Gas-Phase Reactions of Fe (CH2O)+ and Fe (CH2S)+ with Small
... bonding differences between Fe(CH2O)+ and Fe(CH2S)+. To do this, product ion structures were probed by collision-induced dissociation, specific ion-molecule reactions, and use of labeled compounds, and experimental bond energies were obtained by using ion-molecule bracketing and competitive collisio ...
... bonding differences between Fe(CH2O)+ and Fe(CH2S)+. To do this, product ion structures were probed by collision-induced dissociation, specific ion-molecule reactions, and use of labeled compounds, and experimental bond energies were obtained by using ion-molecule bracketing and competitive collisio ...
Green synthesis of 2-amino-7-hydroxy-4-aryl-4H
... groups. Obviously, functionalization of chromene derivatives has played an ever increasing role in the synthetic approaches to promising compounds in the field of medicinal chemistry. On the other hand, functionalized chromenes appeared as an important structural component in both biologically activ ...
... groups. Obviously, functionalization of chromene derivatives has played an ever increasing role in the synthetic approaches to promising compounds in the field of medicinal chemistry. On the other hand, functionalized chromenes appeared as an important structural component in both biologically activ ...
- Opus: Online Publications Store
... Additional problems associated with the activation of C–H bonds are their low dipole moments, low HOMO and high LUMO energy levels [9]. Furthermore, the activation methods developed should be able to introduce different functionalities under the same reaction conditions [1c,10]. Because of the previ ...
... Additional problems associated with the activation of C–H bonds are their low dipole moments, low HOMO and high LUMO energy levels [9]. Furthermore, the activation methods developed should be able to introduce different functionalities under the same reaction conditions [1c,10]. Because of the previ ...
Document
... Alkyl ammonium ions, R3NH+ X-, have pKa values in the range of 10-11 (ammonium ion, H4N+ X-, has a pKa ~ 9.3) The ammonium ions of aryl amines and heterocyclic aromatic amines are considerably more acidic than alkyl amines (pKa < 5). The nitrogen lone pair is less basic if it is in an sp2 hybridized ...
... Alkyl ammonium ions, R3NH+ X-, have pKa values in the range of 10-11 (ammonium ion, H4N+ X-, has a pKa ~ 9.3) The ammonium ions of aryl amines and heterocyclic aromatic amines are considerably more acidic than alkyl amines (pKa < 5). The nitrogen lone pair is less basic if it is in an sp2 hybridized ...
Palladium and Ruthenium Catalyzed Reactions By Bryan Jaksic
... Part one of this thesis will discuss research which involves the direct comparison of the activity of commonly used precatalysts with the newly synthesized precatalyst, Pd(η5-C5H5)(η3-1Ph-C3H4), for Sonogashira cross-coupling reactions. Sonogashira reactions are important as they provide a simple me ...
... Part one of this thesis will discuss research which involves the direct comparison of the activity of commonly used precatalysts with the newly synthesized precatalyst, Pd(η5-C5H5)(η3-1Ph-C3H4), for Sonogashira cross-coupling reactions. Sonogashira reactions are important as they provide a simple me ...
Chapter 2 Phenols
... 5- Reactions of Phenols A hydroxyl group is very powerful activating substituent, and electrophilic aromatic substitution in phenol occurs far faster, and under milder condition, than in benzene. ...
... 5- Reactions of Phenols A hydroxyl group is very powerful activating substituent, and electrophilic aromatic substitution in phenol occurs far faster, and under milder condition, than in benzene. ...
Chapter 19. Aldehydes and Ketones
... yield a dipolar intermediate called a betaine The intermediate spontaneously decomposes through a four-membered ring to yield alkene and triphenylphosphine oxide, (Ph)3P=O Formation of the ylide is shown below ...
... yield a dipolar intermediate called a betaine The intermediate spontaneously decomposes through a four-membered ring to yield alkene and triphenylphosphine oxide, (Ph)3P=O Formation of the ylide is shown below ...
Reactions of Acyl Chlorides
... Reactions of Acyl Chlorides Acyl chlorides react with water to give carboxylic acids (carboxylate ion in base): O RCCl + H2O ...
... Reactions of Acyl Chlorides Acyl chlorides react with water to give carboxylic acids (carboxylate ion in base): O RCCl + H2O ...
dr. Zdenko Časar - Fakulteta za kemijo in kemijsko tehnologijo
... Beside the above presented application in the field of medicinal chemistry, there are several other important aspects of chiral boronic esters applications. Indeed, chiral boronates represent valuable building blocks, which were till now prepared with limited number of synthetic methods. Moreover, h ...
... Beside the above presented application in the field of medicinal chemistry, there are several other important aspects of chiral boronic esters applications. Indeed, chiral boronates represent valuable building blocks, which were till now prepared with limited number of synthetic methods. Moreover, h ...
Organic Chemistry: An Indian Journal
... In the year of 1998, a mild and rapid strategy was reported for the synthesis of various ether derivatives [17]. The mixture of potassium carbonate and potassium hydroxide in the presence of tetra-n-butyl ammonium bromide was introduced as an efficient and valuable system to synthesize symmetrical a ...
... In the year of 1998, a mild and rapid strategy was reported for the synthesis of various ether derivatives [17]. The mixture of potassium carbonate and potassium hydroxide in the presence of tetra-n-butyl ammonium bromide was introduced as an efficient and valuable system to synthesize symmetrical a ...
A manganese catalyst for highly reactive yet chemoselective
... while other chemoselective catalysts 1 and [Ru2(hp)4] are less reactive (12 and 25%, respectively)11,15. This electronic insensitivity is further highlighted by the tolerance of electron-withdrawing nitrogen functionality (22, 73%) introduced via palladium-catalysed intermolecular allylic C–H aminat ...
... while other chemoselective catalysts 1 and [Ru2(hp)4] are less reactive (12 and 25%, respectively)11,15. This electronic insensitivity is further highlighted by the tolerance of electron-withdrawing nitrogen functionality (22, 73%) introduced via palladium-catalysed intermolecular allylic C–H aminat ...
2009
... a. Name the phenomenon depicted in scheme 1. b. Draw structural formulas of the compounds A and B. c. Explain the effect of solvent on the distribution of alkylation products described in sub-item 1. d. In sentence: "LDA is a strong/weak Brönsted base and a strong/weak nucleophile" cross out two wor ...
... a. Name the phenomenon depicted in scheme 1. b. Draw structural formulas of the compounds A and B. c. Explain the effect of solvent on the distribution of alkylation products described in sub-item 1. d. In sentence: "LDA is a strong/weak Brönsted base and a strong/weak nucleophile" cross out two wor ...
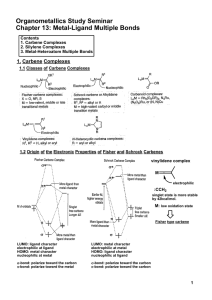
Pincer Complexes. Applications in Catalysis
... of these complexes have shown activity in the dehydrogenation of alkanes to alkenes. However, the extremely low reaction rates and the low turnover numbers or the instability of the employed catalysts under the reaction conditions16 has limited the use of these species. In 1976 Moulton and Shaw repo ...
... of these complexes have shown activity in the dehydrogenation of alkanes to alkenes. However, the extremely low reaction rates and the low turnover numbers or the instability of the employed catalysts under the reaction conditions16 has limited the use of these species. In 1976 Moulton and Shaw repo ...
lecture 11 catalysis_hydrogenation of alkenes
... Once CoH(CN)53− has been formed, a H• atom is transferred to the substrate in the second step, a reaction that does not require a vacant site at the metal, but does require the resulting organic radical to be moderately stable—hence the fact that the Iguchi catalyst will reduce only activated alken ...
... Once CoH(CN)53− has been formed, a H• atom is transferred to the substrate in the second step, a reaction that does not require a vacant site at the metal, but does require the resulting organic radical to be moderately stable—hence the fact that the Iguchi catalyst will reduce only activated alken ...
Carbon-Carbon Bond Formation by Reductive
... Hydrocarbons: Although titanium (II) chlo ride in the form of complexes 1, 2 and 3 and ad mixed with a six to eight-fold excess of M e2AlCl is able to catalyze the polymerization of ethylene and other alpha-olefins [4], complex 1 in TH F or unsolvated TiCl2 suspended in toluene [6] caused neither ...
... Hydrocarbons: Although titanium (II) chlo ride in the form of complexes 1, 2 and 3 and ad mixed with a six to eight-fold excess of M e2AlCl is able to catalyze the polymerization of ethylene and other alpha-olefins [4], complex 1 in TH F or unsolvated TiCl2 suspended in toluene [6] caused neither ...
Process for polymerizing olefins
... pounds. Mixtures of two or more polar compounds may also be used. ...
... pounds. Mixtures of two or more polar compounds may also be used. ...
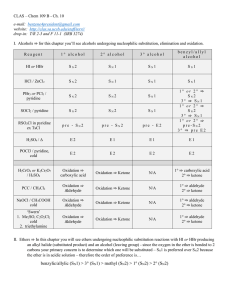
Chapter 10 - UCSB CLAS
... II. Ethers ⇒ In this chapter you will see ethers undergoing nucleophilic substitution reactions with HI or HBr producing an alkyl halide (substituted product) and an alcohol (leaving group) - since the oxygen in the ether is bonded to 2 carbons your primary concern is to determine which one will be ...
... II. Ethers ⇒ In this chapter you will see ethers undergoing nucleophilic substitution reactions with HI or HBr producing an alkyl halide (substituted product) and an alcohol (leaving group) - since the oxygen in the ether is bonded to 2 carbons your primary concern is to determine which one will be ...
Now we turn to the study of chemical kinetics. Kinetics is the study of
... reactants is higher, then they will be closer together, and it won't take as long for them to come together and react. Temperature can also affect reaction rates. The reason that it's bad for you to have a fever is that the elevated temperature increases the speed with which the reactions that allow ...
... reactants is higher, then they will be closer together, and it won't take as long for them to come together and react. Temperature can also affect reaction rates. The reason that it's bad for you to have a fever is that the elevated temperature increases the speed with which the reactions that allow ...
Carbon-Carbon Bond Formation by Reductive Coupling with
... Hydrocarbons: Although titanium (II) chlo ride in the form of complexes 1, 2 and 3 and ad mixed with a six to eight-fold excess of M e2AlCl is able to catalyze the polymerization of ethylene and other alpha-olefins [4], complex 1 in TH F or unsolvated TiCl2 suspended in toluene [6] caused neither ...
... Hydrocarbons: Although titanium (II) chlo ride in the form of complexes 1, 2 and 3 and ad mixed with a six to eight-fold excess of M e2AlCl is able to catalyze the polymerization of ethylene and other alpha-olefins [4], complex 1 in TH F or unsolvated TiCl2 suspended in toluene [6] caused neither ...
Heterogeneous Catalysts for Biodiesel Production
... (c) pre-esterification method. FFAs are first esterified to FAMEs using an acid catalyst, and then, transesterification is performed, as usual, by using an alkaline catalyst.5,10 Enzyme-based transesterification is carried out at moderate temperatures with high yields, but this method cannot be used ...
... (c) pre-esterification method. FFAs are first esterified to FAMEs using an acid catalyst, and then, transesterification is performed, as usual, by using an alkaline catalyst.5,10 Enzyme-based transesterification is carried out at moderate temperatures with high yields, but this method cannot be used ...
幻灯片 1
... • Stereochemistry of the SN1 Reaction: • Since an SN1 reaction occurs through a carbocation intermediate, its stereochemical outcome should be different from that for an SN2 reaction. Since carbocations are planar and are achiral. The carbocation intermediate can be attacked by a nucleophile equally ...
... • Stereochemistry of the SN1 Reaction: • Since an SN1 reaction occurs through a carbocation intermediate, its stereochemical outcome should be different from that for an SN2 reaction. Since carbocations are planar and are achiral. The carbocation intermediate can be attacked by a nucleophile equally ...
stereochemistry of internucleotide bond formation by the h
... stereoselectivity during condensing agents-promoted formation of an internucleotidic bond1,2. The activation of ribonucleoside H-phosphonates of type 1 with pivaloyl chloride yields two diastereomers (A and B, Fig. 1) of mixed anhydrides 2. These isomers have to exist in a rapid equilibrium to regen ...
... stereoselectivity during condensing agents-promoted formation of an internucleotidic bond1,2. The activation of ribonucleoside H-phosphonates of type 1 with pivaloyl chloride yields two diastereomers (A and B, Fig. 1) of mixed anhydrides 2. These isomers have to exist in a rapid equilibrium to regen ...
Oxidation-reduction reaction of chromium (VI) and iron (III) with
... because the oxidizing power of the oxyanions risesas a result of both the kinetic and thermodynamic factors [18]. The reaction pathway even though involves the M - O bond rapture, and the bond strength was observed to beCr6+> Fe3+, which seems to be more consistence with the oxidation potential valu ...
... because the oxidizing power of the oxyanions risesas a result of both the kinetic and thermodynamic factors [18]. The reaction pathway even though involves the M - O bond rapture, and the bond strength was observed to beCr6+> Fe3+, which seems to be more consistence with the oxidation potential valu ...
Checking the Kinetics of Acetic Acid Production by
... Piret [1] obtained the pseudo-first-order reaction rate constant using a batch reactor. In order to determine the acetic anhydride concentration, samples from the reactor were withdrawn into tarred flasks containing 15∼20 times the quantity of saturated aniline-water required to react with the sampl ...
... Piret [1] obtained the pseudo-first-order reaction rate constant using a batch reactor. In order to determine the acetic anhydride concentration, samples from the reactor were withdrawn into tarred flasks containing 15∼20 times the quantity of saturated aniline-water required to react with the sampl ...
Ene reaction

The ene reaction (also known as the Alder-ene reaction) is a chemical reaction between an alkene with an allylic hydrogen (the ene) and a compound containing a multiple bond (the enophile), in order to form a new σ-bond with migration of the ene double bond and 1,5 hydrogen shift. The product is a substituted alkene with the double bond shifted to the allylic position.This transformation is a group transfer pericyclic reaction, and therefore, usually requires highly activated substrates and/or high temperatures. Nonetheless, the reaction is compatible with a wide variety of functional groups that can be appended to the ene and enophile moieties. Also,many useful Lewis acid-catalyzed ene reactions have been developed which can afford high yields and selectivities at significantly lower temperatures, making the ene reaction a useful C–C forming tool for the synthesis of complex molecules and natural products.