POST-TRAVEL CONSULTATION
... Most travelers’ diarrhea is brief, self-limiting and non-inflammatory (about 4 days in duration) About 20% of travelers have fever and/or bloody diarrhea Enterotoxigenic Escherichia Coli is probably the most frequent pathogen in about 40-75 of cases ...
... Most travelers’ diarrhea is brief, self-limiting and non-inflammatory (about 4 days in duration) About 20% of travelers have fever and/or bloody diarrhea Enterotoxigenic Escherichia Coli is probably the most frequent pathogen in about 40-75 of cases ...
Biosecurity & Disaster Preparedness
... Keep situation reports and activity logs of past scenarios. ...
... Keep situation reports and activity logs of past scenarios. ...
Digestive System Powerpoint[
... • Because of a sensitivity to gluten, which is found in wheat, rye, barley, and oats. • This disease interferes with the absorption of nutrients from food. • If you eat gluten this disease damages your small intestines. ...
... • Because of a sensitivity to gluten, which is found in wheat, rye, barley, and oats. • This disease interferes with the absorption of nutrients from food. • If you eat gluten this disease damages your small intestines. ...
sore throat
... Contact Surgeon before giving any medication marked with an asterisk. In an emergency or during Loss of Signal, begin appropriate treatment; then call Surgeon as soon as possible. DIAGNOSIS Signs Red throat Swollen glands in neck White blotches on tonsils Symptoms Pain on swallowing Possible fever A ...
... Contact Surgeon before giving any medication marked with an asterisk. In an emergency or during Loss of Signal, begin appropriate treatment; then call Surgeon as soon as possible. DIAGNOSIS Signs Red throat Swollen glands in neck White blotches on tonsils Symptoms Pain on swallowing Possible fever A ...
Nutra Biotic - Reed Chiropractic Clinic
... Societal factors including cesarean deliveries, bottle feeding of infants, the over use of antibiotics in agriculture and medicine, and the consumption of essentially sterile processed foods may lead to dysbiosis. Dysbiosis is an unhealthy balance of bacterial flora that can negatively impact the di ...
... Societal factors including cesarean deliveries, bottle feeding of infants, the over use of antibiotics in agriculture and medicine, and the consumption of essentially sterile processed foods may lead to dysbiosis. Dysbiosis is an unhealthy balance of bacterial flora that can negatively impact the di ...
Basic Human Needs Bowel Elimination
... Most at risk: confused, unconscious (all are at risk for dehydration) ...
... Most at risk: confused, unconscious (all are at risk for dehydration) ...
Bacillary Dysentery (shigellosis)
... Chronic obscure type: acute history in 1 year, no symptoms, stool culture Pos. or sigmoidscopy Acute ...
... Chronic obscure type: acute history in 1 year, no symptoms, stool culture Pos. or sigmoidscopy Acute ...
Chapter 23 Diseases of the Digestive System
... • Portal of entry: Mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract • Signs/Symptoms: Parotitis, face pain, fever, sore throat • Incubation period: Twelve to twenty-four days • Susceptibility: Unimmunized children • Diagnosis: Symptoms are usually diagnostic • Treatment: Supportive care for symptoms • ...
... • Portal of entry: Mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract • Signs/Symptoms: Parotitis, face pain, fever, sore throat • Incubation period: Twelve to twenty-four days • Susceptibility: Unimmunized children • Diagnosis: Symptoms are usually diagnostic • Treatment: Supportive care for symptoms • ...
Disease and Diagnostic Update
... • Vitamin E and/or selenium deficiency (1970s) • Has been experimentally replicated with diets deficient in both vitamin E and selenium ...
... • Vitamin E and/or selenium deficiency (1970s) • Has been experimentally replicated with diets deficient in both vitamin E and selenium ...
Surface and Occupational Exposure
... • Water samples from water-play tables in each center were also collected during the study period. • During an infectious disease outbreak, fomites were sampled from the rooms in which the outbreak occurred. • A total of 96 fomite samples were tested for presence of rotavirus from the two centers, o ...
... • Water samples from water-play tables in each center were also collected during the study period. • During an infectious disease outbreak, fomites were sampled from the rooms in which the outbreak occurred. • A total of 96 fomite samples were tested for presence of rotavirus from the two centers, o ...
ENTERO HEALTH PRO - Vetriproline.com
... L-Glutamine — a key component in the maintenance of healthy intestinal mucosa. A lack of glutamine may lead to a loss of enterocyte (cells in the small intestine) integrity in the lining of the intestines, which may affect digestion and absorption or allow the passage of pathogens into the body. Sli ...
... L-Glutamine — a key component in the maintenance of healthy intestinal mucosa. A lack of glutamine may lead to a loss of enterocyte (cells in the small intestine) integrity in the lining of the intestines, which may affect digestion and absorption or allow the passage of pathogens into the body. Sli ...
General Microbiology Fact Sheet(PDF 3.5MB)
... 1-6 hours, average 4 hours; Infectious dose is greater than 10e6 organisms by characterized by two forms: an emetic form diarrheal form 6-24 hours ingestion (>10e5 organisms/g of food). with severe nausea and vomiting and a (average 17 hours) diarrheal form with abdominal cramps and diarrhea. Usuall ...
... 1-6 hours, average 4 hours; Infectious dose is greater than 10e6 organisms by characterized by two forms: an emetic form diarrheal form 6-24 hours ingestion (>10e5 organisms/g of food). with severe nausea and vomiting and a (average 17 hours) diarrheal form with abdominal cramps and diarrhea. Usuall ...
Large Intestine
... Muscle layers wrap around the entire length and help move food material through to the rectum. ...
... Muscle layers wrap around the entire length and help move food material through to the rectum. ...
let`s see if you can swallow this…
... Caused by both virus and bacteria, but both usually resolve without specific treatment. Need to think twice if lasts > 10 days, bloody diarrhea. Supportive care: HYDRATION, help with the nausea/vomiting. Diarrhea usually happens for a reason. Probiotics. Signs of dehydration: dry mouth/tongue, no te ...
... Caused by both virus and bacteria, but both usually resolve without specific treatment. Need to think twice if lasts > 10 days, bloody diarrhea. Supportive care: HYDRATION, help with the nausea/vomiting. Diarrhea usually happens for a reason. Probiotics. Signs of dehydration: dry mouth/tongue, no te ...
V3ch11b - SchultzMedic
... Sudden onset of sore throat and fever, with swelling of the palate, tonsils, and lymph nodes Common in 5- to 11-year-old patients ...
... Sudden onset of sore throat and fever, with swelling of the palate, tonsils, and lymph nodes Common in 5- to 11-year-old patients ...
Salmonella - UCSF | Department of Medicine
... • Classically, temperature-pulse dissociation (relative bradycardia) and rose spots • 50% have hepatosplenomegaly; “moderately” elevated LFTs are fairly common • If untreated, may result in perforation • Endovascular infection in 10-25% of those over 50 years old who are bacteremic, most commonly in ...
... • Classically, temperature-pulse dissociation (relative bradycardia) and rose spots • 50% have hepatosplenomegaly; “moderately” elevated LFTs are fairly common • If untreated, may result in perforation • Endovascular infection in 10-25% of those over 50 years old who are bacteremic, most commonly in ...
Additional Bacteria of Medical Importance
... The organism grows better at 25°C to 30°C than most other enterobacteria. Some strains possess plasmid-mediated virulence factors ...
... The organism grows better at 25°C to 30°C than most other enterobacteria. Some strains possess plasmid-mediated virulence factors ...
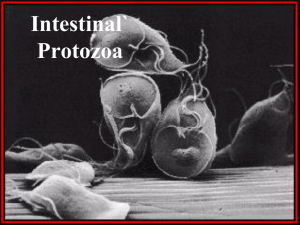
Intestinal Protozoa
... Amebiasis occurs worldwide; the prevalence is increased in developing countries because of poor socioeconomic conditions and sanitation levels. The parasite exists in two forms, a cyst stage (the infective form) and a trophozoite stage which causes invasive disease. The cysts pass through the stomac ...
... Amebiasis occurs worldwide; the prevalence is increased in developing countries because of poor socioeconomic conditions and sanitation levels. The parasite exists in two forms, a cyst stage (the infective form) and a trophozoite stage which causes invasive disease. The cysts pass through the stomac ...
Malabsorption and Vitamin Deficiencies Due
... have a prompt and impressive response to antibiotic therapy. The optimal antibiotic for the treatment of Whipple’s disease is unknown, but many patients respond to trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole. Penicillin, tetracycline, and erythromycin (among others) have all been shown to be effective agents as w ...
... have a prompt and impressive response to antibiotic therapy. The optimal antibiotic for the treatment of Whipple’s disease is unknown, but many patients respond to trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole. Penicillin, tetracycline, and erythromycin (among others) have all been shown to be effective agents as w ...
Diarrhea

Diarrhea, also spelled diarrhoea, is the condition of having at least three loose or liquid bowel movements each day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration due to fluid loss. Signs of dehydration often begin with loss of the normal stretchiness of the skin and changes in personality. This can progress to decreased urination, loss of skin color, a fast heart rate, and a decrease in responsiveness as it becomes more severe. Loose but non watery stools in babies who are breastfed, however, may be normal.The most common cause is an infection of the intestines due to either a virus, bacteria, or parasite; a condition known as gastroenteritis. These infections are often acquired from food or water that has been contaminated by stool, or directly from another person who is infected. It may be divided into three types: short duration watery diarrhea, short duration bloody diarrhea, and if it lasts for more than two weeks, persistent diarrhea. The short duration watery diarrhea may be due to an infection by cholera. If blood is present it is also known as dysentery. A number of non-infectious causes may also result in diarrhea, including hyperthyroidism, lactose intolerance, inflammatory bowel disease, a number of medications, and irritable bowel syndrome. In most cases stool cultures are not required to confirm the exact cause.Prevention of infectious diarrhea is by improved sanitation, clean drinking water, and hand washing with soap. Breastfeeding for at least six months is also recommended as is vaccination against rotavirus. Oral rehydration solution (ORS), which is clean water with modest amounts of salts and sugar, is the treatment of choice. Zinc tablets are also recommended. These treatments have been estimated to have saved 50 million children in the past 25 years. When people have diarrhea it is recommended that they continue to eat healthy food and babies continue to be breastfeed. If commercial ORS are not available, homemade solutions may be used. In those with severe dehydration, intravenous fluids may be required. Most cases; however, can be managed well with fluids by mouth. Antibiotics, while rarely used, may be recommended in a few cases such as those who have bloody diarrhea and a high fever, those with severe diarrhea following travelling, and those who grow specific bacteria or parasites in their stool. Loperamide may help decrease the number of bowel movement but is not recommended in those with severe disease.About 1.7 to 5 billion cases of diarrhea occur per year. It is most common in developing countries, where young children get diarrhea on average three times a year. Total deaths from diarrhea are estimated at 1.26 million in 2013 – down from 2.58 million in 1990. In 2012, it is the second most common cause of deaths in children younger than five (0.76 million or 11%). Frequent episodes of diarrhea are also a common cause of malnutrition and the most common cause in those younger than five years of age. Other long term problems that can result include stunted growth and poor intellectual development.