EP BIOLOGY ANSWERS 1st Quarter - Easy Peasy All-in
... A Paramecium need to remove water to prevent swelling a bursting Your fingertips may look dried out like a prune in the sun, but they actually get creased because they are absorbing a lot of water. They do this because the skin on the palms of your hands and the soles of your feet is thicker and tou ...
... A Paramecium need to remove water to prevent swelling a bursting Your fingertips may look dried out like a prune in the sun, but they actually get creased because they are absorbing a lot of water. They do this because the skin on the palms of your hands and the soles of your feet is thicker and tou ...
BIO_130_132_Test_Questions_files/Bio 130 Final Questions
... c. helpful in conducting impulses d. all of the above e. none of the above ...
... c. helpful in conducting impulses d. all of the above e. none of the above ...
S2 rev pkt 2013(evol - body)
... 6. Some bacteria require a constant supply of oxygen to survive and are known as obligate bacteria must live in the absence of oxygen and are known as Bacteria that can survive with or without oxygen are ...
... 6. Some bacteria require a constant supply of oxygen to survive and are known as obligate bacteria must live in the absence of oxygen and are known as Bacteria that can survive with or without oxygen are ...
Biology Spring Review
... d. It is actively destroying cells Know functions and structures of a virus and understand their ability to cause disease. 4. Explain the interaction between the virus and the cell, using the terms antigen and cell surface receptor in your answer. ____________________________________________________ ...
... d. It is actively destroying cells Know functions and structures of a virus and understand their ability to cause disease. 4. Explain the interaction between the virus and the cell, using the terms antigen and cell surface receptor in your answer. ____________________________________________________ ...
Topic 1.1 Why are cells important?
... Each organelle and cell part has a specific role within a cell. This role is important to the proper functioning of both the cell and the organism. Some cells have more of one type of organelle and less of another. This is because different cells also perform different roles in an organism. For exam ...
... Each organelle and cell part has a specific role within a cell. This role is important to the proper functioning of both the cell and the organism. Some cells have more of one type of organelle and less of another. This is because different cells also perform different roles in an organism. For exam ...
organic compound foundation
... fraction of what scientists believe the total number could be — anywhere from 5 million to 100 million. Because of this abundance and diversity, scientists organize species with similar characteristics into groups based on their structure, function, and relationships. This is known as taxonomy or ta ...
... fraction of what scientists believe the total number could be — anywhere from 5 million to 100 million. Because of this abundance and diversity, scientists organize species with similar characteristics into groups based on their structure, function, and relationships. This is known as taxonomy or ta ...
Workplace Science - Continuing Education at KPR
... A repeating series of events, during which the eukaryotic cell carries out its necessary functions, including metabolism, cellular growth, and division, resulting in two genetically identical daughter cells. cell division Process of cell formation from the division of older cells. chromosome Coiled ...
... A repeating series of events, during which the eukaryotic cell carries out its necessary functions, including metabolism, cellular growth, and division, resulting in two genetically identical daughter cells. cell division Process of cell formation from the division of older cells. chromosome Coiled ...
membr_models_url
... 4. CHAPTER 3 PROCARYOTIC CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION CHAPTER 3 PROCARYOTIC CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION. Morphology. Size. Shape. Bacillus. Coccus. Spiral (including spirochaete) Pleomorphic. Drumsticks of... http://www.rlc.dcccd.edu/micro/chap3.htm - size 4K - 17-Sep-97 - English Translate 5. Learni ...
... 4. CHAPTER 3 PROCARYOTIC CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION CHAPTER 3 PROCARYOTIC CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION. Morphology. Size. Shape. Bacillus. Coccus. Spiral (including spirochaete) Pleomorphic. Drumsticks of... http://www.rlc.dcccd.edu/micro/chap3.htm - size 4K - 17-Sep-97 - English Translate 5. Learni ...
Multicellularity
... P granules, then, are an example of an autonomous signal, which is present only in cells that can trace their lineage back to the P4 cell. The P4 cell was generated by a series of asymmetric cell divisions in which the P granules were only inherited by one of the two daughter cells. Again, you do n ...
... P granules, then, are an example of an autonomous signal, which is present only in cells that can trace their lineage back to the P4 cell. The P4 cell was generated by a series of asymmetric cell divisions in which the P granules were only inherited by one of the two daughter cells. Again, you do n ...
Magnification Worksheet
... IB Biology HL - Magnification & Cells (adapted from Stephen Taylor: thanks, buddy.) Name:______________________________________________ TEM image shows a cell dividing. What is the magnification of this image? ...
... IB Biology HL - Magnification & Cells (adapted from Stephen Taylor: thanks, buddy.) Name:______________________________________________ TEM image shows a cell dividing. What is the magnification of this image? ...
10-4-16 Cells Study Guide - KEY
... could be on the test. Question #5 tells you that you need to know them all, but this question is just to ensure that you studying this information. a. Lysosome – digestion and break down of waste b. Smooth and Rough ER – in general, transport of proteins through the cell before they are exported (bu ...
... could be on the test. Question #5 tells you that you need to know them all, but this question is just to ensure that you studying this information. a. Lysosome – digestion and break down of waste b. Smooth and Rough ER – in general, transport of proteins through the cell before they are exported (bu ...
Gateway - OnMyCalendar
... – mRNA then transported from DNA to a ribosome Eukaryotes—mRNA leaves nucleus to find ribosome Prokaryotes—no nucleus, transcription and translation can occur simultaneously ...
... – mRNA then transported from DNA to a ribosome Eukaryotes—mRNA leaves nucleus to find ribosome Prokaryotes—no nucleus, transcription and translation can occur simultaneously ...
Gateway - Isabella Brown
... order to grow and maintain life come from the nutrients in food. There are 6 classes of nutrients in food- carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, water, vitamins, and minerals. Of these, carbohydrates, proteins, and fats are the major sources of energy for the body. Analyze and evaluate the sample daily d ...
... order to grow and maintain life come from the nutrients in food. There are 6 classes of nutrients in food- carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, water, vitamins, and minerals. Of these, carbohydrates, proteins, and fats are the major sources of energy for the body. Analyze and evaluate the sample daily d ...
Gateway Biology Review
... – mRNA then transported from DNA to a ribosome Eukaryotes—mRNA leaves nucleus to find ribosome Prokaryotes—no nucleus, transcription and translation can occur simultaneously ...
... – mRNA then transported from DNA to a ribosome Eukaryotes—mRNA leaves nucleus to find ribosome Prokaryotes—no nucleus, transcription and translation can occur simultaneously ...
right here - TeacherWeb
... - HOMEOSTASIS – internal equilibrium; the plasma membrane regulates what enters and leaves the cell; a selectively permeable membrane only allows certain substances to pass through - Effect of Concentration on a Cell 1. HYPOTONIC – water moves in; cell bursts 2. HYPERTONIC – water moves out; cell sh ...
... - HOMEOSTASIS – internal equilibrium; the plasma membrane regulates what enters and leaves the cell; a selectively permeable membrane only allows certain substances to pass through - Effect of Concentration on a Cell 1. HYPOTONIC – water moves in; cell bursts 2. HYPERTONIC – water moves out; cell sh ...
AP Biology - TeacherWeb
... coordination between cells protein signals released by body cells that stimulate other cells to divide _____________________________ crowded cells stop dividing each cell binds a bit of growth factor not enough activator left to trigger division in any one cell ...
... coordination between cells protein signals released by body cells that stimulate other cells to divide _____________________________ crowded cells stop dividing each cell binds a bit of growth factor not enough activator left to trigger division in any one cell ...
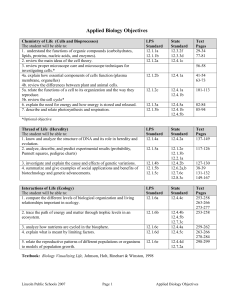
Biology Objectives - Lincoln Public Schools
... Applied Biology Objectives Chemistry of Life (Cells and Bioprocesses) The student will be able to: 1. understand the functions of organic compounds (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids, and enzymes). 2. review the main ideas of the cell theory. 3. review proper microscope care and microsc ...
... Applied Biology Objectives Chemistry of Life (Cells and Bioprocesses) The student will be able to: 1. understand the functions of organic compounds (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids, and enzymes). 2. review the main ideas of the cell theory. 3. review proper microscope care and microsc ...
B2 revision notes
... The chromosomal DNA moves freely around the cytoplasm and is not confined in a distinct nucleus as in plant and animal cells. o Plasmid DNA: Plasmids are small hoops of extra DNA that are separate from the chromosomal DNA. Plasmids contain genes that help tolerance against drugs and can be passe ...
... The chromosomal DNA moves freely around the cytoplasm and is not confined in a distinct nucleus as in plant and animal cells. o Plasmid DNA: Plasmids are small hoops of extra DNA that are separate from the chromosomal DNA. Plasmids contain genes that help tolerance against drugs and can be passe ...
Slide 1
... 7. Vesicles, including lysosomes (digestive enzymes) and peroxisomes (detoxification enzymes), are classified by their contents. ...
... 7. Vesicles, including lysosomes (digestive enzymes) and peroxisomes (detoxification enzymes), are classified by their contents. ...
EOC Review PowerPoint
... Cell to Cell Communication • Chemical Signals (hormones) can be sent from one cell to another • Receptor proteins on the plasma membrane receive the signal ...
... Cell to Cell Communication • Chemical Signals (hormones) can be sent from one cell to another • Receptor proteins on the plasma membrane receive the signal ...
Biology Review
... 4. Use the following terms to fill in the blanks (transcription, replication, translation): _________________ is DNA synthesis. ___________________ is mRNA synthesis. ______________________is protein synthesis. 5. A _________ is an mRNA triplet, not a DNA sequence. 6. The DNA sequence CCG would code ...
... 4. Use the following terms to fill in the blanks (transcription, replication, translation): _________________ is DNA synthesis. ___________________ is mRNA synthesis. ______________________is protein synthesis. 5. A _________ is an mRNA triplet, not a DNA sequence. 6. The DNA sequence CCG would code ...
Biology EOC review
... - HOMEOSTASIS – internal equilibrium; the plasma membrane regulates what enters and leaves the cell; a selectively permeable membrane only allows certain substances to pass through - Effect of Concentration on a Cell 1. HYPOTONIC – water moves in; cell bursts 2. HYPERTONIC – water moves out; cell sh ...
... - HOMEOSTASIS – internal equilibrium; the plasma membrane regulates what enters and leaves the cell; a selectively permeable membrane only allows certain substances to pass through - Effect of Concentration on a Cell 1. HYPOTONIC – water moves in; cell bursts 2. HYPERTONIC – water moves out; cell sh ...
BiologyHonors-CourseExpectation
... 1.2 Describe the basic molecular structures and primary functions of the four major categories of organic molecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids). 1.3 Explain the role of enzymes as catalysts that lower the activation energy of biochemical reactions. Identify factors, such as ...
... 1.2 Describe the basic molecular structures and primary functions of the four major categories of organic molecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids). 1.3 Explain the role of enzymes as catalysts that lower the activation energy of biochemical reactions. Identify factors, such as ...
Cell (biology)

The cell (from Latin cella, meaning ""small room"") is the basic structural, functional, and biological unit of all known living organisms. Cells are the smallest unit of life that can replicate independently, and are often called the ""building blocks of life"". The study of cells is called cell biology.Cells consist of cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, which contains many biomolecules such as proteins and nucleic acids. Organisms can be classified as unicellular (consisting of a single cell; including bacteria) or multicellular (including plants and animals). While the number of cells in plants and animals varies from species to species, humans contain more than 10 trillion (1013) cells. Most plant and animal cells are visible only under the microscope, with dimensions between 1 and 100 micrometres.The cell was discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665, who named the biological unit for its resemblance to cells inhabited by Christian monks in a monastery. Cell theory, first developed in 1839 by Matthias Jakob Schleiden and Theodor Schwann, states that all organisms are composed of one or more cells, that cells are the fundamental unit of structure and function in all living organisms, that all cells come from preexisting cells, and that all cells contain the hereditary information necessary for regulating cell functions and for transmitting information to the next generation of cells. Cells emerged on Earth at least 3.5 billion years ago.