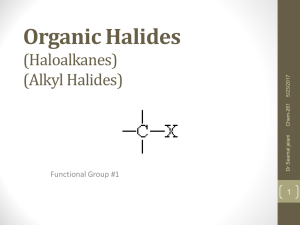NaBH4 Reduction of Vanillin
... The reduction of carbonyl compounds is an important synthetic method for the generation of alcohols. Compounds one oxidation level above alcohols, such as aldehydes and ketones, can be reduced by a variety of reagents to yield the corresponding alcohols. In general, most synthet ...
... The reduction of carbonyl compounds is an important synthetic method for the generation of alcohols. Compounds one oxidation level above alcohols, such as aldehydes and ketones, can be reduced by a variety of reagents to yield the corresponding alcohols. In general, most synthet ...
Get cached
... of both C r ( C N — C H ) (in C H C 1 , v :2070, 2012, 1965 cm" ) and N i ( C N — C H ) (in C H C 1 , *> :2050, 1990 cm" ) show more than one C N — band, is taken as evidence that, in this case at least, the V B approach can afford an adequate explanation of the observations. The I R spectra of Cr(O ...
... of both C r ( C N — C H ) (in C H C 1 , v :2070, 2012, 1965 cm" ) and N i ( C N — C H ) (in C H C 1 , *> :2050, 1990 cm" ) show more than one C N — band, is taken as evidence that, in this case at least, the V B approach can afford an adequate explanation of the observations. The I R spectra of Cr(O ...
Document
... • A second way is to add two protons and two electrons to a substrate— that is, H2 = 2H+ + 2e-. Reductions of this sort use alkali metals as a source of electrons, and liquid ammonia as a source of protons. These are called dissolving metal reductions. ...
... • A second way is to add two protons and two electrons to a substrate— that is, H2 = 2H+ + 2e-. Reductions of this sort use alkali metals as a source of electrons, and liquid ammonia as a source of protons. These are called dissolving metal reductions. ...
Palladium Complexes Bearing Novel Strongly Bent Trans
... majority of bidentate ligands. For example, similar parameters have been observed for trans-coordinated Xantphos ligands and some palladium complexes bearing various metalloligands.23 Clearly, in contrast to earlier precedents, where the distortion originated from the weak palladium-heteroatom or pa ...
... majority of bidentate ligands. For example, similar parameters have been observed for trans-coordinated Xantphos ligands and some palladium complexes bearing various metalloligands.23 Clearly, in contrast to earlier precedents, where the distortion originated from the weak palladium-heteroatom or pa ...
FREE RADICAL REACTIONS IN ORGANIC SYNTHESIS
... • Overcome by only having a very low concentration of radicals present in a reaction • Now there are many ways to use these highly reactive species in selective (& synthetically useful) organic reactions • Good example is the radical chain process for allylic halogenation activated C-H ...
... • Overcome by only having a very low concentration of radicals present in a reaction • Now there are many ways to use these highly reactive species in selective (& synthetically useful) organic reactions • Good example is the radical chain process for allylic halogenation activated C-H ...
Microsoft Word
... protection of alcohols, phenols and amines are fundamental and useful transformations in organic synthesis. Among the many protecting groups for hydroxyls, phenols and amines, acetate is used with high frequency. Although, numerous methods are available for the preparation of acetates using acetic a ...
... protection of alcohols, phenols and amines are fundamental and useful transformations in organic synthesis. Among the many protecting groups for hydroxyls, phenols and amines, acetate is used with high frequency. Although, numerous methods are available for the preparation of acetates using acetic a ...
Organic Halides (Haloalkanes) (Alkyl Halides)
... Poor nucleophiles that are also weak bases (H2O, ROH, CH3COOH, etc.) do not undergo any reaction unless a C+ is formed first If a C+ can form (as with a 2º, 3º, any benzylic, or any allylic halides), then E1 and SN1 generally occur together. ...
... Poor nucleophiles that are also weak bases (H2O, ROH, CH3COOH, etc.) do not undergo any reaction unless a C+ is formed first If a C+ can form (as with a 2º, 3º, any benzylic, or any allylic halides), then E1 and SN1 generally occur together. ...
Group 13 Compounds - University of Ottawa
... Reaction with HCl The metal alkyls (particularly B, Al, Ga) react with one equivalent of hydrogen chloride to eliminate an alkane and form the monochloride: MR3 + HCl R2MCl + RH This reactivity is particularly labile and must be controlled (low T, ...
... Reaction with HCl The metal alkyls (particularly B, Al, Ga) react with one equivalent of hydrogen chloride to eliminate an alkane and form the monochloride: MR3 + HCl R2MCl + RH This reactivity is particularly labile and must be controlled (low T, ...
PTT102 Aldehydes and Ketones
... The benzene ring makes the carbonyl group unreactive towards aldol reactions. A carbonyl group must be connected to two alkyl groups in order to undergo an aldol reaction. The molecule does not possess any hydrogens α to the carbonyl group. Electrophilic aromatic substitution competes favorably with ...
... The benzene ring makes the carbonyl group unreactive towards aldol reactions. A carbonyl group must be connected to two alkyl groups in order to undergo an aldol reaction. The molecule does not possess any hydrogens α to the carbonyl group. Electrophilic aromatic substitution competes favorably with ...
PTT102 Aldehydes and Ketones
... The benzene ring makes the carbonyl group unreactive towards aldol reactions. A carbonyl group must be connected to two alkyl groups in order to undergo an aldol reaction. The molecule does not possess any hydrogens α to the carbonyl group. Electrophilic aromatic substitution competes favorably with ...
... The benzene ring makes the carbonyl group unreactive towards aldol reactions. A carbonyl group must be connected to two alkyl groups in order to undergo an aldol reaction. The molecule does not possess any hydrogens α to the carbonyl group. Electrophilic aromatic substitution competes favorably with ...
Contents - Personal WWW Pages
... It was Sabatier who, in 1927, published the first classification of catalysts and used the terms homogeneous and heterogeneous. A heterogeneous catalyst exists in a separate phase to the reaction medium (most commonly as a solid in either a liquid or gaseous reaction medium). A homogeneous catalyst ...
... It was Sabatier who, in 1927, published the first classification of catalysts and used the terms homogeneous and heterogeneous. A heterogeneous catalyst exists in a separate phase to the reaction medium (most commonly as a solid in either a liquid or gaseous reaction medium). A homogeneous catalyst ...
SN1 vs. SN2 Reactions - Master Organic Chemistry
... in a single step, resulting in inversion of configuration. ...
... in a single step, resulting in inversion of configuration. ...
DCC-promoted peptide coupling
... abbreviated DCC. DCC is a dehydrating agent for the preparation of amides, ketones, nitriles. In these reactions, DCC hydrates to form dicyclohexylurea (DCU), a compound that is insoluble in most organic solvents and in water and hence is readily removed by filtration. DCC can also be used to invert ...
... abbreviated DCC. DCC is a dehydrating agent for the preparation of amides, ketones, nitriles. In these reactions, DCC hydrates to form dicyclohexylurea (DCU), a compound that is insoluble in most organic solvents and in water and hence is readily removed by filtration. DCC can also be used to invert ...
Recent developments in the applications of palladium complexes
... 2.2. Pd-catalyzed reactions in alternative solvents i) Hydrophilic ligands and aqueous Pd-catalyzed reactions. The use of water as solvent has attracted great interest for economical and ecological reasons and so, water-soluble homogenous catalysts are highly desirable. This strategy requires that t ...
... 2.2. Pd-catalyzed reactions in alternative solvents i) Hydrophilic ligands and aqueous Pd-catalyzed reactions. The use of water as solvent has attracted great interest for economical and ecological reasons and so, water-soluble homogenous catalysts are highly desirable. This strategy requires that t ...
View/Open
... (pKa = 4.76), phenol is a much stronger acid than cyclohexanol (by a factor of eight pKa units). Experimental and theoretical results have shown that the greater acidity of phenol owes itself primarily to an electrical charge distribution in phenol that causes the i OH oxygen to be more positive; th ...
... (pKa = 4.76), phenol is a much stronger acid than cyclohexanol (by a factor of eight pKa units). Experimental and theoretical results have shown that the greater acidity of phenol owes itself primarily to an electrical charge distribution in phenol that causes the i OH oxygen to be more positive; th ...
Oxidative Additions of Aryl Halides to Palladium Proceed through
... these difficult substrates is suggested to require a highly reactive, 12-electron, monoligated catalyst, the formation of which is favored by bulky phosphine (or N-heterocyclic carbene) ligands.[15–21] DFT calculations support this hypothesis.[22, 23] Ahlquist and co-workers have gone one step furth ...
... these difficult substrates is suggested to require a highly reactive, 12-electron, monoligated catalyst, the formation of which is favored by bulky phosphine (or N-heterocyclic carbene) ligands.[15–21] DFT calculations support this hypothesis.[22, 23] Ahlquist and co-workers have gone one step furth ...
High-Oxidation-State Palladium Catalysis: New Reactivity for
... transformations involving C O bond formation, but the molecular basis for these processes remained unclear for a long time.[18] Yoneyama and Crabtree reported that the combination of a palladium(II) catalyst and iodosobenzene diacetate led to the catalytic C H activation of an arene, followed by ace ...
... transformations involving C O bond formation, but the molecular basis for these processes remained unclear for a long time.[18] Yoneyama and Crabtree reported that the combination of a palladium(II) catalyst and iodosobenzene diacetate led to the catalytic C H activation of an arene, followed by ace ...
Document
... • In order for ethers to undergo substitution or elimination reactions, their poor leaving group must first be converted into a good leaving group by reaction with strong acids such as HBr and HI. HBr and HI are strong acids that are also sources of good nucleophiles (Br¯ and I¯ respectively). • Whe ...
... • In order for ethers to undergo substitution or elimination reactions, their poor leaving group must first be converted into a good leaving group by reaction with strong acids such as HBr and HI. HBr and HI are strong acids that are also sources of good nucleophiles (Br¯ and I¯ respectively). • Whe ...
Organic Chemistry: An Indian Journal
... pharmaceuticals, and dyestuffs [1,2]. The Williamson reaction is the best technique for the synthesis of symmetrical and unsymmetrical ethers. The Williamson reaction generally involves the employment of an alkali-metal salt of the hydroxyl compound and an alkyl halide. These reactions are generally ...
... pharmaceuticals, and dyestuffs [1,2]. The Williamson reaction is the best technique for the synthesis of symmetrical and unsymmetrical ethers. The Williamson reaction generally involves the employment of an alkali-metal salt of the hydroxyl compound and an alkyl halide. These reactions are generally ...
what are acyl chlorides?
... attractions between its molecules as well as van der Waals dispersion forces. However, it doesn't form hydrogen bonds. Its boiling point is therefore higher than, say, an alkane of similar size (which has no permanent dipoles), but not as high as a similarly sized alcohol (which forms hydrogen bonds ...
... attractions between its molecules as well as van der Waals dispersion forces. However, it doesn't form hydrogen bonds. Its boiling point is therefore higher than, say, an alkane of similar size (which has no permanent dipoles), but not as high as a similarly sized alcohol (which forms hydrogen bonds ...
CH402 Asymmetric catalytic reactions Prof M. Wills
... reaction to one face of a substrate and release the product: Catalyst recycled ...
... reaction to one face of a substrate and release the product: Catalyst recycled ...
7. Alkenes: Reactions and Synthesis
... An Alternative to Bromine Bromine is a difficult reagent to use for this reaction N-Bromosuccinimide (NBS) produces bromine in organic ...
... An Alternative to Bromine Bromine is a difficult reagent to use for this reaction N-Bromosuccinimide (NBS) produces bromine in organic ...
- University at Albany
... Factors influencing what products are formed Substrate/steric effects Strength of nucleophile vs. basicity of ...
... Factors influencing what products are formed Substrate/steric effects Strength of nucleophile vs. basicity of ...
nucleophile (亲核试剂)
... shared the 1979 Nobel Prize for Chemistry. In the Wittig reaction, he first demonstrated 1954, a carbonyl compound (aldehyde or ketone) reacts with an organic phosphorus compound, an alkylidenetriphenylphosphorane, (C6H5)3P=CR2, where R is a hydrogen atom or an organic radical. The alkylidene group ...
... shared the 1979 Nobel Prize for Chemistry. In the Wittig reaction, he first demonstrated 1954, a carbonyl compound (aldehyde or ketone) reacts with an organic phosphorus compound, an alkylidenetriphenylphosphorane, (C6H5)3P=CR2, where R is a hydrogen atom or an organic radical. The alkylidene group ...
Stille reaction

The Stille reaction, or the Migita-Kosugi-Stille coupling, is a chemical reaction widely used in organic synthesis which involves the coupling of an organotin compound (also known as organostannanes) with a variety of organic electrophiles via palladium-catalyzed coupling reaction.The R1 group attached to the trialkyltin is normally sp2-hybridized, including alkenes, and aryl groups; however, conditions have been devised to incorporate both sp3-hybridized groups, such as allylic and benzylic substituents, and sp-hybridized alkynes. These organostannanes are also stable to both air and moisture, and many of these reagents are either commercially available or can be synthesized from literature precedent. However, these tin reagents tend to be highly toxic. X is typically a halide, such as Cl, Br, I, yet pseudohalides such as triflates and sulfonates and phosphates can also be used.The groundwork for the Stille reaction was laid by Colin Eaborn, Toshihiko Migita, and Masanori Kosugi in 1976 and 1977, who explored numerous palladium catalyzed couplings involving organotin reagents. John Stille and David Milstein developed a much milder and more broadly applicable procedure in 1978. Stille’s work on this area might have earned him a share of the 2010 Nobel Prize, which was awarded to Richard Heck, Ei-ichi Negishi, and Akira Suzuki for their work on the Heck, Negishi, and Suzuki coupling reactions. However, Stille died in the plane crash of United Airlines Flight 232 in 1989.Several reviews have been published on the Stille reaction.