Functional Groups
... If necessary, identify the carbon to which the carboxyl group is attached. ...
... If necessary, identify the carbon to which the carboxyl group is attached. ...
IB Chemistry
... Reacting an alcohol with a carboxylic acid in warm sulfuric acid produces an ester and water. This is a condensation reaction (a small extra molecule is produced -- in this case water). The sulfuric acid acts as a catalyst. The equation is in equilibrium. Esters have a "fruity" smell (mostly), and a ...
... Reacting an alcohol with a carboxylic acid in warm sulfuric acid produces an ester and water. This is a condensation reaction (a small extra molecule is produced -- in this case water). The sulfuric acid acts as a catalyst. The equation is in equilibrium. Esters have a "fruity" smell (mostly), and a ...
Inorganic and organic chemistry 1
... A hydrocarbon contains the elements carbon and hydrogen only. Hence there is 84.7 g of carbon present and 100 − 84.7 = 15.3 g of hydrogen. To find the empirical formula it is best to first calculate the number of moles of carbon and of hydrogen present. Moles C = 84.7/12.0 = 7.1 moles H = 15.3/1.0 = ...
... A hydrocarbon contains the elements carbon and hydrogen only. Hence there is 84.7 g of carbon present and 100 − 84.7 = 15.3 g of hydrogen. To find the empirical formula it is best to first calculate the number of moles of carbon and of hydrogen present. Moles C = 84.7/12.0 = 7.1 moles H = 15.3/1.0 = ...
Inorganic and organic chemistry 1
... A hydrocarbon contains the elements carbon and hydrogen only. Hence there is 84.7 g of carbon present and 100 − 84.7 = 15.3 g of hydrogen. To find the empirical formula it is best to first calculate the number of moles of carbon and of hydrogen present. Moles C = 84.7/12.0 = 7.1 moles H = 15.3/1.0 = ...
... A hydrocarbon contains the elements carbon and hydrogen only. Hence there is 84.7 g of carbon present and 100 − 84.7 = 15.3 g of hydrogen. To find the empirical formula it is best to first calculate the number of moles of carbon and of hydrogen present. Moles C = 84.7/12.0 = 7.1 moles H = 15.3/1.0 = ...
Activity 1: Chapter 1: Carbon Compounds and Chemical Bonds
... Alkyl halide = a hydrocarbon having at least one halide connected to a carbon atom. Alkene = a hydrocarbon having at least one double bond between carbon atoms. Alkyne = a hydrocarbon having at least one triple bond between carbon atoms. Alcohol = a hydrocarbon containing an “O-H” functional group c ...
... Alkyl halide = a hydrocarbon having at least one halide connected to a carbon atom. Alkene = a hydrocarbon having at least one double bond between carbon atoms. Alkyne = a hydrocarbon having at least one triple bond between carbon atoms. Alcohol = a hydrocarbon containing an “O-H” functional group c ...
Chapter 13 – Organic Chemistry
... Indeed, straight chain hydrocarbons react so fast and violently that they can cause an engine to “knock.” The octane rating of a gasoline indicates the extent of knocking it causes. The reference molecules are shown in Figure 13.4. The straight chain hydrocarbon C7 H16 causes substantial knocking a ...
... Indeed, straight chain hydrocarbons react so fast and violently that they can cause an engine to “knock.” The octane rating of a gasoline indicates the extent of knocking it causes. The reference molecules are shown in Figure 13.4. The straight chain hydrocarbon C7 H16 causes substantial knocking a ...
The alkanes - misshoughton.net
... Example 1: Write the structural formula for 2-methylpentane. Start decoding the name from the bit that counts the number of carbon atoms in the longest chain - pent counts 5 carbons. Are there any carbon-carbon double bonds? No - an tells you there aren't any. Now draw this carbon skeleton: ...
... Example 1: Write the structural formula for 2-methylpentane. Start decoding the name from the bit that counts the number of carbon atoms in the longest chain - pent counts 5 carbons. Are there any carbon-carbon double bonds? No - an tells you there aren't any. Now draw this carbon skeleton: ...
CH 18 blackboard
... carbon atoms in the longest continuous carbon chain that contains the carbonyl group. The base name is formed by dropping the -e and adding the ending -al. Simple ketones are systematically named according to the longest continuous carbon chain containing the carbonyl group. The base name is formed ...
... carbon atoms in the longest continuous carbon chain that contains the carbonyl group. The base name is formed by dropping the -e and adding the ending -al. Simple ketones are systematically named according to the longest continuous carbon chain containing the carbonyl group. The base name is formed ...
Grant MacEwan College - Faculty Web Pages
... Note: Students are responsible for verifying the date of the final exam (see here). Course Description:(3 credits) This course studies the molecular structure and reactivity of organic compounds based on their functional groups and is intended for students who have obtained at least three credits in ...
... Note: Students are responsible for verifying the date of the final exam (see here). Course Description:(3 credits) This course studies the molecular structure and reactivity of organic compounds based on their functional groups and is intended for students who have obtained at least three credits in ...
Alcohols
... to other alcohol molecules on the average. A water molecule, on the other hand, forms hydrogen bonds to slightly less than 4 other water molecules. Water has an abnormally high boiling point for a molecule of its size due to this hydrogen bonding. ...
... to other alcohol molecules on the average. A water molecule, on the other hand, forms hydrogen bonds to slightly less than 4 other water molecules. Water has an abnormally high boiling point for a molecule of its size due to this hydrogen bonding. ...
A Guide to Organic Molecules
... 11.1.3 Viscosity – a measure of a substance’s resistance to flow – solids and ‘thick’ fluids like oil do not flow so have high viscosity. Gases flow easily hence have low viscosity. ...
... 11.1.3 Viscosity – a measure of a substance’s resistance to flow – solids and ‘thick’ fluids like oil do not flow so have high viscosity. Gases flow easily hence have low viscosity. ...
Functional Groups III
... Amines have relatively high boiling points because they can form hydrogen bonds with each other as well as van der Waals ...
... Amines have relatively high boiling points because they can form hydrogen bonds with each other as well as van der Waals ...
Ground State and Bonding State Electronic Configurations
... The three sp2 hybrids form the skeleton of ethene, by head-on overlap with another sp2 hybrid (carbon) or 1s orbitals (hydrogen), whilst the p orbitals overlap sideways to form a bond, as shown on the next page. Again, the orbital lobes are deliberately elongated, for clarity. ...
... The three sp2 hybrids form the skeleton of ethene, by head-on overlap with another sp2 hybrid (carbon) or 1s orbitals (hydrogen), whilst the p orbitals overlap sideways to form a bond, as shown on the next page. Again, the orbital lobes are deliberately elongated, for clarity. ...
Mass Spectrometry - HCC Learning Web
... Tallest peak is base peak (100%). Other peaks listed as the % of that peak Peak that corresponds to the unfragmented radical cation is parent peak or molecular ion (M+): usually correspond to the highest mass in the spectrum The neutral fragments that may be lost in a fragmentation do not appear in ...
... Tallest peak is base peak (100%). Other peaks listed as the % of that peak Peak that corresponds to the unfragmented radical cation is parent peak or molecular ion (M+): usually correspond to the highest mass in the spectrum The neutral fragments that may be lost in a fragmentation do not appear in ...
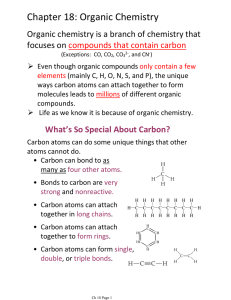
Chapter 18: Organic Chemistry
... bond - this is the parent chain. Name the parent chain like an alkane, but drop the 'ane' ending and add 'ene'. 2) Number the parent chain starting from the end closer to the double bond and designate the location of the first carbon in the double bond as a number in front of the parent chain. 3) Na ...
... bond - this is the parent chain. Name the parent chain like an alkane, but drop the 'ane' ending and add 'ene'. 2) Number the parent chain starting from the end closer to the double bond and designate the location of the first carbon in the double bond as a number in front of the parent chain. 3) Na ...
Organic Chemistry
... Notice the first compound is saturated. One H is switched with one Br. Otherwise, it would have been addition, breaking the bonds. ...
... Notice the first compound is saturated. One H is switched with one Br. Otherwise, it would have been addition, breaking the bonds. ...
IUPAC nomenclature of organic chemistry
... alkane chain is counted as "1", then numbering is chosen so that the smallest number is used. For example, (CH3)2CHCH2CH3 (isopentane) is named 2-methylbutane, not 3methylbutane. ...
... alkane chain is counted as "1", then numbering is chosen so that the smallest number is used. For example, (CH3)2CHCH2CH3 (isopentane) is named 2-methylbutane, not 3methylbutane. ...
Uses and Sources of some Organic Molecules C11-5-14
... electrons are contained within an orbital that extends over several adjacent atoms). They number the same as if they consisted of alternating single and double covalent bonds. The term 'aromatic' was derived from the fact that many of the compounds have a sweet scent. This sweet scent actually came ...
... electrons are contained within an orbital that extends over several adjacent atoms). They number the same as if they consisted of alternating single and double covalent bonds. The term 'aromatic' was derived from the fact that many of the compounds have a sweet scent. This sweet scent actually came ...
Chemistry for Health Sciences Chemistry for Health
... eg. 2-Methylhexane locant: prefix: parent: suffix: ...
... eg. 2-Methylhexane locant: prefix: parent: suffix: ...
alcohols - profpaz.com
... soluble in water. This is in contrast to alkanes which are nonpolar and therefore insoluble in water. · The hydroxyl group in alcohol molecule is responsible for both the solubility and the relatively high boiling point of alcohol. The hydroxyl groups can hydrogen bond between water and alcoh ...
... soluble in water. This is in contrast to alkanes which are nonpolar and therefore insoluble in water. · The hydroxyl group in alcohol molecule is responsible for both the solubility and the relatively high boiling point of alcohol. The hydroxyl groups can hydrogen bond between water and alcoh ...
MHS Student Guide to Organic Chemistry
... With so many new carbon compounds being synthesized by research chemists each year, it became very important to have a systematic method of naming these compounds. Today most chemists use what is called the IUPAC system of nomenclature. (IUPAC standards for International Union of Pure and Applied Ch ...
... With so many new carbon compounds being synthesized by research chemists each year, it became very important to have a systematic method of naming these compounds. Today most chemists use what is called the IUPAC system of nomenclature. (IUPAC standards for International Union of Pure and Applied Ch ...
Organic Chemistry Chapter 2 - Snow College | It's SNOWing
... CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2OH – pentyl alcohol CH3CH2CH2OH – propylalcohol Notice no space in propyl CH3CH2CH2CH2NH2 – butyl amine ...
... CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2OH – pentyl alcohol CH3CH2CH2OH – propylalcohol Notice no space in propyl CH3CH2CH2CH2NH2 – butyl amine ...
10.3 Alcohols
... the carbon attached to the -OH group. • Number the carbons in this chain so that the carbon attached to the -OH group has the lowest number. • Drop the -e ending from the name of the parent alkane and replace it with –ol • Alcohols containing two or three -OH groups are called diols and triols. ...
... the carbon attached to the -OH group. • Number the carbons in this chain so that the carbon attached to the -OH group has the lowest number. • Drop the -e ending from the name of the parent alkane and replace it with –ol • Alcohols containing two or three -OH groups are called diols and triols. ...
Chapter 4 PowerPoint
... • The electron configuration of carbon gives it covalent compatibility with many different elements • The valences of carbon and its most frequent partners (hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen) – Carbon dioxide: CO2 ...
... • The electron configuration of carbon gives it covalent compatibility with many different elements • The valences of carbon and its most frequent partners (hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen) – Carbon dioxide: CO2 ...
Alkane
In organic chemistry, an alkane, or paraffin (a historical name that also has other meanings), is a saturated hydrocarbon. Alkanes consist only of hydrogen and carbon atoms and all bonds are single bonds. Alkanes (technically, always acyclic or open-chain compounds) have the general chemical formula CnH2n+2. For example, Methane is CH4, in which n=1 (n being the number of Carbon atoms). Alkanes belong to a homologous series of organic compounds in which the members differ by a molecular mass of 14.03u (mass of a methanediyl group, —CH2—, one carbon atom of mass 12.01u, and two hydrogen atoms of mass ≈1.01u each). There are two main commercial sources: petroleum (crude oil) and natural gas.Each carbon atom has 4 bonds (either C-H or C-C bonds), and each hydrogen atom is joined to a carbon atom (H-C bonds). A series of linked carbon atoms is known as the carbon skeleton or carbon backbone. The number of carbon atoms is used to define the size of the alkane e.g., C2-alkane.An alkyl group, generally abbreviated with the symbol R, is a functional group or side-chain that, like an alkane, consists solely of single-bonded carbon and hydrogen atoms, for example a methyl or ethyl group.The simplest possible alkane (the parent molecule) is methane, CH4. There is no limit to the number of carbon atoms that can be linked together, the only limitation being that the molecule is acyclic, is saturated, and is a hydrocarbon. Waxes include examples of larger alkanes where the number of carbons in the carbon backbone is greater than about 17, above which the compounds are solids at standard ambient temperature and pressure (SATP).Alkanes are not very reactive and have little biological activity. All alkanes are colourless and odourless. Alkanes can be viewed as a molecular tree upon which can be hung the more biologically active/reactive portions (functional groups) of the molecule.