Explain facilitated diffusion. Name a molecule that moves across th ...
Mitosis - TeacherWeb
... •Number of ribosomes & mitochondria double S Phase •Chromosome replication •DNA molecules duplicate G2 Phase •Final preparation for division •Spindle fibers assemble Mitosis •Actual cell division ...
... •Number of ribosomes & mitochondria double S Phase •Chromosome replication •DNA molecules duplicate G2 Phase •Final preparation for division •Spindle fibers assemble Mitosis •Actual cell division ...
The Unforgetables of Biology
... function, and all cells come from other cells. The main tool that allowed for the discovery of cells and cell theory was the compound light microscope. There are two main types of cells: Prokaryotes do not have a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotes do have a nucleus and membrane-wrapp ...
... function, and all cells come from other cells. The main tool that allowed for the discovery of cells and cell theory was the compound light microscope. There are two main types of cells: Prokaryotes do not have a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotes do have a nucleus and membrane-wrapp ...
Chapter 1 Review and Test Preparation Vocabulary Review Use the
... 1. A structure containing at least two different types of tissues that work together for a common purpose is an _____ . 2. The growth response of plants to gravity is called _____ . 3. The part of a cell that controls what enters and exits the cell is the _____ . 4. Photosynthesis takes place in the ...
... 1. A structure containing at least two different types of tissues that work together for a common purpose is an _____ . 2. The growth response of plants to gravity is called _____ . 3. The part of a cell that controls what enters and exits the cell is the _____ . 4. Photosynthesis takes place in the ...
Use for Nov. 20,12 Unit 2 Cells Test Study Guide
... 20. Water is a good solvent. Explain what this means. 21. The diagram shows two solutions that are separated by a partially permeable membrane. In which direction will most water molecules move in relation to their concentration gradient? Draw an arrow showing the direction of movement. ...
... 20. Water is a good solvent. Explain what this means. 21. The diagram shows two solutions that are separated by a partially permeable membrane. In which direction will most water molecules move in relation to their concentration gradient? Draw an arrow showing the direction of movement. ...
2005 Cell Bio Exam
... QUESTION ONE: CELL SPECIALISATION Cells can be specialised to carry out a specific role. Below are diagrams of two cells specialised for absorbing materials. The diagrams are not to scale. Plant cell: ...
... QUESTION ONE: CELL SPECIALISATION Cells can be specialised to carry out a specific role. Below are diagrams of two cells specialised for absorbing materials. The diagrams are not to scale. Plant cell: ...
5th Grade Science Human Body Vocabulary Cards
... the hard structure (bones and cartilages) that provides a frame for the body ...
... the hard structure (bones and cartilages) that provides a frame for the body ...
Living Systems PowerPoint Notes
... _____________ that works together to carry out a set of functions. Examples of organs include the stomach, intestines, heart, lung, and skin. The _____________ is an organ. This child has chicken pox, a disease that affects the skin. _____________ _____________ include stems, roots, and ...
... _____________ that works together to carry out a set of functions. Examples of organs include the stomach, intestines, heart, lung, and skin. The _____________ is an organ. This child has chicken pox, a disease that affects the skin. _____________ _____________ include stems, roots, and ...
Chapter 3 review
... processes 4. What is the function of channel proteins? Allow substances to pass through the plasma membrane; like H ions for ATP formation 5. What is the function of a carrier protein? To selectively with a specific molecule or ion so that it can cross the plasma membrane 6. A cell that has a large ...
... processes 4. What is the function of channel proteins? Allow substances to pass through the plasma membrane; like H ions for ATP formation 5. What is the function of a carrier protein? To selectively with a specific molecule or ion so that it can cross the plasma membrane 6. A cell that has a large ...
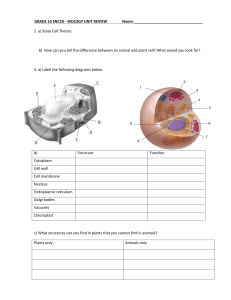
BIOLOGY EXAM REVIEW
... Cell wall Cell membrane Nucleus Endoplasmic reticulum Golgi bodies Vacuoles Chloroplast ...
... Cell wall Cell membrane Nucleus Endoplasmic reticulum Golgi bodies Vacuoles Chloroplast ...
Fact you need to know to pass the Living Environment Regents
... glucose to move from the blood into body cells, resulting in a lower glucose level in the blood. Another hormone called __Glu_____________ hormone secreted by the pancreas works in the opposite way. When the glucose level in the blood is too low, this hormone prompts the release of glucose stored in ...
... glucose to move from the blood into body cells, resulting in a lower glucose level in the blood. Another hormone called __Glu_____________ hormone secreted by the pancreas works in the opposite way. When the glucose level in the blood is too low, this hormone prompts the release of glucose stored in ...
COMMUNICATION
... 8) Fat soluble molecules can pass easily through cell membranes because a. the outside of the cell membrane is hydrophobic b. the outside of the cell membrane is hydrophilic c. the molecules pass through small pores in the membrane d. they are helped through by the large proteins embedded in the mem ...
... 8) Fat soluble molecules can pass easily through cell membranes because a. the outside of the cell membrane is hydrophobic b. the outside of the cell membrane is hydrophilic c. the molecules pass through small pores in the membrane d. they are helped through by the large proteins embedded in the mem ...
Human Bio 11 – Dalesandro
... your body’s defense systems. What kind of cell controls whether or not you have a fever? Describe this cell’s appearance. 2) What blood cell contains histamine and controls allergic reactions? Describe this cell’s appearance. 3) What blood cell controls clotting and stops you from bleeding? Describe ...
... your body’s defense systems. What kind of cell controls whether or not you have a fever? Describe this cell’s appearance. 2) What blood cell contains histamine and controls allergic reactions? Describe this cell’s appearance. 3) What blood cell controls clotting and stops you from bleeding? Describe ...
Bacteria and Viruses
... – Inserts viral nucleic acid and inserts it into the host cell’s chromosome (prophage) – Gets replicated as host cell divides (through mitosis) – Can remain inactive for a long period of time. Like Bacteria, Viruses produce disease by disrupting the body’s normal equilibrium. They either directly at ...
... – Inserts viral nucleic acid and inserts it into the host cell’s chromosome (prophage) – Gets replicated as host cell divides (through mitosis) – Can remain inactive for a long period of time. Like Bacteria, Viruses produce disease by disrupting the body’s normal equilibrium. They either directly at ...
Final Exam Review
... • Complimentary base pairing~ DNA= A-T, C-G; RNA= A-U, C-G • DNA/RNA~ deoxyribonucleic acid (genetic blueprint)/ ribonucleic acid (protein synthesis) • enzymes/ substrate / lock & key~ enzymes (catalyst to jumpstart a reaction) ...
... • Complimentary base pairing~ DNA= A-T, C-G; RNA= A-U, C-G • DNA/RNA~ deoxyribonucleic acid (genetic blueprint)/ ribonucleic acid (protein synthesis) • enzymes/ substrate / lock & key~ enzymes (catalyst to jumpstart a reaction) ...
Document
... Indepdendent assortment- gene pairs separate randomly and independently of each other during meiosis. Multiple alleles- there are more than 2 alleles in a population. Blood type: A,B,O Ch. 12 DNA and RNA Nucleotide- nucleic acid made up of a 5 carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and nitrogenous base Ba ...
... Indepdendent assortment- gene pairs separate randomly and independently of each other during meiosis. Multiple alleles- there are more than 2 alleles in a population. Blood type: A,B,O Ch. 12 DNA and RNA Nucleotide- nucleic acid made up of a 5 carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and nitrogenous base Ba ...
Cell (biology)

The cell (from Latin cella, meaning ""small room"") is the basic structural, functional, and biological unit of all known living organisms. Cells are the smallest unit of life that can replicate independently, and are often called the ""building blocks of life"". The study of cells is called cell biology.Cells consist of cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, which contains many biomolecules such as proteins and nucleic acids. Organisms can be classified as unicellular (consisting of a single cell; including bacteria) or multicellular (including plants and animals). While the number of cells in plants and animals varies from species to species, humans contain more than 10 trillion (1013) cells. Most plant and animal cells are visible only under the microscope, with dimensions between 1 and 100 micrometres.The cell was discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665, who named the biological unit for its resemblance to cells inhabited by Christian monks in a monastery. Cell theory, first developed in 1839 by Matthias Jakob Schleiden and Theodor Schwann, states that all organisms are composed of one or more cells, that cells are the fundamental unit of structure and function in all living organisms, that all cells come from preexisting cells, and that all cells contain the hereditary information necessary for regulating cell functions and for transmitting information to the next generation of cells. Cells emerged on Earth at least 3.5 billion years ago.