Unit 06 Series
... Discuss the properties of series circuits. List three rules for solving electrical values of series circuits. Compute values of voltage, current, resistance, and power for series circuits. Compute the values of voltage drop in a series circuit using the voltage divider ...
... Discuss the properties of series circuits. List three rules for solving electrical values of series circuits. Compute values of voltage, current, resistance, and power for series circuits. Compute the values of voltage drop in a series circuit using the voltage divider ...
Section 29: Electric Circuits
... Draw and interpret circuit diagrams containing diodes Calculate the combined e.m.f. of several sources in series Recall and use the fact that the sum of the p.d.s across the components in a series circuit is equal to the total p.d. across the supply Recall and use the fact that the current f ...
... Draw and interpret circuit diagrams containing diodes Calculate the combined e.m.f. of several sources in series Recall and use the fact that the sum of the p.d.s across the components in a series circuit is equal to the total p.d. across the supply Recall and use the fact that the current f ...
AC Series
... Peak values are useful for time domain representations of signals. RMS values are the standard when dealing with phasor domain representations If you need to represent something in the time domain, you will need to convert RMS->Peak voltage to obtain Em ...
... Peak values are useful for time domain representations of signals. RMS values are the standard when dealing with phasor domain representations If you need to represent something in the time domain, you will need to convert RMS->Peak voltage to obtain Em ...
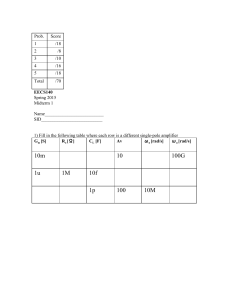
10m 10 100G 1u 1M 10f 1p 100 10M
... 3b) You invent a new transistor, and find that the output current is given by Ixy = K Vzy3 Vxy1/2 ; Iz = 0 What are the formulas for the transconductance and the output resistance? What is the intrinsic gain when the device is biased at Vzy=Vxy=1V? (give a numerical answer ...
... 3b) You invent a new transistor, and find that the output current is given by Ixy = K Vzy3 Vxy1/2 ; Iz = 0 What are the formulas for the transconductance and the output resistance? What is the intrinsic gain when the device is biased at Vzy=Vxy=1V? (give a numerical answer ...
7890 - 1 - Page 1 Name: ____________________________________________ Parallel Circuits Worksheet
... An 18-ohm resistor and a 36-ohm resistor are connected in parallel with a 24-volt battery. A single ammeter is placed in the circuit to read its total current. Draw a diagram of the circuit described using symbols from the Circuit Symbols physics reference table. [Assume the availability of any numb ...
... An 18-ohm resistor and a 36-ohm resistor are connected in parallel with a 24-volt battery. A single ammeter is placed in the circuit to read its total current. Draw a diagram of the circuit described using symbols from the Circuit Symbols physics reference table. [Assume the availability of any numb ...
Systems Repair Worksheet
... 20. Circuits must have consumers or _________, power ____________, & ____________ providing paths along with controllers & protection devices properly located to perform desired operations. 21. In a ___________ circuit, the voltage __________ at each load, the __________ is the same throughout the c ...
... 20. Circuits must have consumers or _________, power ____________, & ____________ providing paths along with controllers & protection devices properly located to perform desired operations. 21. In a ___________ circuit, the voltage __________ at each load, the __________ is the same throughout the c ...
Physics B Midterm Study Guide
... 19. Two charges are 9.98μC and -4.92 μC. What is the electric force if they are a. 100.0 m apart? b. 1.000 m apart? 20. What is the electric field strength 100.0 m away from a charge of – a. 4.3 C? b. 6.45μC? 21. A circuit is created which contains an emf source with a potential difference of 120V, ...
... 19. Two charges are 9.98μC and -4.92 μC. What is the electric force if they are a. 100.0 m apart? b. 1.000 m apart? 20. What is the electric field strength 100.0 m away from a charge of – a. 4.3 C? b. 6.45μC? 21. A circuit is created which contains an emf source with a potential difference of 120V, ...
Alternating Current Electricity
... The meters used to measure the voltage will give rms values, not actual voltages at a point in time The voltages across the resistor and capacitor are out of phase with each other ie they do not both reach maxs and mins at the same time. ...
... The meters used to measure the voltage will give rms values, not actual voltages at a point in time The voltages across the resistor and capacitor are out of phase with each other ie they do not both reach maxs and mins at the same time. ...
Parallel Circuits - Northwest ISD Moodle
... Characteristics in a Parallel Circuit • Parallel Power supplies provide a higher current capacity. (amps add up) Yet the voltage stays the same throughout the circuit • In parallel connection, all positive cell electrodes are connected to one line, and all negative electrodes are connected to one li ...
... Characteristics in a Parallel Circuit • Parallel Power supplies provide a higher current capacity. (amps add up) Yet the voltage stays the same throughout the circuit • In parallel connection, all positive cell electrodes are connected to one line, and all negative electrodes are connected to one li ...
Transistors - BDJ Engineering
... Build the circuit as shown to test using actual components using Snap Circuits® ...
... Build the circuit as shown to test using actual components using Snap Circuits® ...
PowerPoint
... calculate V across a capacitor use VR=IR to calculate V across a resistor or I through a resistor or use V0-Vc to calculate V across R ...
... calculate V across a capacitor use VR=IR to calculate V across a resistor or I through a resistor or use V0-Vc to calculate V across R ...
RLC circuit

A RLC circuit is an electrical circuit consisting of a resistor (R), an inductor (L), and a capacitor (C), connected in series or in parallel. The name of the circuit is derived from the letters that are used to denote the constituent components of this circuit, where the sequence of the components may vary from RLC.The circuit forms a harmonic oscillator for current, and resonates in a similar way as an LC circuit. Introducing the resistor increases the decay of these oscillations, which is also known as damping. The resistor also reduces the peak resonant frequency. Some resistance is unavoidable in real circuits even if a resistor is not specifically included as a component. An ideal, pure LC circuit is an abstraction used in theoretical considerations.RLC circuits have many applications as oscillator circuits. Radio receivers and television sets use them for tuning to select a narrow frequency range from ambient radio waves. In this role the circuit is often referred to as a tuned circuit. An RLC circuit can be used as a band-pass filter, band-stop filter, low-pass filter or high-pass filter. The tuning application, for instance, is an example of band-pass filtering. The RLC filter is described as a second-order circuit, meaning that any voltage or current in the circuit can be described by a second-order differential equation in circuit analysis.The three circuit elements, R,L and C can be combined in a number of different topologies. All three elements in series or all three elements in parallel are the simplest in concept and the most straightforward to analyse. There are, however, other arrangements, some with practical importance in real circuits. One issue often encountered is the need to take into account inductor resistance. Inductors are typically constructed from coils of wire, the resistance of which is not usually desirable, but it often has a significant effect on the circuit.