Synthesis of esterified solid fat from fractionated
... Response surface methodology (RSM) The effects of three variables such as reaction time (12, 24 and 36 h), enzyme (5, 10 and 15%) and substrate mole ratio (S-RSO to PS, 1:1, 1:2 and 1:3) on SFC of TSF were considered. Uncoded variables were transferred into coded variables with a zero mean and the s ...
... Response surface methodology (RSM) The effects of three variables such as reaction time (12, 24 and 36 h), enzyme (5, 10 and 15%) and substrate mole ratio (S-RSO to PS, 1:1, 1:2 and 1:3) on SFC of TSF were considered. Uncoded variables were transferred into coded variables with a zero mean and the s ...
Chapter 18 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
... readily with water to give two molecules of carboxylic acid. – Higher-molecular-weight anhydrides also react with water, but less readily. O O CH3 COCCH3 + H2 O ...
... readily with water to give two molecules of carboxylic acid. – Higher-molecular-weight anhydrides also react with water, but less readily. O O CH3 COCCH3 + H2 O ...
Synthesis of Fatty Acids
... stimulated by insulin. When blood glucose is high, insulin • moves glucose into the cells, stimulating glycolysis and the oxidation of pyruvate. • produces acetyl CoA for fatty acid synthesis. Two carbons are added to the growing fatty acid chain by using three-carbon malonyl units. The transport of ...
... stimulated by insulin. When blood glucose is high, insulin • moves glucose into the cells, stimulating glycolysis and the oxidation of pyruvate. • produces acetyl CoA for fatty acid synthesis. Two carbons are added to the growing fatty acid chain by using three-carbon malonyl units. The transport of ...
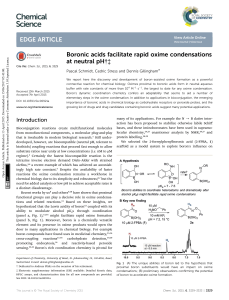
Boronic acids facilitate rapid oxime condensations at neutral pH
... A great advantage of the present method over many coupling reactions is the simplicity and ready availability of the starting materials. There are commercial libraries of phenylboronic acid and boronic ester compounds, many of which contain an aldehyde or can be trivially elaborated to incorporate o ...
... A great advantage of the present method over many coupling reactions is the simplicity and ready availability of the starting materials. There are commercial libraries of phenylboronic acid and boronic ester compounds, many of which contain an aldehyde or can be trivially elaborated to incorporate o ...
8.5 Translation KEY CONCEPT Translation converts an mRNA message into a
... • Regardless of the organism, codons code for the same amino acid. ...
... • Regardless of the organism, codons code for the same amino acid. ...
CHAPtER 9 Properties and reactions of organic compounds
... It is interesting to note that the melting points do not follow the same pattern as the boiling points. In the solid state, the trans isomers can pack more closely than the cis isomers, making the intermolecular forces more effective. cis and trans isomers can also occur in ring structures. cis–tran ...
... It is interesting to note that the melting points do not follow the same pattern as the boiling points. In the solid state, the trans isomers can pack more closely than the cis isomers, making the intermolecular forces more effective. cis and trans isomers can also occur in ring structures. cis–tran ...
Word Version of Answer Key
... belongs to a class of compounds called alcohols (which is why we call drinks with this type of molecule alcohol). All alcohols have a hydroxide molecule (-OH) attached to one of the carbon atoms in the molecule, and it is this chemical makeup that makes the breakdown of alcohol so much different fro ...
... belongs to a class of compounds called alcohols (which is why we call drinks with this type of molecule alcohol). All alcohols have a hydroxide molecule (-OH) attached to one of the carbon atoms in the molecule, and it is this chemical makeup that makes the breakdown of alcohol so much different fro ...
How is Alcohol Metabolized?
... belongs to a class of compounds called alcohols (which is why we call drinks with this type of molecule alcohol). All alcohols have a hydroxide molecule (-OH) attached to one of the carbon atoms in the molecule, and it is this chemical makeup that makes the breakdown of alcohol so much different fro ...
... belongs to a class of compounds called alcohols (which is why we call drinks with this type of molecule alcohol). All alcohols have a hydroxide molecule (-OH) attached to one of the carbon atoms in the molecule, and it is this chemical makeup that makes the breakdown of alcohol so much different fro ...
Working with Hazardous Chemicals
... 3. Potassium hydroxide pellets were purchased from J. T. Baker and ground with a mortar and pestle immediately before use. 4. The submitters purchased toluene from VWR and passed it through neutral alumina and 4Å molecular sieves columns under argon atmosphere before use. The checkers obtained ACS g ...
... 3. Potassium hydroxide pellets were purchased from J. T. Baker and ground with a mortar and pestle immediately before use. 4. The submitters purchased toluene from VWR and passed it through neutral alumina and 4Å molecular sieves columns under argon atmosphere before use. The checkers obtained ACS g ...
IB Chemistry
... • 20.4.1 Reactions of alcohols with carboxylic acids to form esters. State uses of esters. Reacting an alcohol with a carboxylic acid in warm sulfuric acid produces an ester and water. This is a condensation reaction (a small extra molecule is produced -- in this case water). The sulfuric acid acts ...
... • 20.4.1 Reactions of alcohols with carboxylic acids to form esters. State uses of esters. Reacting an alcohol with a carboxylic acid in warm sulfuric acid produces an ester and water. This is a condensation reaction (a small extra molecule is produced -- in this case water). The sulfuric acid acts ...
Hydrothermal Reactions of Pyruvic Acid
... decomposes at T >150°C to a mixture of H2O+CO2 +H2, and thus provides a convenient method to explore effects of volatile chemistry on reaction products. We employed pyruvic acid (Aldrich 98%), oxalic acid dihydrate (Aldrich >99%), and distilled deionized water in these experiments. We loaded each go ...
... decomposes at T >150°C to a mixture of H2O+CO2 +H2, and thus provides a convenient method to explore effects of volatile chemistry on reaction products. We employed pyruvic acid (Aldrich 98%), oxalic acid dihydrate (Aldrich >99%), and distilled deionized water in these experiments. We loaded each go ...
Alcohols, Ethers and Epoxides Alcohols contain a hydroxy group (OH)
... the equilibrium. One consequence of this is that removing a product from a reaction mixture as it is formed drives the equilibrium to the right, forming more product. Thus, the alkene, which usually has a lower boiling point than the starting alcohol, can be removed by distillation as it is formed, ...
... the equilibrium. One consequence of this is that removing a product from a reaction mixture as it is formed drives the equilibrium to the right, forming more product. Thus, the alkene, which usually has a lower boiling point than the starting alcohol, can be removed by distillation as it is formed, ...
Epoxidation and oxidation reactions using 1,4
... hydroperoxide reagent was used it is assumed to follow pseudo first-order kinetics. The reaction is assumed to involve the nucleophilic attack of the olefin on the hydroperoxide followed by proton transfer probably by a concerted intramolecular process. The intermediate formed then decays to give th ...
... hydroperoxide reagent was used it is assumed to follow pseudo first-order kinetics. The reaction is assumed to involve the nucleophilic attack of the olefin on the hydroperoxide followed by proton transfer probably by a concerted intramolecular process. The intermediate formed then decays to give th ...
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Nucleophilic Addition to the
... The carbonyl p electrons shift to oxygen to give the alkoxide The carbonyl carbon changes from trigonal planar to tetrahedral ...
... The carbonyl p electrons shift to oxygen to give the alkoxide The carbonyl carbon changes from trigonal planar to tetrahedral ...
Reactions of Acyl Chlorides
... From dicarboxylic acids Cyclic anhydrides with 5- and 6-membered rings can be prepared by dehydration of dicarboxylic acids O H ...
... From dicarboxylic acids Cyclic anhydrides with 5- and 6-membered rings can be prepared by dehydration of dicarboxylic acids O H ...
Reacciones redox
... • 1° Alcohols are oxidized to aldehydes (RCHO) under mild reaction conditions using PCC in CH2Cl2. • 1° Alcohols are oxidized to carboxylic acids (RCOOH) under harsher reaction conditions: Na2Cr2O7, K2Cr2O7, or CrO3 in the presence of H2O and H2SO4. ...
... • 1° Alcohols are oxidized to aldehydes (RCHO) under mild reaction conditions using PCC in CH2Cl2. • 1° Alcohols are oxidized to carboxylic acids (RCOOH) under harsher reaction conditions: Na2Cr2O7, K2Cr2O7, or CrO3 in the presence of H2O and H2SO4. ...
Chapter 15. α-AMINO ACIDS, PEPTIDES AND PROTEINS
... Amino acids can be classified as neutral, acidic, or basic, depending on the nature of their side chain, the R substituent. Most amino acids (fifteen of the twenty listed in Table 15.1) have the neutral R's. Two amino acids (aspartic and glutamic acids) have an extra carboxyl group and are acidic. T ...
... Amino acids can be classified as neutral, acidic, or basic, depending on the nature of their side chain, the R substituent. Most amino acids (fifteen of the twenty listed in Table 15.1) have the neutral R's. Two amino acids (aspartic and glutamic acids) have an extra carboxyl group and are acidic. T ...
Petasis reaction

The Petasis reaction (alternatively called the Petasis borono–Mannich (PBM) reaction) is the chemical reaction of an amine, aldehyde, and vinyl- or aryl-boronic acid to form substituted amines.Reported in 1993 by Nicos Petasis as a practical method towards the synthesis of a geometrically pure antifungal agent, naftifine, the Petasis reaction can be described as a variation of the Mannich reaction. Rather than generating an enolate to form the substituted amine product, in the Petasis reaction, the vinyl group of the organoboronic acid serves as the nucleophile. In comparison to other methods of generating allyl amines, the Petasis reaction tolerates a multifunctional scaffold, with a variety of amines and organoboronic acids as potential starting materials. Additionally, the reaction does not require anhydrous or inert conditions. As a mild, selective synthesis, the Petasis reaction is useful in generating α-amino acids, and is utilized in combinatorial chemistry and drug discovery.