Fast Photodetection in Functional Near Infra-Red Spectroscopy
... In order to operate the single photon avalanche photodiode (SAPD) in Geiger mode for single photon counting, a new controllable mixed quenched circuit (MQC) with ability to real-time control of hold-off time in photoreceptor front-end is proposed in this paper. It exhibits an ultra-fast quench time ...
... In order to operate the single photon avalanche photodiode (SAPD) in Geiger mode for single photon counting, a new controllable mixed quenched circuit (MQC) with ability to real-time control of hold-off time in photoreceptor front-end is proposed in this paper. It exhibits an ultra-fast quench time ...
CLASS XII EMI and AC Sure shot Questions 2015-16
... 2. What are the advantages and disadvantages of a.c. over d.c.? 3. Two identical coils carry similar current s and approach each other. How the current in each coil is affected? ( Any questions from applications of Lenz’s law to determine the direction of induced current) ...
... 2. What are the advantages and disadvantages of a.c. over d.c.? 3. Two identical coils carry similar current s and approach each other. How the current in each coil is affected? ( Any questions from applications of Lenz’s law to determine the direction of induced current) ...
IOSR Journal of Computer Engineering (IOSR-JCE)
... without an instructor and the display of it’s transfer function characteristics in the time domain or frequency domain so that one can control the system in order to achieve the desire output. The transfer function is an important factor to consider in the design of any system because with the help ...
... without an instructor and the display of it’s transfer function characteristics in the time domain or frequency domain so that one can control the system in order to achieve the desire output. The transfer function is an important factor to consider in the design of any system because with the help ...
Video Transcript - Rose
... Firstly, let’s label the terminal characteristics of the two ports. We can see that there are four terminal variables. There are two equations to relate these variables together in terms of z parameters. Let’s take a look at the first equation. When I2 is zero, z11 can be solved by dividing V1 by I1 ...
... Firstly, let’s label the terminal characteristics of the two ports. We can see that there are four terminal variables. There are two equations to relate these variables together in terms of z parameters. Let’s take a look at the first equation. When I2 is zero, z11 can be solved by dividing V1 by I1 ...
Exercise 4
... Kirchoff’s Current Law is a statement of the conservation of current. For the picture on the right, it implies that i1=i2+i3. In other words, the sum of the currents at any node must be zero. As you know, you can add electrical load to a circuit in two ways. The first is to serially connect the load ...
... Kirchoff’s Current Law is a statement of the conservation of current. For the picture on the right, it implies that i1=i2+i3. In other words, the sum of the currents at any node must be zero. As you know, you can add electrical load to a circuit in two ways. The first is to serially connect the load ...
Matt Kemp`s take on the EE interview process
... ohm resistor, 5 V source, button press and an LED • Build a circuit that will take a sinusoidal input and give a DC output = to the sinusoids amplitude • Analyzed a simple circuit they had built and point out the flaws (When the board was populated the manufacture put parts on backward and wrong val ...
... ohm resistor, 5 V source, button press and an LED • Build a circuit that will take a sinusoidal input and give a DC output = to the sinusoids amplitude • Analyzed a simple circuit they had built and point out the flaws (When the board was populated the manufacture put parts on backward and wrong val ...
Self Study Unit 1.2
... equals current (I) multiplied by resistance (R). (T5D02) When you know the voltage across a circuit and the current in the circuit, the formula used to calculate resistance in a circuit is resistance (R) equals voltage (E) divided by current (I). (T5D03) We can also write this formula as R = E ÷ I W ...
... equals current (I) multiplied by resistance (R). (T5D02) When you know the voltage across a circuit and the current in the circuit, the formula used to calculate resistance in a circuit is resistance (R) equals voltage (E) divided by current (I). (T5D03) We can also write this formula as R = E ÷ I W ...
Physics 536 - Assignment #2
... calculate the measured voltage, vmeasured in terms of vin , R and Z, assuming vin is a constant, ideal voltage source. (b) Draw the equivalent circuit if a 3 ft length of cable was treated as a single capacitor with C = 0.05 pF and calculate the time needed for the measured voltage to reach 90% of i ...
... calculate the measured voltage, vmeasured in terms of vin , R and Z, assuming vin is a constant, ideal voltage source. (b) Draw the equivalent circuit if a 3 ft length of cable was treated as a single capacitor with C = 0.05 pF and calculate the time needed for the measured voltage to reach 90% of i ...
34-35 Direct Current
... motion • A. Circuit – a continuous loop through which electricity can flow. It must contain – 1. Energy source – battery, generator – 2. Conductor – copper wire is common – 3. Load – device(s) that converts electrical energy to other useful forms of energy ...
... motion • A. Circuit – a continuous loop through which electricity can flow. It must contain – 1. Energy source – battery, generator – 2. Conductor – copper wire is common – 3. Load – device(s) that converts electrical energy to other useful forms of energy ...
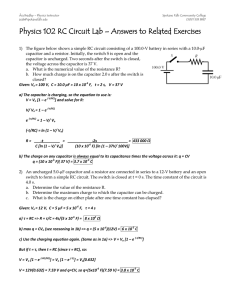
Physics 102 RC Circuit Lab – Answers to Related Exercises
... q = (10 x 10-6 F)( 37 V) = 3.7 x 10-4 C 2) An uncharged 5.0-µF capacitor and a resistor are connected in series to a 12-V battery and an open switch to form a simple RC circuit. The switch is closed at t = 0 s. The time constant of the circuit is 4.0 s. a. Determine the value of the resistance R. b. ...
... q = (10 x 10-6 F)( 37 V) = 3.7 x 10-4 C 2) An uncharged 5.0-µF capacitor and a resistor are connected in series to a 12-V battery and an open switch to form a simple RC circuit. The switch is closed at t = 0 s. The time constant of the circuit is 4.0 s. a. Determine the value of the resistance R. b. ...
RLC circuit

A RLC circuit is an electrical circuit consisting of a resistor (R), an inductor (L), and a capacitor (C), connected in series or in parallel. The name of the circuit is derived from the letters that are used to denote the constituent components of this circuit, where the sequence of the components may vary from RLC.The circuit forms a harmonic oscillator for current, and resonates in a similar way as an LC circuit. Introducing the resistor increases the decay of these oscillations, which is also known as damping. The resistor also reduces the peak resonant frequency. Some resistance is unavoidable in real circuits even if a resistor is not specifically included as a component. An ideal, pure LC circuit is an abstraction used in theoretical considerations.RLC circuits have many applications as oscillator circuits. Radio receivers and television sets use them for tuning to select a narrow frequency range from ambient radio waves. In this role the circuit is often referred to as a tuned circuit. An RLC circuit can be used as a band-pass filter, band-stop filter, low-pass filter or high-pass filter. The tuning application, for instance, is an example of band-pass filtering. The RLC filter is described as a second-order circuit, meaning that any voltage or current in the circuit can be described by a second-order differential equation in circuit analysis.The three circuit elements, R,L and C can be combined in a number of different topologies. All three elements in series or all three elements in parallel are the simplest in concept and the most straightforward to analyse. There are, however, other arrangements, some with practical importance in real circuits. One issue often encountered is the need to take into account inductor resistance. Inductors are typically constructed from coils of wire, the resistance of which is not usually desirable, but it often has a significant effect on the circuit.