B2 exam: Key words to understand
... inserting it into the DNA in a cell from another organism. An organism that has had a gene from another species inserted into its own DNA. The hormone which decreases blood glucose concentration. Used in the treatment of type I diabetes. Cutting or restriction enzymes are enzymes that cut a DNA mole ...
... inserting it into the DNA in a cell from another organism. An organism that has had a gene from another species inserted into its own DNA. The hormone which decreases blood glucose concentration. Used in the treatment of type I diabetes. Cutting or restriction enzymes are enzymes that cut a DNA mole ...
essential vocabulary for biology staar
... A reshuffling of genes that usually occurs when parental DNA is combined to form offspring. A theory that states that eukaryotes originated from prokaryotes living inside other prokaryotic cells, forming mitochondria and chloroplasts. Classification of organisms based on similarities in structure, g ...
... A reshuffling of genes that usually occurs when parental DNA is combined to form offspring. A theory that states that eukaryotes originated from prokaryotes living inside other prokaryotic cells, forming mitochondria and chloroplasts. Classification of organisms based on similarities in structure, g ...
Binomial Nomenclature- system of assigning 2 names to every species
... - all Multicellular, & Eukaryotic, - most are photosynthetic and have something that anchors them to surfaces - Cell wall made of cellulose (a type of polysaccharide) - Not capable of movement - Reproduce sexually, some produce spores and others produce seeds. Some can reproduce asexually. Land Life ...
... - all Multicellular, & Eukaryotic, - most are photosynthetic and have something that anchors them to surfaces - Cell wall made of cellulose (a type of polysaccharide) - Not capable of movement - Reproduce sexually, some produce spores and others produce seeds. Some can reproduce asexually. Land Life ...
Diffusion: Allowing Earthworms to Breathe
... exception of polar and arid climates. While earthworms vary greatly from other living organisms, certain shared characteristics give them the ability to perform necessary functions of life, such as breathing. All living organisms – from earthworms to humans – are made up of cells. We can look at the ...
... exception of polar and arid climates. While earthworms vary greatly from other living organisms, certain shared characteristics give them the ability to perform necessary functions of life, such as breathing. All living organisms – from earthworms to humans – are made up of cells. We can look at the ...
Cell - General Science, Science and Technology, Ecology and
... microscopic units called cells. They are the smallest part of the living organism that can lead an independent existence. Cell is the basic structural and functional unit of living organisms. There is no known form of life that does not depend on the cell. Robert Hooke in 1665 observed in a thin sli ...
... microscopic units called cells. They are the smallest part of the living organism that can lead an independent existence. Cell is the basic structural and functional unit of living organisms. There is no known form of life that does not depend on the cell. Robert Hooke in 1665 observed in a thin sli ...
File - Contemporary Publishing Company of Raleigh, Inc.
... Like the animal cell, the plant cell has an outer covering called the cell wall. However, this covering is not flexible like the animal cell membrane, it is a rigid, protective covering. These rigid cell walls, lined up tightly together, help plants stand up. Like the animal cell, the plant cell has ...
... Like the animal cell, the plant cell has an outer covering called the cell wall. However, this covering is not flexible like the animal cell membrane, it is a rigid, protective covering. These rigid cell walls, lined up tightly together, help plants stand up. Like the animal cell, the plant cell has ...
Characteristics of Living Things
... one or more cells. A cell is a membrane-covered structure that contains all of the materials necessary for life. The membrane that surrounds a cell separates the contents of the cell from the cell’s environment. Most cells are too small to be seen with the naked eye. Some organisms are made up of tr ...
... one or more cells. A cell is a membrane-covered structure that contains all of the materials necessary for life. The membrane that surrounds a cell separates the contents of the cell from the cell’s environment. Most cells are too small to be seen with the naked eye. Some organisms are made up of tr ...
Single-Celled Organisms and Viruses
... Make a list of places where you might find living things that are too small to be seen by your unaided eye. Then use a hand lens, magnifying glass, or microscope, to investigate some of the places on your list. Observe and Think What ...
... Make a list of places where you might find living things that are too small to be seen by your unaided eye. Then use a hand lens, magnifying glass, or microscope, to investigate some of the places on your list. Observe and Think What ...
Grade 11 College Biology Unit 4 Test
... b. A respiration process that produces lactic acid c. The number of times the heart contracts per minute d. The process by which ventricles fill up with blood Part B – Short Answer 31. With the support of a diagram, explain OSMOSIS? The movement of water that does not require energy across a cell ...
... b. A respiration process that produces lactic acid c. The number of times the heart contracts per minute d. The process by which ventricles fill up with blood Part B – Short Answer 31. With the support of a diagram, explain OSMOSIS? The movement of water that does not require energy across a cell ...
Structure
... Multicellular – organisms made up of many independent cells working together (plants and animals) ...
... Multicellular – organisms made up of many independent cells working together (plants and animals) ...
Module Homework # 2 Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum.
... of your textbook. Why does the water move in the direction indicated in Figures A & C? ...
... of your textbook. Why does the water move in the direction indicated in Figures A & C? ...
Cells1 - ClickBiology
... • Identify and describe the structure of plant cells and animal cells, and describe the functions of their parts. • Describe the difference between animal cells and plant cells. • Explain the structure and function of specialised cells: red blood cell, muscle cells, ciliated cells, xylem vessels and ...
... • Identify and describe the structure of plant cells and animal cells, and describe the functions of their parts. • Describe the difference between animal cells and plant cells. • Explain the structure and function of specialised cells: red blood cell, muscle cells, ciliated cells, xylem vessels and ...
Edexcel AS Level Biology
... • Identify and describe the structure of plant cells and animal cells, and describe the functions of their parts. • Describe the difference between animal cells and plant cells. • Explain the structure and function of specialised cells: red blood cell, muscle cells, ciliated cells, xylem vessels and ...
... • Identify and describe the structure of plant cells and animal cells, and describe the functions of their parts. • Describe the difference between animal cells and plant cells. • Explain the structure and function of specialised cells: red blood cell, muscle cells, ciliated cells, xylem vessels and ...
Biology Review
... 2.02 Investigate and describe the structure and function of cells including cell organelles, cell specialization, and communication among cells within an organism. Cell theory and Organelles. 9. What does the term “membrane bound organelles mean?” What cell type are they found in? 10. What are the t ...
... 2.02 Investigate and describe the structure and function of cells including cell organelles, cell specialization, and communication among cells within an organism. Cell theory and Organelles. 9. What does the term “membrane bound organelles mean?” What cell type are they found in? 10. What are the t ...
Power Reviews PPT
... plant from bad soil, and transports water to rest of the plant Stems – support system for the plant body, transport system for water and nutrients Leaves – plants main photosynthetic system ...
... plant from bad soil, and transports water to rest of the plant Stems – support system for the plant body, transport system for water and nutrients Leaves – plants main photosynthetic system ...
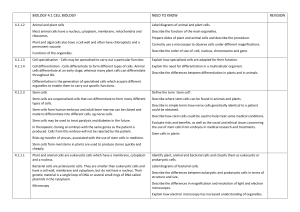
BIOLOGY 4.1 CELL BIOLOGY NEED TO KNOW REVISION
... plant tissue. 1. Investigate the effect of different concentrations of salt solutions on plant tissue. 2. Calculate percentage change in mass. 3. Plot a graph of the results using negative and positive values and use it to determine the isotonic concentration. 4. Plan, carry out and present results ...
... plant tissue. 1. Investigate the effect of different concentrations of salt solutions on plant tissue. 2. Calculate percentage change in mass. 3. Plot a graph of the results using negative and positive values and use it to determine the isotonic concentration. 4. Plan, carry out and present results ...
Non-Living Inclusions
... with the addition of nitrogen, commonly sulphur and sometimes phosphorus. A protein molecule is made up of hundreds or thousands of amino acid molecules joined together by peptide links into one or more chains, which are variously folded. y There are twenty different kinds of amino‐acids commonl ...
... with the addition of nitrogen, commonly sulphur and sometimes phosphorus. A protein molecule is made up of hundreds or thousands of amino acid molecules joined together by peptide links into one or more chains, which are variously folded. y There are twenty different kinds of amino‐acids commonl ...
Document
... nucleus and can be called bacteria - Two types of monerans include bacteria and blue-green algae - Bacteria come in 3 shapes; rod shaped, round and spiral - Monerans have a cell wall; a tough, rigid outer covering that supports and protects. A cell membrane; controls what enters and leaves the cell. ...
... nucleus and can be called bacteria - Two types of monerans include bacteria and blue-green algae - Bacteria come in 3 shapes; rod shaped, round and spiral - Monerans have a cell wall; a tough, rigid outer covering that supports and protects. A cell membrane; controls what enters and leaves the cell. ...
Unit 5 Notes - Flushing Community Schools
... Mitosis is the second stage (of 3) of the cell cycle Mitosis is the stage during which the cell’s nucleus divides into two new nuclei Four Phases of Mitosis: Phase 1 of Mitosis: Prophase Chromatin in nucleus condenses to make chromosomes Spindle fibers form a bridge between the ends of the cel ...
... Mitosis is the second stage (of 3) of the cell cycle Mitosis is the stage during which the cell’s nucleus divides into two new nuclei Four Phases of Mitosis: Phase 1 of Mitosis: Prophase Chromatin in nucleus condenses to make chromosomes Spindle fibers form a bridge between the ends of the cel ...
MCAS And Final Review Packet 2014
... factors can change the shape of the enzyme. The change in shape alters the effectiveness of the enzyme by preventing the substrate and the enzyme fitting together. The lock and key no longer fit together. Sometimes the enzyme does not work at all or it may work with reduced efficiency 2. Cell Biolog ...
... factors can change the shape of the enzyme. The change in shape alters the effectiveness of the enzyme by preventing the substrate and the enzyme fitting together. The lock and key no longer fit together. Sometimes the enzyme does not work at all or it may work with reduced efficiency 2. Cell Biolog ...
function - mselder
... = a section of DNA with genetic information required for a particular job. small differences between each of our genes, making us all different ...
... = a section of DNA with genetic information required for a particular job. small differences between each of our genes, making us all different ...
Cell Structure - SAVE MY EXAMS!
... Mr and Mrs Smith both have a history of cystic fibrosis in their families. Neither of them has cystic fibrosis. Mr and Mrs Smith are concerned that they may have a child with cystic fibrosis. Use a genetic diagram to show how they could have a child with cystic fibrosis. Use the symbol A for the dom ...
... Mr and Mrs Smith both have a history of cystic fibrosis in their families. Neither of them has cystic fibrosis. Mr and Mrs Smith are concerned that they may have a child with cystic fibrosis. Use a genetic diagram to show how they could have a child with cystic fibrosis. Use the symbol A for the dom ...
Cell (biology)

The cell (from Latin cella, meaning ""small room"") is the basic structural, functional, and biological unit of all known living organisms. Cells are the smallest unit of life that can replicate independently, and are often called the ""building blocks of life"". The study of cells is called cell biology.Cells consist of cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, which contains many biomolecules such as proteins and nucleic acids. Organisms can be classified as unicellular (consisting of a single cell; including bacteria) or multicellular (including plants and animals). While the number of cells in plants and animals varies from species to species, humans contain more than 10 trillion (1013) cells. Most plant and animal cells are visible only under the microscope, with dimensions between 1 and 100 micrometres.The cell was discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665, who named the biological unit for its resemblance to cells inhabited by Christian monks in a monastery. Cell theory, first developed in 1839 by Matthias Jakob Schleiden and Theodor Schwann, states that all organisms are composed of one or more cells, that cells are the fundamental unit of structure and function in all living organisms, that all cells come from preexisting cells, and that all cells contain the hereditary information necessary for regulating cell functions and for transmitting information to the next generation of cells. Cells emerged on Earth at least 3.5 billion years ago.