File
... so there are 1000s of them. Increases in temperature will increase speed of reactions to a point, excessive heat denatures proteins. Substrate: Substance acted upon by enzyme. Active Site: Portion of enzyme which interacts with substrate Nucleaic Acids: Made up of nucleotides, which are made up of n ...
... so there are 1000s of them. Increases in temperature will increase speed of reactions to a point, excessive heat denatures proteins. Substrate: Substance acted upon by enzyme. Active Site: Portion of enzyme which interacts with substrate Nucleaic Acids: Made up of nucleotides, which are made up of n ...
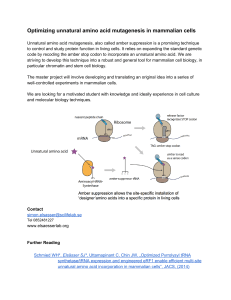
Optimizing unnatural amino acid mutagenesis in mammalian cells
... Unnatural amino acid mutagenesis, also called amber suppression is a promising technique to control and study protein function in living cells. It relies on expanding the standard genetic code by recoding the amber stop codon to incorporate an unnatural amino acid. We are striving to develop this ...
... Unnatural amino acid mutagenesis, also called amber suppression is a promising technique to control and study protein function in living cells. It relies on expanding the standard genetic code by recoding the amber stop codon to incorporate an unnatural amino acid. We are striving to develop this ...
Unit 1 Test Review Guide: 5 pts Extra Credit on Summative Category
... 22. Label the Left Upper Quadrant and the nine abdominopelvic regions on the figure to the right. Organization of the Human Body 23. How is the human body organized? How are a cell, tissue, organ, and organ system related? ...
... 22. Label the Left Upper Quadrant and the nine abdominopelvic regions on the figure to the right. Organization of the Human Body 23. How is the human body organized? How are a cell, tissue, organ, and organ system related? ...
Food Chain
... RNA from the DNA template So when the DNA base is ADENINE, If nitrogen base in DNA is CGATGTACGGTAA the mRNA that pairs what is sequence of nitrogen bases in mRNA? with that base will be URACIL ...
... RNA from the DNA template So when the DNA base is ADENINE, If nitrogen base in DNA is CGATGTACGGTAA the mRNA that pairs what is sequence of nitrogen bases in mRNA? with that base will be URACIL ...
Levels of Cellular Organization
... Can be neutral, negative, or positively charged A group of atoms is called a molecule ...
... Can be neutral, negative, or positively charged A group of atoms is called a molecule ...
HERE
... If a woman with a type A blood has a child with a man with type B blood and their first child has type O blood. Give the genotypes of the woman and the man and do the cross. What are the odds that they will have a child with type O blood again? 1 of 4, 25% What are the odds they will have a child wi ...
... If a woman with a type A blood has a child with a man with type B blood and their first child has type O blood. Give the genotypes of the woman and the man and do the cross. What are the odds that they will have a child with type O blood again? 1 of 4, 25% What are the odds they will have a child wi ...
biology sol review sheet
... 6. ____________________- contains digestive enzymes to break down old cell parts and debris 7. ____________________- storage tank of the cell 8. ____________________- power center of the cell 9. ____________________- organelle for photosynthesis; contains chlorophyll 10. ____________________- assist ...
... 6. ____________________- contains digestive enzymes to break down old cell parts and debris 7. ____________________- storage tank of the cell 8. ____________________- power center of the cell 9. ____________________- organelle for photosynthesis; contains chlorophyll 10. ____________________- assist ...
Grade 7: A re-introduction to Biology - gillammscience
... Use your books and the internet to complete the following tasks. When you are finished go back to www.gillammscience.pbworks.com go to your class page, then to cell respiration activities. Insert your name in the table, upload the document into the column next to your name. ...
... Use your books and the internet to complete the following tasks. When you are finished go back to www.gillammscience.pbworks.com go to your class page, then to cell respiration activities. Insert your name in the table, upload the document into the column next to your name. ...
Lesson 3.3 – Passive and Active Transport
... • This is used to transport small molecules (O2, CO2, H2O) across the cell membrane, directly through the lipid bilayer – Ex. The exchange of O2 and CO2 between the lungs and the blood vessels • The amount of O2 in the lungs is HIGH so it moves into the blood vessels to be carried to the body cells ...
... • This is used to transport small molecules (O2, CO2, H2O) across the cell membrane, directly through the lipid bilayer – Ex. The exchange of O2 and CO2 between the lungs and the blood vessels • The amount of O2 in the lungs is HIGH so it moves into the blood vessels to be carried to the body cells ...
DNA
... • Function- energy storage and insulation • Tests: brown paper test , potato chips on a napkin will leave a greasey residue • Examples: fats and steroids Example: Bears store fat to hibernate ...
... • Function- energy storage and insulation • Tests: brown paper test , potato chips on a napkin will leave a greasey residue • Examples: fats and steroids Example: Bears store fat to hibernate ...
File - Mr. Downing Science 10
... suspended in the cytoplasm and can move around through the process of cytoplasmic streaming – stores nutrients until organelles are ready to use them ...
... suspended in the cytoplasm and can move around through the process of cytoplasmic streaming – stores nutrients until organelles are ready to use them ...
Chapter 3
... 32) All are structures involved in synthesis of biomolecules. All but ribosomes are membranous structures. Ribosomes may be free or attached to ER, making it rough. See Fig. 3-12 in the chapter. 33) The cytoskeleton consists of actin microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules and forms ...
... 32) All are structures involved in synthesis of biomolecules. All but ribosomes are membranous structures. Ribosomes may be free or attached to ER, making it rough. See Fig. 3-12 in the chapter. 33) The cytoskeleton consists of actin microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules and forms ...
Chapters 4 and 5 Cell Structures, Functions and Transport
... • All living things are made up of cells. • All cells come from preexisting cells through cell division. • There are two types of cells: 1) Prokaryotic 2) Eukaryotic ...
... • All living things are made up of cells. • All cells come from preexisting cells through cell division. • There are two types of cells: 1) Prokaryotic 2) Eukaryotic ...
Life Science Review MCAS
... • All living things are made up of cells. • All cells come from preexisting cells through cell division. • There are two types of cells: 1) Prokaryotic 2) Eukaryotic ...
... • All living things are made up of cells. • All cells come from preexisting cells through cell division. • There are two types of cells: 1) Prokaryotic 2) Eukaryotic ...
Cell Specialisation - NCEA Level 2 Biology
... 1. What are the beating hairs for movement of a unicellular organism called? Cilia 2. What organism uses these? Paramecium 3. These structures also help with feeding by moving food into a specialised area, what is this called? Cilia 4. Amoeba use extensions of the flexible cell membrane to move, wha ...
... 1. What are the beating hairs for movement of a unicellular organism called? Cilia 2. What organism uses these? Paramecium 3. These structures also help with feeding by moving food into a specialised area, what is this called? Cilia 4. Amoeba use extensions of the flexible cell membrane to move, wha ...
Intro Unit Notes - Reading Community Schools
... • Generate ATP energy through cellular respiration ...
... • Generate ATP energy through cellular respiration ...
Module A-1 (Principles of Biology)
... (A) cellular reactions that release energy (B) photosynthetic reactions that store energy (C) muscle reactions that use energy A) A and B, only C) A and C, only ...
... (A) cellular reactions that release energy (B) photosynthetic reactions that store energy (C) muscle reactions that use energy A) A and B, only C) A and C, only ...
Cells
... Cytoplasm refers to cytosol plus organelles and inclusions. cytosol - contains proteins, enzymes, nutrients, ions, and other small molecules organelles -“little organs” - highly organized structures with characteristic shapes that are specialized for specific cellular activities. inclusions - are ...
... Cytoplasm refers to cytosol plus organelles and inclusions. cytosol - contains proteins, enzymes, nutrients, ions, and other small molecules organelles -“little organs” - highly organized structures with characteristic shapes that are specialized for specific cellular activities. inclusions - are ...
Ch.1 Invitation to Biology - OCC
... Ch.1 The Science of Biology OCC BIO 114 Created by Dave Werner ...
... Ch.1 The Science of Biology OCC BIO 114 Created by Dave Werner ...
Cells Study Guide
... o All organisms take in raw materials and energy and get rid of wastes. o Larger organisms are made of more cells, not larger cells. o Unicellular organisms have only one cell and life is limited to the life of that cell. o Multicellular organisms are made of many cells and their lifespan is not lim ...
... o All organisms take in raw materials and energy and get rid of wastes. o Larger organisms are made of more cells, not larger cells. o Unicellular organisms have only one cell and life is limited to the life of that cell. o Multicellular organisms are made of many cells and their lifespan is not lim ...
Grade 7 - Humble ISD
... • All living things move, respond, obtain and use energy, are made up of cells, grow/reproduce, and have a set life span. • Living organisms must be able to maintain balance. • All organisms are made up of smaller units called cells. Cell theory states that all cells come from pre-existing cells. Ce ...
... • All living things move, respond, obtain and use energy, are made up of cells, grow/reproduce, and have a set life span. • Living organisms must be able to maintain balance. • All organisms are made up of smaller units called cells. Cell theory states that all cells come from pre-existing cells. Ce ...
Biology Chp 1 Notes (The Science of Life)
... a. the sum of all the chemical reactions that take in and transform energy and materials from the environment. 5. Growth and Development ...
... a. the sum of all the chemical reactions that take in and transform energy and materials from the environment. 5. Growth and Development ...
COMMUNICATION
... Muscle cells require more energy, and so would be expected to carry out more respiration. As a result, we would expect to find a higher density of mitochondria in these cells as their primary function is to carry out respiration. ...
... Muscle cells require more energy, and so would be expected to carry out more respiration. As a result, we would expect to find a higher density of mitochondria in these cells as their primary function is to carry out respiration. ...
Cell (biology)

The cell (from Latin cella, meaning ""small room"") is the basic structural, functional, and biological unit of all known living organisms. Cells are the smallest unit of life that can replicate independently, and are often called the ""building blocks of life"". The study of cells is called cell biology.Cells consist of cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, which contains many biomolecules such as proteins and nucleic acids. Organisms can be classified as unicellular (consisting of a single cell; including bacteria) or multicellular (including plants and animals). While the number of cells in plants and animals varies from species to species, humans contain more than 10 trillion (1013) cells. Most plant and animal cells are visible only under the microscope, with dimensions between 1 and 100 micrometres.The cell was discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665, who named the biological unit for its resemblance to cells inhabited by Christian monks in a monastery. Cell theory, first developed in 1839 by Matthias Jakob Schleiden and Theodor Schwann, states that all organisms are composed of one or more cells, that cells are the fundamental unit of structure and function in all living organisms, that all cells come from preexisting cells, and that all cells contain the hereditary information necessary for regulating cell functions and for transmitting information to the next generation of cells. Cells emerged on Earth at least 3.5 billion years ago.