Electrical Currents
... 4. If Ammeter 1 (A1) detects a current of 6 A, what would be the readings on A2-A5? (Hint: all resistors are identical). ...
... 4. If Ammeter 1 (A1) detects a current of 6 A, what would be the readings on A2-A5? (Hint: all resistors are identical). ...
(p.946) Ch 33 Alternating Current Circuits 33.3
... CT4: For the RLC series circuit shown, which of these statements is/are true: (i) Potential energy oscillates between C and L. (ii) The source does no net work: Energy lost in R is compensated by energy stored in C and L. (iii) The current through C is 90° out of phase with the current through ...
... CT4: For the RLC series circuit shown, which of these statements is/are true: (i) Potential energy oscillates between C and L. (ii) The source does no net work: Energy lost in R is compensated by energy stored in C and L. (iii) The current through C is 90° out of phase with the current through ...
Title of Lesson
... one direction and goes through each part of the circuit. A flashlight with two batteries is a series circuit, because the power goes through the batteries to the lightbulb. The impedance (resistance to current) of an element can be represented using the complex number, V + Ii, where V is the element ...
... one direction and goes through each part of the circuit. A flashlight with two batteries is a series circuit, because the power goes through the batteries to the lightbulb. The impedance (resistance to current) of an element can be represented using the complex number, V + Ii, where V is the element ...
Building a VLSI Neuron
... dm/dt=B*m-A*(1-m) • Input is a’s and b’s • Output should be current representing ‘m’,’h’, and ‘n’ ...
... dm/dt=B*m-A*(1-m) • Input is a’s and b’s • Output should be current representing ‘m’,’h’, and ‘n’ ...
Electric Field
... The Formula that is used is V = I x R Using the formula allows you to work out the Voltage of a circuit if you know its Current and Resistance. From this formula we can also swap around the values to find Current (I) and Resistance (R) ...
... The Formula that is used is V = I x R Using the formula allows you to work out the Voltage of a circuit if you know its Current and Resistance. From this formula we can also swap around the values to find Current (I) and Resistance (R) ...
Slide 1
... current Ibottom=V/(2R) compared to Itop=V/R. Lets call Ibottom= I and then Itop= 2I. Bulb A burns with P=(2I)2R while B or C burns Individually with P=I2R. The bottom branch as a whole has two bulbs burning 2I2R, but we are asked to compare each bulb. ...
... current Ibottom=V/(2R) compared to Itop=V/R. Lets call Ibottom= I and then Itop= 2I. Bulb A burns with P=(2I)2R while B or C burns Individually with P=I2R. The bottom branch as a whole has two bulbs burning 2I2R, but we are asked to compare each bulb. ...
Ohms Law Presentation File
... Suppose we have a battery operated circuit that uses a push button switch as shown in the circuit diagram. When the switch is pressed current will be flowing through the resistor. If a lot of current flows through the resistor the batteries won't last long. If we are using a 9 volt battery and ...
... Suppose we have a battery operated circuit that uses a push button switch as shown in the circuit diagram. When the switch is pressed current will be flowing through the resistor. If a lot of current flows through the resistor the batteries won't last long. If we are using a 9 volt battery and ...
3.0 Principles of Electrical Engineering.docx
... Capacitance and Inductance are two methods for energy storage in a circuit. Both these methods store energy in an electromagnetic field. Two electrical components that can induce capacitance and inductance in a circuit are called capacitors and inductors, respectively. 1.2.1.1 Capacitors The most ba ...
... Capacitance and Inductance are two methods for energy storage in a circuit. Both these methods store energy in an electromagnetic field. Two electrical components that can induce capacitance and inductance in a circuit are called capacitors and inductors, respectively. 1.2.1.1 Capacitors The most ba ...
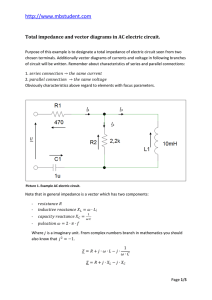
Designation of total impedance and vector
... Now vectors of currents and voltages in circuit will be plotted. Note that lengths of vectors depend from their values. We have formulas only with symbols. We don’t calculate numeric value of vectors lengths. We will start plotting vectors from lasts elements in circuit. These elements are inductivi ...
... Now vectors of currents and voltages in circuit will be plotted. Note that lengths of vectors depend from their values. We have formulas only with symbols. We don’t calculate numeric value of vectors lengths. We will start plotting vectors from lasts elements in circuit. These elements are inductivi ...
resonance
... sharpness of resonance, is indicated by the factor Q. The higher the ratio of the reactance at resonance to the series resistance, the higher the Q and the sharper the resonance effect. The Q of the resonant circuit can be considered a magnification factor that determines how much the voltage ac ...
... sharpness of resonance, is indicated by the factor Q. The higher the ratio of the reactance at resonance to the series resistance, the higher the Q and the sharper the resonance effect. The Q of the resonant circuit can be considered a magnification factor that determines how much the voltage ac ...
RLC circuit

A RLC circuit is an electrical circuit consisting of a resistor (R), an inductor (L), and a capacitor (C), connected in series or in parallel. The name of the circuit is derived from the letters that are used to denote the constituent components of this circuit, where the sequence of the components may vary from RLC.The circuit forms a harmonic oscillator for current, and resonates in a similar way as an LC circuit. Introducing the resistor increases the decay of these oscillations, which is also known as damping. The resistor also reduces the peak resonant frequency. Some resistance is unavoidable in real circuits even if a resistor is not specifically included as a component. An ideal, pure LC circuit is an abstraction used in theoretical considerations.RLC circuits have many applications as oscillator circuits. Radio receivers and television sets use them for tuning to select a narrow frequency range from ambient radio waves. In this role the circuit is often referred to as a tuned circuit. An RLC circuit can be used as a band-pass filter, band-stop filter, low-pass filter or high-pass filter. The tuning application, for instance, is an example of band-pass filtering. The RLC filter is described as a second-order circuit, meaning that any voltage or current in the circuit can be described by a second-order differential equation in circuit analysis.The three circuit elements, R,L and C can be combined in a number of different topologies. All three elements in series or all three elements in parallel are the simplest in concept and the most straightforward to analyse. There are, however, other arrangements, some with practical importance in real circuits. One issue often encountered is the need to take into account inductor resistance. Inductors are typically constructed from coils of wire, the resistance of which is not usually desirable, but it often has a significant effect on the circuit.