ECE51602012springfinals
... d) What are the Bergeron diagrams? Draw the Bergeron diagram at the source end and load end for a transmitter with a voltage source 0 to 2.5V and edge rate 100ps and a series resistance 12.5 ohm. The impedance of transmission line is 50 ohms and the transit time is 3 nano seconds. The termination re ...
... d) What are the Bergeron diagrams? Draw the Bergeron diagram at the source end and load end for a transmitter with a voltage source 0 to 2.5V and edge rate 100ps and a series resistance 12.5 ohm. The impedance of transmission line is 50 ohms and the transit time is 3 nano seconds. The termination re ...
Review with answers
... ____ 13. As the distance between two positively charged objects increases, the force between them: a. increases. c. cannot be determined. b. decreases. d. remains the same. ____ 14. The electric force between a 5-coulomb charge and a 1-coulomb charge 9,000 meters apart is: a. 5,000,000 newtons. b. 6 ...
... ____ 13. As the distance between two positively charged objects increases, the force between them: a. increases. c. cannot be determined. b. decreases. d. remains the same. ____ 14. The electric force between a 5-coulomb charge and a 1-coulomb charge 9,000 meters apart is: a. 5,000,000 newtons. b. 6 ...
L43-DynamicElec-Jan10
... • Series circuit – All in a row – 1 path for electricity – 1 light goes out and the circuit is broken ...
... • Series circuit – All in a row – 1 path for electricity – 1 light goes out and the circuit is broken ...
Chapters 5-6
... VR = ITR The polarity of a voltage drop across a resistor is positive at the end of the resistor that is closest to the positive terminal of the voltage source An open in a series circuit prevents current; and, there is zero voltage drop across each series resistor. ...
... VR = ITR The polarity of a voltage drop across a resistor is positive at the end of the resistor that is closest to the positive terminal of the voltage source An open in a series circuit prevents current; and, there is zero voltage drop across each series resistor. ...
L45-kirchhoff- Jan13-ch5
... The sum of the drops in potential difference equals the potential difference at the source (Remember the loop rule?) The voltage in each loop is the same as the source of potential: Equation: ...
... The sum of the drops in potential difference equals the potential difference at the source (Remember the loop rule?) The voltage in each loop is the same as the source of potential: Equation: ...
ammeters/voltmeters
... around a circuit. • It has the unit volt (V). • Further explanation: A supply voltage of 1 volt means that 1 joule of energy is supplied to each coulomb of charge. ...
... around a circuit. • It has the unit volt (V). • Further explanation: A supply voltage of 1 volt means that 1 joule of energy is supplied to each coulomb of charge. ...
Deriving Voltage and Current from HF RFID/NFC Reader Field
... begins to output about 1.7VDC. The MSP430 is on and executing code. – @ 9cm, +3VDC is being provided and @ 8cm distance away, the full output of this particular regulator (+3.3VDC) is provided to the MSP430. – To summarize, MSP430 turns on @ 10cm out and executes the –F2013 demo code (flashing LED) ...
... begins to output about 1.7VDC. The MSP430 is on and executing code. – @ 9cm, +3VDC is being provided and @ 8cm distance away, the full output of this particular regulator (+3.3VDC) is provided to the MSP430. – To summarize, MSP430 turns on @ 10cm out and executes the –F2013 demo code (flashing LED) ...
TORTURE BY ELECTRICITY
... 5. In the two circuits below, each resistor has a resistance of 50 Ω. What is the total resistance of each circuit? ...
... 5. In the two circuits below, each resistor has a resistance of 50 Ω. What is the total resistance of each circuit? ...
Electricity Jeopardy
... This type of magnet that is produced by an electric current, usually a core of iron wrapped in a ...
... This type of magnet that is produced by an electric current, usually a core of iron wrapped in a ...
Word Document - UCSD VLSI CAD Laboratory
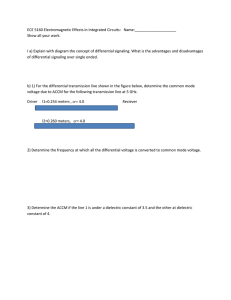
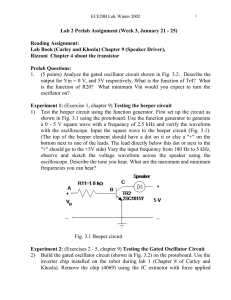
... a 0 - 5 V square wave with a frequency of 2.5 kHz and verify the waveform with the oscilloscope. Input the square wave to the beeper circuit (Fig. 3.1). (The top of the beeper element should have a dot on it or else a "+" on the bottom next to one of the leads. The lead directly below this dot or ne ...
... a 0 - 5 V square wave with a frequency of 2.5 kHz and verify the waveform with the oscilloscope. Input the square wave to the beeper circuit (Fig. 3.1). (The top of the beeper element should have a dot on it or else a "+" on the bottom next to one of the leads. The lead directly below this dot or ne ...
RLC circuit

A RLC circuit is an electrical circuit consisting of a resistor (R), an inductor (L), and a capacitor (C), connected in series or in parallel. The name of the circuit is derived from the letters that are used to denote the constituent components of this circuit, where the sequence of the components may vary from RLC.The circuit forms a harmonic oscillator for current, and resonates in a similar way as an LC circuit. Introducing the resistor increases the decay of these oscillations, which is also known as damping. The resistor also reduces the peak resonant frequency. Some resistance is unavoidable in real circuits even if a resistor is not specifically included as a component. An ideal, pure LC circuit is an abstraction used in theoretical considerations.RLC circuits have many applications as oscillator circuits. Radio receivers and television sets use them for tuning to select a narrow frequency range from ambient radio waves. In this role the circuit is often referred to as a tuned circuit. An RLC circuit can be used as a band-pass filter, band-stop filter, low-pass filter or high-pass filter. The tuning application, for instance, is an example of band-pass filtering. The RLC filter is described as a second-order circuit, meaning that any voltage or current in the circuit can be described by a second-order differential equation in circuit analysis.The three circuit elements, R,L and C can be combined in a number of different topologies. All three elements in series or all three elements in parallel are the simplest in concept and the most straightforward to analyse. There are, however, other arrangements, some with practical importance in real circuits. One issue often encountered is the need to take into account inductor resistance. Inductors are typically constructed from coils of wire, the resistance of which is not usually desirable, but it often has a significant effect on the circuit.