Biology CPA Cell Organelles and Features J.Dolce
... 9. Describe the different types of plasma membrane proteins, with regard to structure, location and function. ...
... 9. Describe the different types of plasma membrane proteins, with regard to structure, location and function. ...
Immunity - 1st and 2nd lines of defense
... attack pathogens, but don’t “remember” for next time leukocytes phagocytic white blood cells macrophages, neutrophils, natural killer cells ...
... attack pathogens, but don’t “remember” for next time leukocytes phagocytic white blood cells macrophages, neutrophils, natural killer cells ...
anatomy of the body
... Translation (tRNA) picks up amino acids Cell Division Cell division is the process by which a cell reproduces itself Two types of cell division o Mitosis One cell with the diploid number of chromosomes divides once to form two cells, each with the diploid number of chromosomes (46) Stages ...
... Translation (tRNA) picks up amino acids Cell Division Cell division is the process by which a cell reproduces itself Two types of cell division o Mitosis One cell with the diploid number of chromosomes divides once to form two cells, each with the diploid number of chromosomes (46) Stages ...
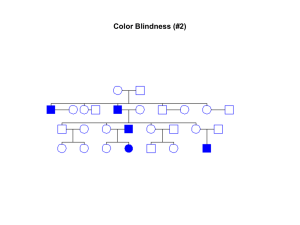
Extra Pedigree Problem - Winona State University
... kidney damage and loss of body water in urine painful erections in men (priapism) blood blockage in the spleen or liver (sequestration) eye damage low red blood cell counts (anemia) delayed growth ...
... kidney damage and loss of body water in urine painful erections in men (priapism) blood blockage in the spleen or liver (sequestration) eye damage low red blood cell counts (anemia) delayed growth ...
BIO 1101 - Makerere University Courses
... theory and origin of life. It also describes the functions, structures and division processes of biological cells. COURSE OBJECTIVES By the end of this course, learners are expected to be able to: 1. Describe the cellular basis of life and types of cells. 2. Describe the structures and adaptation of ...
... theory and origin of life. It also describes the functions, structures and division processes of biological cells. COURSE OBJECTIVES By the end of this course, learners are expected to be able to: 1. Describe the cellular basis of life and types of cells. 2. Describe the structures and adaptation of ...
Homework Exercise 1 - Cells, Tissues and Organs 1. Place the
... Job Vacancies for Specialised Cells ...
... Job Vacancies for Specialised Cells ...
MOLECULES OF LIFE
... a. Selective movement of materials into and out of cell b. communication with other cells and the environment 2. NUCLEUS: Usually the largest structure in a cell. Functions of the nucleus: a. Stores DNA (genetic material that makes up chromosomes). Our genes are on the chromosomes) 3. MITOCHONDRIA C ...
... a. Selective movement of materials into and out of cell b. communication with other cells and the environment 2. NUCLEUS: Usually the largest structure in a cell. Functions of the nucleus: a. Stores DNA (genetic material that makes up chromosomes). Our genes are on the chromosomes) 3. MITOCHONDRIA C ...
Sc 8 Unit 2 Topic 5 Notes WP
... Nerve cells have long, branched fibers running from the main part of the cell, shaped to carry nerve signals from one part of the body to another. ...
... Nerve cells have long, branched fibers running from the main part of the cell, shaped to carry nerve signals from one part of the body to another. ...
Cells: Practice Questions #1 1.
... 2. B 15. D 3. B 16. A 4. A 17. A 5. C 18. D 6. A 19. A 7. D 20. chloroplast 8. A 21. ribosome 9. C 22. B 10. B 23. A 11. A 24. D 12. B 25. C 13. C ...
... 2. B 15. D 3. B 16. A 4. A 17. A 5. C 18. D 6. A 19. A 7. D 20. chloroplast 8. A 21. ribosome 9. C 22. B 10. B 23. A 11. A 24. D 12. B 25. C 13. C ...
Types of cellls sem 2 2011
... • Proteins within the cell form bands of varying density and thickness. • Contraction of these cells cause the heart to beat. ...
... • Proteins within the cell form bands of varying density and thickness. • Contraction of these cells cause the heart to beat. ...
Molecular Biology of B Cells. Edition No. 2 Brochure
... Molecular Biology of B Cells, Second Edition is a comprehensive reference to how B cells are generated, selected, activated and engaged in antibody production. All of these developmental and stimulatory processes are described in molecular, immunological, and genetic terms to give a clear understand ...
... Molecular Biology of B Cells, Second Edition is a comprehensive reference to how B cells are generated, selected, activated and engaged in antibody production. All of these developmental and stimulatory processes are described in molecular, immunological, and genetic terms to give a clear understand ...
Cells - Effingham County Schools
... make food by using the energy of sunlight chloroplasts Photosynthesis takes place in the ___________ and depends on a green pigment called chlorophyll. ...
... make food by using the energy of sunlight chloroplasts Photosynthesis takes place in the ___________ and depends on a green pigment called chlorophyll. ...
Final Exam Review Packet (Scary, Isn`t It?) Date: Time: Room
... ___Prokaryotic (BACTERIA)- contains DNA, cytoplasm, ribosomes, cell membrane, cell wall (NO membrane bound organelles); Eukaryotic cell (ANIMAL, PLANT, FUNGI, PROTISTS)- more complex with membrane bound organelles and DNA contained in a nucleus_____ 3. What is the difference between a unicellular a ...
... ___Prokaryotic (BACTERIA)- contains DNA, cytoplasm, ribosomes, cell membrane, cell wall (NO membrane bound organelles); Eukaryotic cell (ANIMAL, PLANT, FUNGI, PROTISTS)- more complex with membrane bound organelles and DNA contained in a nucleus_____ 3. What is the difference between a unicellular a ...
Dev Biol L1
... multicellular organism, with hundreds of different cell types, all formed at the correct time and in the correct place to build a functioning body and perform all the individual functions of life. ...
... multicellular organism, with hundreds of different cell types, all formed at the correct time and in the correct place to build a functioning body and perform all the individual functions of life. ...
CURRICULUM PLAN 2015-16 (Department of Botany, Kalindi
... Karp, G. (2010). Cell Biology, John 6. To prepare temporary stained preparation of Wiley & Sons, U.S.A. 6th edition. mitochondria from striated muscle cells /cheek epithelial cells using vital stain Janus green 7. To prepare temporary stained squash from root tips of Allium cepa and to study the var ...
... Karp, G. (2010). Cell Biology, John 6. To prepare temporary stained preparation of Wiley & Sons, U.S.A. 6th edition. mitochondria from striated muscle cells /cheek epithelial cells using vital stain Janus green 7. To prepare temporary stained squash from root tips of Allium cepa and to study the var ...
CENTRO ESCOLAR UNIVERSITY Biological Sciences Department
... interactions; structures of the cells and their functions; cell growth and oncogenic transformation transport and cell signaling and communications; cytoskeleton and the extracellular matrix; chromatin structure and RNA synthesis; genetic mechanisms of heritability of characteristics; and cell movem ...
... interactions; structures of the cells and their functions; cell growth and oncogenic transformation transport and cell signaling and communications; cytoskeleton and the extracellular matrix; chromatin structure and RNA synthesis; genetic mechanisms of heritability of characteristics; and cell movem ...
SMK CONVENT BUKIT NANAS, KUALA LUMPUR
... A student is able to: structure and function compare the epidermal cells of • draw and label an onion or cells of Hydrilla leaf animal cell. with human cheek cells. • draw and label a Study electron micrographs of plant cell animal cells and plant cells to • identify the cellular identify cellular c ...
... A student is able to: structure and function compare the epidermal cells of • draw and label an onion or cells of Hydrilla leaf animal cell. with human cheek cells. • draw and label a Study electron micrographs of plant cell animal cells and plant cells to • identify the cellular identify cellular c ...
Surface Area to Volume Ratio
... Why are cells the size and shape that they are? Cells must be able to carry out functions efficiently. Many of these functions involve transporting substances throughout the cell and outside of the cell to other targets. ...
... Why are cells the size and shape that they are? Cells must be able to carry out functions efficiently. Many of these functions involve transporting substances throughout the cell and outside of the cell to other targets. ...
Unit 2 Exam Cell Cell organelles Plant and Animal Tissue
... some signals are long lived, reach distant organs by way of the circulatory system. These signals are called…. ...
... some signals are long lived, reach distant organs by way of the circulatory system. These signals are called…. ...
Biology Review Notes
... o Cytoplasm: clear, gel like fluid inside of all cells o Ribosomes: site of protein synthesis; where proteins are made; look like small dots o Endoplasmic Reticulum: folded membrane system where chemical reactions take place o Vacuole: storage organelle where materials are stored for the cell o Lyso ...
... o Cytoplasm: clear, gel like fluid inside of all cells o Ribosomes: site of protein synthesis; where proteins are made; look like small dots o Endoplasmic Reticulum: folded membrane system where chemical reactions take place o Vacuole: storage organelle where materials are stored for the cell o Lyso ...
cell - Jordan High School
... ability to form a physical barrier between the cell’s internal and external ...
... ability to form a physical barrier between the cell’s internal and external ...
Respiratory System
... Correct CH & Collect Clean out notes OBJ How the respiratory system cleans the air before it reaches the lungs Understand Organs=tissues=cells What are the parts of a cell ...
... Correct CH & Collect Clean out notes OBJ How the respiratory system cleans the air before it reaches the lungs Understand Organs=tissues=cells What are the parts of a cell ...
Practice Questions - the Elevate Student Portal.
... 9. What is the function of cholesterol in cell membranes? 10. What is the role of the Golgi apparatus in protein export? 11. What is apoptosis? 12. Why does apoptosis occur? Give 2 reasons. ...
... 9. What is the function of cholesterol in cell membranes? 10. What is the role of the Golgi apparatus in protein export? 11. What is apoptosis? 12. Why does apoptosis occur? Give 2 reasons. ...
Cell (biology)

The cell (from Latin cella, meaning ""small room"") is the basic structural, functional, and biological unit of all known living organisms. Cells are the smallest unit of life that can replicate independently, and are often called the ""building blocks of life"". The study of cells is called cell biology.Cells consist of cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, which contains many biomolecules such as proteins and nucleic acids. Organisms can be classified as unicellular (consisting of a single cell; including bacteria) or multicellular (including plants and animals). While the number of cells in plants and animals varies from species to species, humans contain more than 10 trillion (1013) cells. Most plant and animal cells are visible only under the microscope, with dimensions between 1 and 100 micrometres.The cell was discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665, who named the biological unit for its resemblance to cells inhabited by Christian monks in a monastery. Cell theory, first developed in 1839 by Matthias Jakob Schleiden and Theodor Schwann, states that all organisms are composed of one or more cells, that cells are the fundamental unit of structure and function in all living organisms, that all cells come from preexisting cells, and that all cells contain the hereditary information necessary for regulating cell functions and for transmitting information to the next generation of cells. Cells emerged on Earth at least 3.5 billion years ago.