Diffusion, Osmosis and Active Transport
... In animal cells, the cell membrane is the partially permeable membrane that allows osmosis to occur. If red blood cells are placed into a hypotonic solution (i.e. distilled water), the water will cross ...
... In animal cells, the cell membrane is the partially permeable membrane that allows osmosis to occur. If red blood cells are placed into a hypotonic solution (i.e. distilled water), the water will cross ...
Macro Respiration
... The pathway a molecule of oxygen takes from the air until it is picked up by the hemoglobin of a red blood cell. ...
... The pathway a molecule of oxygen takes from the air until it is picked up by the hemoglobin of a red blood cell. ...
Biology Keystone Exam Review Packet
... Eukaryotic cells contain membrane-bound organelles and organelles such as: – Mitochondria – Endoplasmic reticulum – Vacuoles – Lysosomes – Golgi apparatus – Nucleus with DNA – Nucleolus – Ribosomes Have a greater division of labor. Organelles are specialized. Prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells b ...
... Eukaryotic cells contain membrane-bound organelles and organelles such as: – Mitochondria – Endoplasmic reticulum – Vacuoles – Lysosomes – Golgi apparatus – Nucleus with DNA – Nucleolus – Ribosomes Have a greater division of labor. Organelles are specialized. Prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells b ...
MCAS Biology Review Packet Answer Key
... Store nutrients & keeps cell pressure Plant Cell wall Supports & maintains shape, protects Plant cell from damage, connectsnearbycells Chloroplast Use light energy to make food Plant (carbohydrates) through photosynthesis Cytoskeleton Helps to maintain cell shape & aids in Both movement of materials ...
... Store nutrients & keeps cell pressure Plant Cell wall Supports & maintains shape, protects Plant cell from damage, connectsnearbycells Chloroplast Use light energy to make food Plant (carbohydrates) through photosynthesis Cytoskeleton Helps to maintain cell shape & aids in Both movement of materials ...
Special topics in electrical and systems engineering
... • There are specialized receptors on the cell surface • Receptors transduce signals (binding of their ligand) into the cytosol (the inside of the cell) • Signaling cascades originate in the initial binding event • Complicated networks of multistep phosphorylation ...
... • There are specialized receptors on the cell surface • Receptors transduce signals (binding of their ligand) into the cytosol (the inside of the cell) • Signaling cascades originate in the initial binding event • Complicated networks of multistep phosphorylation ...
Chapter 18: Viruses and Bacteria
... own food Some are chemosynthetic autotrophs o Carry out chemosynthesis: process of breaking down and releasing energy of inorganic compounds containing sulfur and nitrogen o They use this energy, rather than sunlight, to make their own food o These include the nitrogen-fixing bacteria in the nitro ...
... own food Some are chemosynthetic autotrophs o Carry out chemosynthesis: process of breaking down and releasing energy of inorganic compounds containing sulfur and nitrogen o They use this energy, rather than sunlight, to make their own food o These include the nitrogen-fixing bacteria in the nitro ...
Biology 11 17.3 Domains and Kingdoms Grouping Species The
... § Protists are eukaryotic organisms that can be unicellular, colonial, or multicellular. § Protists are classified into three different groups—plantlike, animal-like, and funguslike. ...
... § Protists are eukaryotic organisms that can be unicellular, colonial, or multicellular. § Protists are classified into three different groups—plantlike, animal-like, and funguslike. ...
EOC Review Answer Key- Friday
... nerve cell functions differently from a muscle cell. Different genes are turned on in different types of cells. 2. Why does a pancreas cell produce insulin in great amounts but a blood cell does not? Because the insulin gene is turned on in the pancreas cell but not as much in a blood cell. 3. There ...
... nerve cell functions differently from a muscle cell. Different genes are turned on in different types of cells. 2. Why does a pancreas cell produce insulin in great amounts but a blood cell does not? Because the insulin gene is turned on in the pancreas cell but not as much in a blood cell. 3. There ...
Practice Questions 1: Cell Membrane
... B. The cell membrane is capable of receiving and recognizing chemical signals. C. The cell membrane forms a barrier that keeps all substances that might harm the cell from entering the cell. D. The cell membrane controls the movement of molecules into and out of the cell. ...
... B. The cell membrane is capable of receiving and recognizing chemical signals. C. The cell membrane forms a barrier that keeps all substances that might harm the cell from entering the cell. D. The cell membrane controls the movement of molecules into and out of the cell. ...
Outline
... Nuclear membrane or nuclear envelope Regulates transport of substances into and out of the cell Nucleoplasm A clear, semi-liquid ________ that fills the spaces around the chromatin and the nucleoli Nucleolus Reservoir for RNA Ribosomes Serve as site for protein synthesis Cytoplasm Provides an ______ ...
... Nuclear membrane or nuclear envelope Regulates transport of substances into and out of the cell Nucleoplasm A clear, semi-liquid ________ that fills the spaces around the chromatin and the nucleoli Nucleolus Reservoir for RNA Ribosomes Serve as site for protein synthesis Cytoplasm Provides an ______ ...
Chemical Composition of Living Cells
... vast array of vital macromolecules (Fig 1-1). There are four general classes of macromolecules within living cells: nucleic acids, proteins, polysaccharides, and lipids. These compounds, which have molecular weights ranging from 1 x 103 to 1 x 106, are created through polymerization of building bloc ...
... vast array of vital macromolecules (Fig 1-1). There are four general classes of macromolecules within living cells: nucleic acids, proteins, polysaccharides, and lipids. These compounds, which have molecular weights ranging from 1 x 103 to 1 x 106, are created through polymerization of building bloc ...
or Print Your Own Glossary Only 5 Pages Long!!
... Pancreas - the organ that lies behind the stomach and that produces and secretes insulin, glucagon, and digestive enzymes Parasite - an organism that feeds on an organism of another species (the host) and that usually harms the host; the host never benefits from the presence of the parasite Pathogen ...
... Pancreas - the organ that lies behind the stomach and that produces and secretes insulin, glucagon, and digestive enzymes Parasite - an organism that feeds on an organism of another species (the host) and that usually harms the host; the host never benefits from the presence of the parasite Pathogen ...
SYLLABUS Advanced Cell Biology BIOL 3301 (3
... Fundamental knowledge in cell biology will be discussed. Topics include DNAs, RNAs, proteins, cell structure, cell motility, bio-membrane, endocytosis, exocytosis, nucleocytoplasmic transport, vesicular transport, cancers, visualizing macromolecular trafficking in cells with advanced microscopy imag ...
... Fundamental knowledge in cell biology will be discussed. Topics include DNAs, RNAs, proteins, cell structure, cell motility, bio-membrane, endocytosis, exocytosis, nucleocytoplasmic transport, vesicular transport, cancers, visualizing macromolecular trafficking in cells with advanced microscopy imag ...
Important Properties of Water
... cell. It is also evident outside the cell and can involve substances other than molecules in an aqueous environment (e.g. O2 into the capillaries of the lungs). Osmosis = the diffusion of water across a differentially permeable membrane. There are three possible conditions in regards to a cell's w ...
... cell. It is also evident outside the cell and can involve substances other than molecules in an aqueous environment (e.g. O2 into the capillaries of the lungs). Osmosis = the diffusion of water across a differentially permeable membrane. There are three possible conditions in regards to a cell's w ...
Traits of Life PPT
... All living things obtain and use energy. All living things are made up of one or more cells. 5. All living things respond to stimuli. 6. All living things maintain an internal ...
... All living things obtain and use energy. All living things are made up of one or more cells. 5. All living things respond to stimuli. 6. All living things maintain an internal ...
1 - Cloudfront.net
... Frogs and Toads tend to lay many many eggs because there are many hazards between fertalization and full grown frogness! Those eggs that die tend to turn white or opaque. The lucky ones that actually manage to hatch still start out on a journey of many perils. Life starts right as the central yolk s ...
... Frogs and Toads tend to lay many many eggs because there are many hazards between fertalization and full grown frogness! Those eggs that die tend to turn white or opaque. The lucky ones that actually manage to hatch still start out on a journey of many perils. Life starts right as the central yolk s ...
A Journey Through the Cell: Part One—Cells: An Introduction
... photosynthesis: The process in green plants and certain other organisms by which carbohydrates are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water using light as an energy source. Most forms of photosynthesis release oxygen as a by-product. plant: An organism that uses photosynthesis to produce its own fo ...
... photosynthesis: The process in green plants and certain other organisms by which carbohydrates are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water using light as an energy source. Most forms of photosynthesis release oxygen as a by-product. plant: An organism that uses photosynthesis to produce its own fo ...
cells - local.brookings.k12.sd.us
... http://academic.brooklyn.cuny.edu/biology/bio4fv/page/cell-movement.html ...
... http://academic.brooklyn.cuny.edu/biology/bio4fv/page/cell-movement.html ...
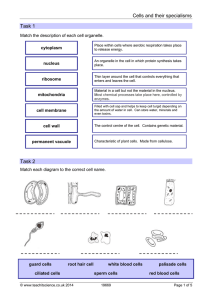
Cells and their specialisms Task 1 Task 2
... Cells and their specialisms Teaching notes and answers For the first three tasks students could be asked to cut and paste or simply draw a line to match up the correct statements. ...
... Cells and their specialisms Teaching notes and answers For the first three tasks students could be asked to cut and paste or simply draw a line to match up the correct statements. ...
Cells - Peoria Public Schools
... Budding- a small projection grows on the surface of the parent organism, forming a separate new individual. Fragmentation- a parent organism splits into pieces, each of which can grow into a new organism. ...
... Budding- a small projection grows on the surface of the parent organism, forming a separate new individual. Fragmentation- a parent organism splits into pieces, each of which can grow into a new organism. ...
EOC Review Packet
... 2. Nucleolus – small organelle in the nucleus that makes ribosomes 3. Ribosomes – small spheres made of rRNA in the cytoplasm that make proteins 4. Endoplasmic reticulum – transport system of the cell 5. Golgi body / golgi apparatus – collects, packages and distributes proteins 6. Lysosomes – contai ...
... 2. Nucleolus – small organelle in the nucleus that makes ribosomes 3. Ribosomes – small spheres made of rRNA in the cytoplasm that make proteins 4. Endoplasmic reticulum – transport system of the cell 5. Golgi body / golgi apparatus – collects, packages and distributes proteins 6. Lysosomes – contai ...
Cells - Dr Magrann
... Two fatty acid groups (“tails”) and a phosphorus group (“head”) Main use- major component of cell membranes Lipids made from one fatty acid Cholesterol- all animal cells have this in the membrane Steroids –modified cholesterol- estrogen, progesterone, testosterone (hormones) 3. PROTEINS are ...
... Two fatty acid groups (“tails”) and a phosphorus group (“head”) Main use- major component of cell membranes Lipids made from one fatty acid Cholesterol- all animal cells have this in the membrane Steroids –modified cholesterol- estrogen, progesterone, testosterone (hormones) 3. PROTEINS are ...
The major organs involved in the cardio
... A. Due to osmosis it lost water because it had higher concentration than the solution B Due to osmosis it gained water because it had higher concentration than the solution C Due to osmosis it lost water because it had lower concentration than the solution D Due to osmosis it lost water because it h ...
... A. Due to osmosis it lost water because it had higher concentration than the solution B Due to osmosis it gained water because it had higher concentration than the solution C Due to osmosis it lost water because it had lower concentration than the solution D Due to osmosis it lost water because it h ...
Exam Summary Points 2013
... composed of chitin, rather than cellulose as it is in a plant cells. Bacteria also possess a cell wall; however it is composed of a complex polysaccharide other than cellulose.) Microscopy skills: in particular magnification, size, scale, field of view, sharpening images, getting more contrast in ...
... composed of chitin, rather than cellulose as it is in a plant cells. Bacteria also possess a cell wall; however it is composed of a complex polysaccharide other than cellulose.) Microscopy skills: in particular magnification, size, scale, field of view, sharpening images, getting more contrast in ...
review for Bio. I HSA
... How do enzymes lower the activation energy? Explain at the molecular level. A. Body temperature cannot be too great so there isn’t enough activation energy to get chemical reactions to go so enzymes must lower the activation energy B. If reactions could happen on their own (if body temperature provi ...
... How do enzymes lower the activation energy? Explain at the molecular level. A. Body temperature cannot be too great so there isn’t enough activation energy to get chemical reactions to go so enzymes must lower the activation energy B. If reactions could happen on their own (if body temperature provi ...
Cell (biology)

The cell (from Latin cella, meaning ""small room"") is the basic structural, functional, and biological unit of all known living organisms. Cells are the smallest unit of life that can replicate independently, and are often called the ""building blocks of life"". The study of cells is called cell biology.Cells consist of cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, which contains many biomolecules such as proteins and nucleic acids. Organisms can be classified as unicellular (consisting of a single cell; including bacteria) or multicellular (including plants and animals). While the number of cells in plants and animals varies from species to species, humans contain more than 10 trillion (1013) cells. Most plant and animal cells are visible only under the microscope, with dimensions between 1 and 100 micrometres.The cell was discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665, who named the biological unit for its resemblance to cells inhabited by Christian monks in a monastery. Cell theory, first developed in 1839 by Matthias Jakob Schleiden and Theodor Schwann, states that all organisms are composed of one or more cells, that cells are the fundamental unit of structure and function in all living organisms, that all cells come from preexisting cells, and that all cells contain the hereditary information necessary for regulating cell functions and for transmitting information to the next generation of cells. Cells emerged on Earth at least 3.5 billion years ago.