Chapter 19. Aldehydes and Ketones
... Originally carried out at high temperatures but with dimethyl sulfoxide as solvent takes place near room temperature ...
... Originally carried out at high temperatures but with dimethyl sulfoxide as solvent takes place near room temperature ...
Chlorotrimethylsilane/Sodium Iodide, a
... Isolated yield. T h e products were characterized by comparing IR, N M R , a n d b p or m p with those of the authentic samples. 10% of N-(1-adamanty1)acetamidewas also isolated in this experiment. c Cholesterol was solubilized using a mixture of chloroform a n d acetonitrile as the sohent. mmol) an ...
... Isolated yield. T h e products were characterized by comparing IR, N M R , a n d b p or m p with those of the authentic samples. 10% of N-(1-adamanty1)acetamidewas also isolated in this experiment. c Cholesterol was solubilized using a mixture of chloroform a n d acetonitrile as the sohent. mmol) an ...
Expt RO 1 Determination of Reaction Order (RO) Background Bonds
... economic methods to break down cellulose into its component glucose molecules can be worked out then switchgrass will be a far better source of ethanol than the corn that is currently grown and its sugar used to make ethanol. In this experiment we will explore the kinetics involved in using not an e ...
... economic methods to break down cellulose into its component glucose molecules can be worked out then switchgrass will be a far better source of ethanol than the corn that is currently grown and its sugar used to make ethanol. In this experiment we will explore the kinetics involved in using not an e ...
$doc.title
... • Alkanes: Compounds with C-‐C single bonds and C-‐H bonds only (no func)onal groups), non-‐polar molecule • Easy to rotate around C-‐C single bonds • Connec)ng carbons can lead to large or small mole ...
... • Alkanes: Compounds with C-‐C single bonds and C-‐H bonds only (no func)onal groups), non-‐polar molecule • Easy to rotate around C-‐C single bonds • Connec)ng carbons can lead to large or small mole ...
Substitution Rxns
... halogenoalkanes have a polar bond. Reagents that have a non-bonding pair of electrons are attracted to the carbon atom in halogenoalkanes and a substitution rxn occurs. Such reagents are called nucleophiles. ...
... halogenoalkanes have a polar bond. Reagents that have a non-bonding pair of electrons are attracted to the carbon atom in halogenoalkanes and a substitution rxn occurs. Such reagents are called nucleophiles. ...
Microsoft Word - Open Access Repository of Indian Theses
... regiochemistry. The methodology was further extended to the ring opening of aliphatic epoxides and substituted styrene oxide with amines to afford the corresponding products in good yields. Chapter IV. Aza-Michael Addition Reactions using Recyclable Copper Catalysts The conjugate addition (1,4-addit ...
... regiochemistry. The methodology was further extended to the ring opening of aliphatic epoxides and substituted styrene oxide with amines to afford the corresponding products in good yields. Chapter IV. Aza-Michael Addition Reactions using Recyclable Copper Catalysts The conjugate addition (1,4-addit ...
35 - TAMU Chemistry
... • very soluble in H2O due to H-bonding ability. It is a weak base in H2O. NH3(aq) + H2O NH4+(aq) + OH-(aq) (an equilibrium exists in H2O) • Reacts completely with strong acids NH3(aq) + HCl(aq) → NH4Cl(aq) • Dissolves Group IA, IIA metals Na + NH3(l) → Na+ + NH3(l) + eThe e- is “solvated” by NH3!! ...
... • very soluble in H2O due to H-bonding ability. It is a weak base in H2O. NH3(aq) + H2O NH4+(aq) + OH-(aq) (an equilibrium exists in H2O) • Reacts completely with strong acids NH3(aq) + HCl(aq) → NH4Cl(aq) • Dissolves Group IA, IIA metals Na + NH3(l) → Na+ + NH3(l) + eThe e- is “solvated” by NH3!! ...
SECONDARY METABOLISM: THE BUILDING BLOCKS AND
... These eight building blocks will form the basis of many of the natural product structures discussed in the following chapters. Simple examples of how compounds can be visualized as a combination of building blocks are shown in Figure 2.3. At this stage, it is inappropriate to justify why a particula ...
... These eight building blocks will form the basis of many of the natural product structures discussed in the following chapters. Simple examples of how compounds can be visualized as a combination of building blocks are shown in Figure 2.3. At this stage, it is inappropriate to justify why a particula ...
Alcohols from Alkenes: Oxymercuration–Demercuration
... form of the starting material reacts in such a way that it gives a specific stereoisomeric form of the product. ...
... form of the starting material reacts in such a way that it gives a specific stereoisomeric form of the product. ...
친환경 촉매 Iron (III) phosphate: 실온/무용매 반응조건에서 알코올과
... some shortcomings limit them being widely applied in industry such as higher wastage for materials, lower yield of product or higher cost in catalyst preparation. Based on these reasons, isoamyl alcohol was chosen as a starting material and isoamyl acetate was resulted in 95% yield (entry 5). This m ...
... some shortcomings limit them being widely applied in industry such as higher wastage for materials, lower yield of product or higher cost in catalyst preparation. Based on these reasons, isoamyl alcohol was chosen as a starting material and isoamyl acetate was resulted in 95% yield (entry 5). This m ...
Amines
... to -CH2Amides can be reduced by LiAlH4 but NOT the less reactive NaBH4 Typical reagents : LiAlH4 / ether solvent, followed by aqueous work-up. Note that this reaction is different to that of other C=O compounds which reduce to alcohols (for example esters) The nature of the amine obtained depends on ...
... to -CH2Amides can be reduced by LiAlH4 but NOT the less reactive NaBH4 Typical reagents : LiAlH4 / ether solvent, followed by aqueous work-up. Note that this reaction is different to that of other C=O compounds which reduce to alcohols (for example esters) The nature of the amine obtained depends on ...
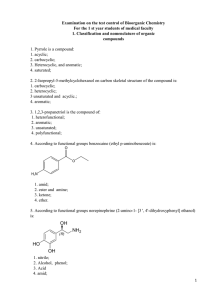
2. 2-Isopropyl-5-methylcyclohexanol on carbon skeletal
... 92. The unimolecular substitution reaction (SN1 ) takes place at a maximum speed of alcohols: 1. neo-hexyl; 2. propyl; 3. tert-butyl; 4. benzyl; 93. Stereospecificity are the reactions occurring at the chiral centers of electrophilic substrates alcohols according to the mechanism: 1. SN1; 2. SN2; 3. ...
... 92. The unimolecular substitution reaction (SN1 ) takes place at a maximum speed of alcohols: 1. neo-hexyl; 2. propyl; 3. tert-butyl; 4. benzyl; 93. Stereospecificity are the reactions occurring at the chiral centers of electrophilic substrates alcohols according to the mechanism: 1. SN1; 2. SN2; 3. ...
Reduction of Camphor to Borneol
... showing the expected stereochemistry of the products. Label the products as having been formed from exo approach or endo approach. 2. How might the geometry of the product change (OH in an endo or exo position?) if all the methyl groups of camphor were replaced with H? 3. The reduction mechanism is ...
... showing the expected stereochemistry of the products. Label the products as having been formed from exo approach or endo approach. 2. How might the geometry of the product change (OH in an endo or exo position?) if all the methyl groups of camphor were replaced with H? 3. The reduction mechanism is ...
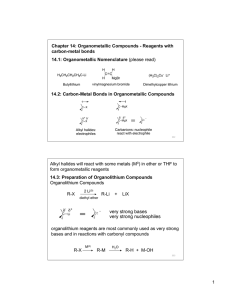
Organometallic Compounds - Reagents
... Acetylide anions react with ketones and aldehydes to form a C-C bond; the product is an acetylenic (propargyl) alcohols R1 C C ...
... Acetylide anions react with ketones and aldehydes to form a C-C bond; the product is an acetylenic (propargyl) alcohols R1 C C ...
Translation - WordPress.com
... Where does the first step take place? Nucleus Where does the second step take place? Cytoplasm ...
... Where does the first step take place? Nucleus Where does the second step take place? Cytoplasm ...
7. Alkenes: Reactions and Synthesis
... cyclization to give a bromonium ion This bromonium ion is a reactive electrophile and bromide ion is a ...
... cyclization to give a bromonium ion This bromonium ion is a reactive electrophile and bromide ion is a ...
Synthesis of esterified solid fat from fractionated
... Response surface methodology (RSM) The effects of three variables such as reaction time (12, 24 and 36 h), enzyme (5, 10 and 15%) and substrate mole ratio (S-RSO to PS, 1:1, 1:2 and 1:3) on SFC of TSF were considered. Uncoded variables were transferred into coded variables with a zero mean and the s ...
... Response surface methodology (RSM) The effects of three variables such as reaction time (12, 24 and 36 h), enzyme (5, 10 and 15%) and substrate mole ratio (S-RSO to PS, 1:1, 1:2 and 1:3) on SFC of TSF were considered. Uncoded variables were transferred into coded variables with a zero mean and the s ...
Petasis reaction

The Petasis reaction (alternatively called the Petasis borono–Mannich (PBM) reaction) is the chemical reaction of an amine, aldehyde, and vinyl- or aryl-boronic acid to form substituted amines.Reported in 1993 by Nicos Petasis as a practical method towards the synthesis of a geometrically pure antifungal agent, naftifine, the Petasis reaction can be described as a variation of the Mannich reaction. Rather than generating an enolate to form the substituted amine product, in the Petasis reaction, the vinyl group of the organoboronic acid serves as the nucleophile. In comparison to other methods of generating allyl amines, the Petasis reaction tolerates a multifunctional scaffold, with a variety of amines and organoboronic acids as potential starting materials. Additionally, the reaction does not require anhydrous or inert conditions. As a mild, selective synthesis, the Petasis reaction is useful in generating α-amino acids, and is utilized in combinatorial chemistry and drug discovery.