appendix a - Modern Chemistry Textbook
... the most stable or most common isotope. The atomic masses of most of these elements are believed to have an error no greater than ±1 in the last digit given. ...
... the most stable or most common isotope. The atomic masses of most of these elements are believed to have an error no greater than ±1 in the last digit given. ...
CHAPTER 22 ORGANIC AND BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES 1
... An alkane is a saturated hydrocarbon composed of only CC and CH single bonds. Each carbon in an alkane is bonded to four other atoms (either C or H atoms). If the compound contains a ring in the structure and is composed of only CC and CH single bonds, then it is called a cyclic alkane. Alkanes: ...
... An alkane is a saturated hydrocarbon composed of only CC and CH single bonds. Each carbon in an alkane is bonded to four other atoms (either C or H atoms). If the compound contains a ring in the structure and is composed of only CC and CH single bonds, then it is called a cyclic alkane. Alkanes: ...
AMIDES AND AMINES: ORGANIC NITROGEN COMPOUNDS
... Amides: Unsubstituted amides (except formamide) are solids at room temperature. Many are odorless and colorless. Low molar-mass amides are water soluble. Solubility in water decreases as the molar mass increases. Amides are neutral compounds. The group is capable of hydrogen bonding. Amines: Low mol ...
... Amides: Unsubstituted amides (except formamide) are solids at room temperature. Many are odorless and colorless. Low molar-mass amides are water soluble. Solubility in water decreases as the molar mass increases. Amides are neutral compounds. The group is capable of hydrogen bonding. Amines: Low mol ...
Complete Solution Manual
... An alkane is a saturated hydrocarbon composed of only CC and CH single bonds. Each carbon in an alkane is bonded to four other atoms (either C or H atoms). If the compound contains a ring in the structure and is composed of only CC and CH single bonds, then it is called a cyclic alkane. Alkanes: ...
... An alkane is a saturated hydrocarbon composed of only CC and CH single bonds. Each carbon in an alkane is bonded to four other atoms (either C or H atoms). If the compound contains a ring in the structure and is composed of only CC and CH single bonds, then it is called a cyclic alkane. Alkanes: ...
Metallocenyl Dendrimers and Their Applications in
... effects. As a result, these metallodendrimers have applications in the molecular recognition, sensing, and titration of anions (e.g., ATP2-) and cations (e.g., transition metal complexes). When the recognition properties are coupled with catalysis, the metallodendrimers function in an enzyme-like ma ...
... effects. As a result, these metallodendrimers have applications in the molecular recognition, sensing, and titration of anions (e.g., ATP2-) and cations (e.g., transition metal complexes). When the recognition properties are coupled with catalysis, the metallodendrimers function in an enzyme-like ma ...
Main Group Metallocenes - Macdonald Research Group
... sigma bonded (and the elements often act as a bridge connecting two Cp’ groups). The compounds containing low oxidation state group 14 elements have a greater tendency to have π-bonded Cp’ groups. The Pb compounds are often polymeric or oligomeric in the solid state because of the large size and low ...
... sigma bonded (and the elements often act as a bridge connecting two Cp’ groups). The compounds containing low oxidation state group 14 elements have a greater tendency to have π-bonded Cp’ groups. The Pb compounds are often polymeric or oligomeric in the solid state because of the large size and low ...
Chapter 4 Metal nanoparticles stabilized by chiral ligands with carbohydrate backbone
... mild conditions, generally using a reducing gas, hydrogen or carbon monoxide (Scheme 4.5). The ideal precursor is a zerovalent olefinic complex, which leads to the production of an alkane unable to form strong bonds with the growing metal surface in these conditions. Precursors of this type are [Ni( ...
... mild conditions, generally using a reducing gas, hydrogen or carbon monoxide (Scheme 4.5). The ideal precursor is a zerovalent olefinic complex, which leads to the production of an alkane unable to form strong bonds with the growing metal surface in these conditions. Precursors of this type are [Ni( ...
adjacent to - dl1.ponato.com
... cording to overall transformations. This rather unusual organizational structure, borrowed from Miller and Solomon, is better suited to teaching students how to draw reasonable mechanisms than the more traditional structures, perhaps because the all-important first steps of mechanisms are usually mo ...
... cording to overall transformations. This rather unusual organizational structure, borrowed from Miller and Solomon, is better suited to teaching students how to draw reasonable mechanisms than the more traditional structures, perhaps because the all-important first steps of mechanisms are usually mo ...
LIPIDS
... carbon and oxygen are involved in the structure of complex lipids, in addition to phosphorus and sulphur as in phospholipids ...
... carbon and oxygen are involved in the structure of complex lipids, in addition to phosphorus and sulphur as in phospholipids ...
PDF document
... where MOXI is the deprotonated molecule of the ligand. Fully protonated moxifloxacin is denoted as H2MOXI+. In this study, the convention has been adopted whereby a complex containing a metal ion, M, proton, H and ligand L, takes the general formula MpHqLr, where p, q and r are the stoichiometric in ...
... where MOXI is the deprotonated molecule of the ligand. Fully protonated moxifloxacin is denoted as H2MOXI+. In this study, the convention has been adopted whereby a complex containing a metal ion, M, proton, H and ligand L, takes the general formula MpHqLr, where p, q and r are the stoichiometric in ...
Slide 1
... Ether cleavage is not usually selective; both sets of cleavage products are to be expected. In methyl ethers, the X preferentially attacks the methyl group. In excess HX, both C-O are cleaved, producing water and two C-X bonds. In phenyl ethers, the benzene ring is not attacked, even in excess HX. ...
... Ether cleavage is not usually selective; both sets of cleavage products are to be expected. In methyl ethers, the X preferentially attacks the methyl group. In excess HX, both C-O are cleaved, producing water and two C-X bonds. In phenyl ethers, the benzene ring is not attacked, even in excess HX. ...
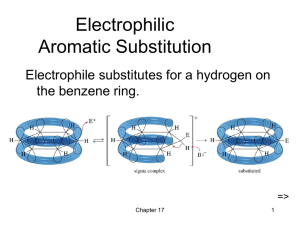
Electrophilic Aromatic Substit
... Activating, O-, PDirecting Substituents • Alkyl groups stabilize the sigma complex by induction, donating electron density through the sigma bond. • Substituents with a lone pair of electrons stabilize the sigma complex by resonance. ...
... Activating, O-, PDirecting Substituents • Alkyl groups stabilize the sigma complex by induction, donating electron density through the sigma bond. • Substituents with a lone pair of electrons stabilize the sigma complex by resonance. ...
Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane
... onto mesoporous silica particles because of the strong affinity of thiol to Pd2þ ions and Pd(0) NPs.39,40 Typically, there are four raw materials—metal salts, reductants, stabilizer, and phase-transfer agents—that are required for the chemical synthesis of metal NPs. Using a hydrophobic stabilizer, a ...
... onto mesoporous silica particles because of the strong affinity of thiol to Pd2þ ions and Pd(0) NPs.39,40 Typically, there are four raw materials—metal salts, reductants, stabilizer, and phase-transfer agents—that are required for the chemical synthesis of metal NPs. Using a hydrophobic stabilizer, a ...
Physical properties study for TBP-HNO3-diluent system
... different authors is also cited. The various studies carried out by different investigators to measure physical properties like vapor pressure, solubility and density of TBP and its degradation products at different temperatures in TBP-diluent-nitric acid system have also been discussed in the revie ...
... different authors is also cited. The various studies carried out by different investigators to measure physical properties like vapor pressure, solubility and density of TBP and its degradation products at different temperatures in TBP-diluent-nitric acid system have also been discussed in the revie ...
Ch14_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best
... Alcohols and ethers can be considered to be derivatives of water. Similar physical properties include: Polarity: Water is a very polar molecule; alcohols and ethers also display polarity. Boiling point: Water has a higher boiling point than predicted on the basis of its molar mass. Alcohols also sha ...
... Alcohols and ethers can be considered to be derivatives of water. Similar physical properties include: Polarity: Water is a very polar molecule; alcohols and ethers also display polarity. Boiling point: Water has a higher boiling point than predicted on the basis of its molar mass. Alcohols also sha ...
Reaction of Nitrogen Chelates with the [Rh2]4+ Core: Bis
... with two cis bridging RCO2- groups and two syn-bpy chelate groups in a near-eclipsed conformation about the Rh-Rh vector. Reaction of [Rh2(tpy)2(MeCN)4](BF4)4 (15) (tpy ) 2,2′:6′,2′′-terpyridine) with NBun4(O2CPh) gives [Rh2(O2CPh)(tpy)2(MeCN)2](BF4)3‚MeCN (16). Complex 16 crystallizes in triclinic ...
... with two cis bridging RCO2- groups and two syn-bpy chelate groups in a near-eclipsed conformation about the Rh-Rh vector. Reaction of [Rh2(tpy)2(MeCN)4](BF4)4 (15) (tpy ) 2,2′:6′,2′′-terpyridine) with NBun4(O2CPh) gives [Rh2(O2CPh)(tpy)2(MeCN)2](BF4)3‚MeCN (16). Complex 16 crystallizes in triclinic ...
Acid-Catalyzed Hydration of Alkenes
... Optically inactive reactants produce optically inactive products. (Racemic mixtures are optically inactive) The correlary is that an optically active starting material MAY produce an optically active product depending on the mechanism. ...
... Optically inactive reactants produce optically inactive products. (Racemic mixtures are optically inactive) The correlary is that an optically active starting material MAY produce an optically active product depending on the mechanism. ...
Chapter 19
... atoms attached to each carbon atom. Unsaturated compounds: Have fewer hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon chain than alkanes. • Containing double bond are alkenes. ...
... atoms attached to each carbon atom. Unsaturated compounds: Have fewer hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon chain than alkanes. • Containing double bond are alkenes. ...
SUPPORTED LIGANDS FOR METAL CATALYZED REACTIONS Rocío Marcos Escartín ISBN:
... 1.1 METAL-CATALYZED REACTIONS Homogeneous metal catalysts are composed by a metal complex modified with organic ligands. Although the first non enzymatic asymmetric catalysts known were simple organic molecules,[1] the research regarding catalysis reached full development with metal-based systems, w ...
... 1.1 METAL-CATALYZED REACTIONS Homogeneous metal catalysts are composed by a metal complex modified with organic ligands. Although the first non enzymatic asymmetric catalysts known were simple organic molecules,[1] the research regarding catalysis reached full development with metal-based systems, w ...
No Slide Title
... the attraction extends to the shared pair of electrons in water’s O-H bonds the electron pair is pulled towards the O, making the bond more polar this makes the H more acidic (more d+) it can then be removed by solvent water molecules to form H3O+(aq). ...
... the attraction extends to the shared pair of electrons in water’s O-H bonds the electron pair is pulled towards the O, making the bond more polar this makes the H more acidic (more d+) it can then be removed by solvent water molecules to form H3O+(aq). ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.














![Reaction of Nitrogen Chelates with the [Rh2]4+ Core: Bis](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/016109229_1-82def2167f1fa4f2a4186d949c34cb3c-300x300.png)