CH. 21 DISEASES OF THE RESPIRATORY TRACT
... fluids intercranial pressure Onset: High fever, chills, headache, stiff painful neck delirium convulsions shock. Skin rash due to hemorrhages (capillaries). Coma death. Identification: Spinal tap number PMN's, Gram negative intracellular diplococci in PMN's Vaccine: Capsular antige ...
... fluids intercranial pressure Onset: High fever, chills, headache, stiff painful neck delirium convulsions shock. Skin rash due to hemorrhages (capillaries). Coma death. Identification: Spinal tap number PMN's, Gram negative intracellular diplococci in PMN's Vaccine: Capsular antige ...
(including Rocky Mountain spotted fever) 09-ID-16
... Spotted fever rickettsioses are a group of tickborne infections caused by some members of the genus Rickettsia. Rocky Mountain spotted fever (RMSF) is an illness caused by Rickettsia rickettsii, a bacterial pathogen transmitted to humans through contact with ticks. Dermacentor species of ticks are m ...
... Spotted fever rickettsioses are a group of tickborne infections caused by some members of the genus Rickettsia. Rocky Mountain spotted fever (RMSF) is an illness caused by Rickettsia rickettsii, a bacterial pathogen transmitted to humans through contact with ticks. Dermacentor species of ticks are m ...
Epidemiology_PowerPoint_ajb
... Reservoirs: humans, animals, plants, soils or inanimate organic matter (feces or food) in which infectious organisms live and multiply ...
... Reservoirs: humans, animals, plants, soils or inanimate organic matter (feces or food) in which infectious organisms live and multiply ...
rift valley fever contingency plan for the netherlands
... and physical misery. An outbreak in South Africa in 1951 was estimated to have infected 20,000 people and killed 100,000 sheep and cattle. In Egypt in 1977 there were 18,000 human cases of this disease with 698 deaths. 1.3 Clinical Signs In young lambs the incubation period varies from 20 to 72 hour ...
... and physical misery. An outbreak in South Africa in 1951 was estimated to have infected 20,000 people and killed 100,000 sheep and cattle. In Egypt in 1977 there were 18,000 human cases of this disease with 698 deaths. 1.3 Clinical Signs In young lambs the incubation period varies from 20 to 72 hour ...
10 TABLE . Recommended Evidence
... Cyanosis Grunting respiration Tachycardia Capillary refill time > 2seconds Hypoxemia (SpO2 < 92%) Infants: RR >70breaths/min moderate-severe recession intermittent apnea not feeding Older children: RR >50breaths/min severe difficulty in breathing dehydration ...
... Cyanosis Grunting respiration Tachycardia Capillary refill time > 2seconds Hypoxemia (SpO2 < 92%) Infants: RR >70breaths/min moderate-severe recession intermittent apnea not feeding Older children: RR >50breaths/min severe difficulty in breathing dehydration ...
Infection Control Guidelines for Community Shelters and Group
... Infection results from the interaction of an infectious agent with a susceptible host. The interaction occurs by one or more methods of spread within the environmental context. These inter-related factors are known as the “chain of infection.” Infection control measures target the various links in a ...
... Infection results from the interaction of an infectious agent with a susceptible host. The interaction occurs by one or more methods of spread within the environmental context. These inter-related factors are known as the “chain of infection.” Infection control measures target the various links in a ...
Board review - Viral infections
... Resolution occurs within 3-7 days of onset Transmitted by respiratory secretions, replicates in the RBC precursors in the bone marrow Can cause aplastic crisis in patients with sickle cell disease, other hemogloblinopathies, and other forms in hemolytic anemia ...
... Resolution occurs within 3-7 days of onset Transmitted by respiratory secretions, replicates in the RBC precursors in the bone marrow Can cause aplastic crisis in patients with sickle cell disease, other hemogloblinopathies, and other forms in hemolytic anemia ...
A Guide to Common Infections
... Many children infected have no signs of illness or rash. May have mild fever, sore throat, swollen glands in neck and behind the ears. Rash consists of small red spots which start on scalp and face and spread rapidly over entire body. ...
... Many children infected have no signs of illness or rash. May have mild fever, sore throat, swollen glands in neck and behind the ears. Rash consists of small red spots which start on scalp and face and spread rapidly over entire body. ...
P.Stefanowicz_Rola pielegniarki.indd
... midwife should introduce the vaccine slowly, injecting 0.1 ml of the vaccine intracutaneously into the 1/3 length of the outer upper part of the arm. If the inoculation has been done properly a whitish nodule of 5-10 mm in diameter appears and vanishes after a few minutes. The irritated skin usually ...
... midwife should introduce the vaccine slowly, injecting 0.1 ml of the vaccine intracutaneously into the 1/3 length of the outer upper part of the arm. If the inoculation has been done properly a whitish nodule of 5-10 mm in diameter appears and vanishes after a few minutes. The irritated skin usually ...
Tdap - Health and Community Services
... cause skin or ear infections, can lead to heart failure, nerve damage, or even death. 10% of people who get diphtheria will die from it. Pertussis Pertussis (whooping cough) is caused by a bacterial infection that can be spread very easily from one person to another. It causes severe coughing that i ...
... cause skin or ear infections, can lead to heart failure, nerve damage, or even death. 10% of people who get diphtheria will die from it. Pertussis Pertussis (whooping cough) is caused by a bacterial infection that can be spread very easily from one person to another. It causes severe coughing that i ...
The Causes of Acute Fever Requiring Hospitalization in Geriatric
... those of their younger counterparts, because of either the well-known diminution of activity or the suppression due to intercurrent infection or other treatment. Secondly, elderly patients may live in a different climate, preferring warmer temperatures and increased humidity. Third, their behavior ma ...
... those of their younger counterparts, because of either the well-known diminution of activity or the suppression due to intercurrent infection or other treatment. Secondly, elderly patients may live in a different climate, preferring warmer temperatures and increased humidity. Third, their behavior ma ...
Press Release
... Children should get certain vaccines when they reach certain ages, according to the recommended immunization schedule. Vaccinating children on time helps to give them the best protection possible. Prevnar® is one of the vaccines in the recommended childhood immunization schedule. This vaccine protec ...
... Children should get certain vaccines when they reach certain ages, according to the recommended immunization schedule. Vaccinating children on time helps to give them the best protection possible. Prevnar® is one of the vaccines in the recommended childhood immunization schedule. This vaccine protec ...
Case Studies in Pediatric Infectious Diseases - Assets
... There is little mention of broad-spectrum laboratory testing such as blood counts because it is my view that these seldom help in differentiating between the different diagnostic possibilities. The discussions often include noninfectious diseases, because patients do not present waving a flag that t ...
... There is little mention of broad-spectrum laboratory testing such as blood counts because it is my view that these seldom help in differentiating between the different diagnostic possibilities. The discussions often include noninfectious diseases, because patients do not present waving a flag that t ...
doc
... Soon after the identification of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) in 1983, some health officials were predicting that a vaccine would be developed within a couple of years. The search has proven to be much more difficult than anticipated, but scientists are confident that a HIV vaccine will be ...
... Soon after the identification of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) in 1983, some health officials were predicting that a vaccine would be developed within a couple of years. The search has proven to be much more difficult than anticipated, but scientists are confident that a HIV vaccine will be ...
pathophysiology of fever
... to his ideas regarding the significance of fever and implications thereof. He was known to have used heat therapy in his routine clinical practice. Fever is a common,non-specific response to various types of infectious or noninfectious stimuli (16) and has been associated with increased mortality in ...
... to his ideas regarding the significance of fever and implications thereof. He was known to have used heat therapy in his routine clinical practice. Fever is a common,non-specific response to various types of infectious or noninfectious stimuli (16) and has been associated with increased mortality in ...
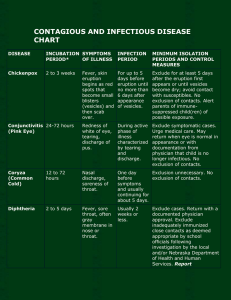
CONTAGIOUS AND INFECTIOUS DISEASE CHART
... until after the vesicles have dried. Individuals with shingles /zoster should be instructed to wash their hands if they touch the potentially infectious vesicles. ...
... until after the vesicles have dried. Individuals with shingles /zoster should be instructed to wash their hands if they touch the potentially infectious vesicles. ...
Children and Infants with Fever - Acute Management
... This policy applies to all facilities where paediatric patients are managed. It requires all Health Services to have local guidelines/protocols based on the attached clinical practice guideline in place in all hospitals and facilities likely to be required to assess or manage children with fever. Th ...
... This policy applies to all facilities where paediatric patients are managed. It requires all Health Services to have local guidelines/protocols based on the attached clinical practice guideline in place in all hospitals and facilities likely to be required to assess or manage children with fever. Th ...
Policy Directive
... This policy applies to all facilities where paediatric patients are managed. It requires all Health Services to have local guidelines/protocols based on the attached clinical practice guideline in place in all hospitals and facilities likely to be required to assess or manage children with fever. Th ...
... This policy applies to all facilities where paediatric patients are managed. It requires all Health Services to have local guidelines/protocols based on the attached clinical practice guideline in place in all hospitals and facilities likely to be required to assess or manage children with fever. Th ...
New meningitis vaccine has desired impact in sub
... a contiguous block of immunized populations across the heart of the meningitis belt. Counting those vaccinated during the December 2010 campaigns, nearly 65 million people are expected to have received the MenAfriVac vaccine by the end of the year. Experts from PATH, WHO, and partner organizations a ...
... a contiguous block of immunized populations across the heart of the meningitis belt. Counting those vaccinated during the December 2010 campaigns, nearly 65 million people are expected to have received the MenAfriVac vaccine by the end of the year. Experts from PATH, WHO, and partner organizations a ...
Approach to the Adult Patient with Fever of Unknown Origin
... more invasive or expensive. These preliminary investigations should include a complete blood count, liver function test, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, urinalysis, and basic cultures. Simple clues found during initial testing often will guide the clinician toward one of the major subgroups of FUO. ...
... more invasive or expensive. These preliminary investigations should include a complete blood count, liver function test, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, urinalysis, and basic cultures. Simple clues found during initial testing often will guide the clinician toward one of the major subgroups of FUO. ...
Quinox®
... abdominal infections, typhoid fever, bone and joint infections, skin and skin structure infections, lower respiratory infections, urinary tract infection, urethral and cervical gonococcal infections, chronic bacterial prostatitis, acute sinusitis. DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATIONS The dosage of ciprofloxac ...
... abdominal infections, typhoid fever, bone and joint infections, skin and skin structure infections, lower respiratory infections, urinary tract infection, urethral and cervical gonococcal infections, chronic bacterial prostatitis, acute sinusitis. DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATIONS The dosage of ciprofloxac ...
Revised: May 2014 AN: 00161/2014 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT
... vaccination and challenge experiment, but experience from use in the field suggests that the actual duration of immunity may be 3 – 4 months. 4.3. Contraindications Do not use in unhealthy chickens. ...
... vaccination and challenge experiment, but experience from use in the field suggests that the actual duration of immunity may be 3 – 4 months. 4.3. Contraindications Do not use in unhealthy chickens. ...
Acute Infection Guideline Summary
... particularly those at high risk – teachers, day care and healthcare workers. Persons with exposure to infants (parents, child care workers or family members) should be vaccinated and tested if they have symptoms. Vaccination per ACIP recommendations is highly encouraged to prevent outbreaks. All pre ...
... particularly those at high risk – teachers, day care and healthcare workers. Persons with exposure to infants (parents, child care workers or family members) should be vaccinated and tested if they have symptoms. Vaccination per ACIP recommendations is highly encouraged to prevent outbreaks. All pre ...
Non-infectious fever in the neurological intensive
... vasospasm induced damage on the hypothalamus and related structures.13 This study has several limitations. We did not include parameters of severity of acute systemic illness in our analysis; however, it is unlikely that including these parameters would have modified our main results. The effects of ...
... vasospasm induced damage on the hypothalamus and related structures.13 This study has several limitations. We did not include parameters of severity of acute systemic illness in our analysis; however, it is unlikely that including these parameters would have modified our main results. The effects of ...
Typhoid fever

Typhoid fever, also known simply as typhoid, is a symptomatic bacterial infection due to Salmonella typhi. Symptoms may vary from mild to severe and usually begin six to thirty days after exposure. Often there is a gradual onset of a high fever over several days. Weakness, abdominal pain, constipation, and headaches also commonly occur. Diarrhea and vomiting are uncommon. Some people develop a skin rash with rose colored spots. In severe cases there may be confusion. Without treatment symptoms may last weeks or months. Other people may carry the bacterium without being affected; however, they are still able to spread the disease to others. Typhoid fever is a type of enteric fever along with paratyphoid fever.The cause is the bacterium Salmonella typhi, also known as Salmonella enterica serotype typhi, growing in the intestines and blood. Typhoid is spread by eating or drinking food or water contaminated with the feces of an infected person. Risk factors include poor sanitation and poor hygiene. Those who travel to the developing world are also at risk. Humans are the only animal infected. Diagnosis is by either culturing the bacteria or detecting the bacterium's DNA in the blood, stool, or bone marrow. Culturing the bacterium can be difficult. Bone marrow testing is the most accurate. Symptoms are similar to that of many other infectious diseases. Typhus is a different disease.A typhoid vaccine can prevent about 50% to 70% of cases. The vaccine may be effective for up to seven years. It is recommended for those at high risk or people traveling to areas where the disease is common. Other efforts to prevent the disease include providing clean drinking water, better sanitation, and better handwashing. Until it has been confirmed that an individual's infection is cleared, the individual should not prepare food for others. Treatment of disease is with antibiotics such as azithromycin, fluoroquinolones or third generation cephalosporins. Resistance to these antibiotics has been developing, which has made treatment of the disease more difficult.In 2010 there were 27 million cases reported. The disease is most common in India, and children are most commonly affected. Rates of disease decreased in the developed world in the 1940s as a result of improved sanitation and use of antibiotics to treat the disease. About 400 cases are reported and the disease is estimated to occur in about 6,000 people per year in the United States. In 2013 it resulted in about 161,000 deaths – down from 181,000 in 1990 (about 0.3% of the global total). The risk of death may be as high as 25% without treatment, while with treatment it is between 1 and 4%. The name typhoid means ""resembling typhus"" due to the similarity in symptoms.