Exclusion of Enteric Cases and their Contacts from High Risk Settings
... Exclusion and microbiological clearance of confirmed cases and symptomatic or asymptomatic contacts of confirmed cases of enteric infections due to common causes other than those mentioned above (e.g. Salmonella nonTyphi/Paratyphi, Campylobacter, Norovirus, Giardia) can be managed as per probable ca ...
... Exclusion and microbiological clearance of confirmed cases and symptomatic or asymptomatic contacts of confirmed cases of enteric infections due to common causes other than those mentioned above (e.g. Salmonella nonTyphi/Paratyphi, Campylobacter, Norovirus, Giardia) can be managed as per probable ca ...
Disease Control Day Care Manual - Jefferson County Department of
... The close, long-term contact that occurs in day care centers makes it essential that certain cleaning and disinfection techniques be followed by those working in the day care setting. Following these techniques will decrease the chance of spreading the harmful germs that may cause illness in childre ...
... The close, long-term contact that occurs in day care centers makes it essential that certain cleaning and disinfection techniques be followed by those working in the day care setting. Following these techniques will decrease the chance of spreading the harmful germs that may cause illness in childre ...
Public Health IS a National Security Issue!
... • Rift Valley Fever • West Nile Encephalitis • Tuberculosis (Multiresistant ...
... • Rift Valley Fever • West Nile Encephalitis • Tuberculosis (Multiresistant ...
Adolescent Vaccination: Protecting Adolescents Now and Into the
... Pertussis is substantially underreported,13 but some estimates range from 1 million to over 3 million cases per year.14,15 Whether cases in adolescents are subclinical, of minor clinical importance, or more severe, infected adolescents may serve as an important reservoir of infection for neonates an ...
... Pertussis is substantially underreported,13 but some estimates range from 1 million to over 3 million cases per year.14,15 Whether cases in adolescents are subclinical, of minor clinical importance, or more severe, infected adolescents may serve as an important reservoir of infection for neonates an ...
2014 Annual Summary of Reportable Infectious Diseases for
... Cryptosporidium parvum, protozoan parasites that produce oocysts. The oocysts are highly infective for humans and most animals. The oocysts are also resistant to chlorine and other disinfectants. Mode of Transmission: Fecal-oral route, including person-to-person, animal-to-person, waterborne and foo ...
... Cryptosporidium parvum, protozoan parasites that produce oocysts. The oocysts are highly infective for humans and most animals. The oocysts are also resistant to chlorine and other disinfectants. Mode of Transmission: Fecal-oral route, including person-to-person, animal-to-person, waterborne and foo ...
Vaccine Epidemiology - Hospital Industry Data Institute
... vaccination. A monovalent rotavirus vaccine is also licensed for use in the United States [2, 3] but was not available during the study period. The Curns et al [6] study is timely and important and also highlights the distinction between the epidemiologic concepts of vaccine efficacy and vaccine eff ...
... vaccination. A monovalent rotavirus vaccine is also licensed for use in the United States [2, 3] but was not available during the study period. The Curns et al [6] study is timely and important and also highlights the distinction between the epidemiologic concepts of vaccine efficacy and vaccine eff ...
Meningitis Fact Sheet
... Haemophilus influenzae (Hib) vaccine is usually given at 2, 4, 6 and between 12 and 15 months of age. The total number of doses depends on the age at which the series was begun. Children over 5 years of age usually do not need this vaccine. But, some older children or adults with special health cond ...
... Haemophilus influenzae (Hib) vaccine is usually given at 2, 4, 6 and between 12 and 15 months of age. The total number of doses depends on the age at which the series was begun. Children over 5 years of age usually do not need this vaccine. But, some older children or adults with special health cond ...
Strep Throat - Ennis Pediatrics
... In most cases, doctors prescribe about 10 days of antibiotic medication to treat strep throat. Within about 24 hours after starting on antibiotics, your child will probably no longer have a fever and won't be contagious. By the second or third day after taking antibiotics, the other symptoms should ...
... In most cases, doctors prescribe about 10 days of antibiotic medication to treat strep throat. Within about 24 hours after starting on antibiotics, your child will probably no longer have a fever and won't be contagious. By the second or third day after taking antibiotics, the other symptoms should ...
1.0 Introduction Integrated Disease Surveillance Project (IDSP) is a
... collection, analysis and dissemination linked to public health programs (CDC 1988). Surveillance is the backbone of public health programme and provides information so that effective action can be taken in controlling and preventing diseases of public health importance. In some cases action must be ...
... collection, analysis and dissemination linked to public health programs (CDC 1988). Surveillance is the backbone of public health programme and provides information so that effective action can be taken in controlling and preventing diseases of public health importance. In some cases action must be ...
OzFoodNet 2016, 1st quarterly report (Word 1.3 MB)
... It has been estimated that there are 5.4 million cases of foodborne illness in Australia each year at a cost of $1.2 billion per year1. This is likely to be an underestimate of the total burden of gastrointestinal illness as not all enteric infections are caused by foodborne transmission. Other impo ...
... It has been estimated that there are 5.4 million cases of foodborne illness in Australia each year at a cost of $1.2 billion per year1. This is likely to be an underestimate of the total burden of gastrointestinal illness as not all enteric infections are caused by foodborne transmission. Other impo ...
Symptoms - alunsfordkhs
... • How it’s contracted: • Spread by body fluids (both sexual fluids and urine) • Airborne transmission is very rare, but has been reported • Spread quickly among dogs that are kept in closely confined areas especially during breeding times and when abortions occur ...
... • How it’s contracted: • Spread by body fluids (both sexual fluids and urine) • Airborne transmission is very rare, but has been reported • Spread quickly among dogs that are kept in closely confined areas especially during breeding times and when abortions occur ...
THE GLOBAL THREAT OF EMERGENT/REEMERGENT VECTOR
... At the beginning of the 20th century, epidemic vector-borne diseases were among the most important global public health problems (Gubler, 1998, 2002a). Diseases such as yellow fever (YF), dengue fever (DF), plague, louse-borne Typhus, malaria, etc., caused explosive epidemics affecting thousands of ...
... At the beginning of the 20th century, epidemic vector-borne diseases were among the most important global public health problems (Gubler, 1998, 2002a). Diseases such as yellow fever (YF), dengue fever (DF), plague, louse-borne Typhus, malaria, etc., caused explosive epidemics affecting thousands of ...
Facts About Chickenpox and Shingles for Adults
... Chickenpox can be prevented by vaccination. Children who have never had chickenpox should get two doses of chickenpox vaccine, with the 1st dose administered at 12 – 15 months of age and the 2nd at 4-6 years of age. Two doses, administered 4-8 weeks apart, are also recommended for people 13 years of ...
... Chickenpox can be prevented by vaccination. Children who have never had chickenpox should get two doses of chickenpox vaccine, with the 1st dose administered at 12 – 15 months of age and the 2nd at 4-6 years of age. Two doses, administered 4-8 weeks apart, are also recommended for people 13 years of ...
PREVALENCE OF RELATIVE BRADYCARDIA IN ORIENTIA
... heart rate increase in response to microbial invasion or exogenously administered, noninfectious pyrogens ranges from 10 to 18 beats/minute/1°C increase in temperature, although there is considerable individual variation.1,3−6 Relative bradycardia, an unexpectedly low heart rate response for a given ...
... heart rate increase in response to microbial invasion or exogenously administered, noninfectious pyrogens ranges from 10 to 18 beats/minute/1°C increase in temperature, although there is considerable individual variation.1,3−6 Relative bradycardia, an unexpectedly low heart rate response for a given ...
Immunization for the Elderly - Sarasota Memorial Health Care System
... malaise, myalgia, and headache) are rare among vaccinated older adults. Immediate, presumably allergic, reactions (eg, hives, angioedema, allergic asthma, and systemic anaphylaxis) rarely occur after influenza vaccination. These reactions probably result from hypersensitivity to residual egg protein ...
... malaise, myalgia, and headache) are rare among vaccinated older adults. Immediate, presumably allergic, reactions (eg, hives, angioedema, allergic asthma, and systemic anaphylaxis) rarely occur after influenza vaccination. These reactions probably result from hypersensitivity to residual egg protein ...
A guide to vaccinations at three years and four months of age
... continue to be immunised, the diseases will come back, as seen with the recent high numbers of measles and mumps cases. The diseases are still around in Europe and other parts of the world and, as people travel more, and more people come to visit this country, there is always a risk that the disease ...
... continue to be immunised, the diseases will come back, as seen with the recent high numbers of measles and mumps cases. The diseases are still around in Europe and other parts of the world and, as people travel more, and more people come to visit this country, there is always a risk that the disease ...
What is plague? Plague is an infection caused by bacteria called
... How do people get infected with plague? The most common route of infection for humans is through a bite by a rat flea infected with the disease. People can also get infected through direct contact with infected bodily fluids or tissues whist handling a sick or dead animal that was infected with plag ...
... How do people get infected with plague? The most common route of infection for humans is through a bite by a rat flea infected with the disease. People can also get infected through direct contact with infected bodily fluids or tissues whist handling a sick or dead animal that was infected with plag ...
Chickenpox - Branch-Hillsdale-St. Joseph Community Health Agency
... way to prevent chickenpox. Vaccination not only protects vaccinated persons, it also reduces the risk for exposure in the community for persons unable to be vaccinated because of illness or other conditions, including those who may be at greater risk for severe disease. While no vaccine is 100% effe ...
... way to prevent chickenpox. Vaccination not only protects vaccinated persons, it also reduces the risk for exposure in the community for persons unable to be vaccinated because of illness or other conditions, including those who may be at greater risk for severe disease. While no vaccine is 100% effe ...
Effects of Specific Vaccines
... Vaccination, Social Violence, and Criminality,28concludes otherwise.29 Regarding infectious diseases of the past, he states, “The incidence of all of these infectious diseases was dropping very rapidly, starting in the 1930s. After World War II, the incidence continued to drop as living conditions i ...
... Vaccination, Social Violence, and Criminality,28concludes otherwise.29 Regarding infectious diseases of the past, he states, “The incidence of all of these infectious diseases was dropping very rapidly, starting in the 1930s. After World War II, the incidence continued to drop as living conditions i ...
Study Session 3 Bacterial Vaccine
... Before we can tell you about the vaccine-preventable diseases, you need to understand what is meant by a vaccine. Vaccines are medical products prepared from whole or parts of bacteria, viruses, or the toxins (poisonous substances) that some bacteria produce. The contents of the vaccine have first b ...
... Before we can tell you about the vaccine-preventable diseases, you need to understand what is meant by a vaccine. Vaccines are medical products prepared from whole or parts of bacteria, viruses, or the toxins (poisonous substances) that some bacteria produce. The contents of the vaccine have first b ...
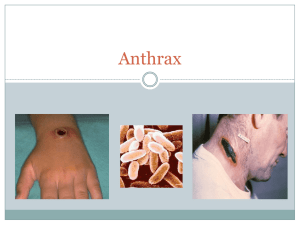
Anthrax
... Begins with fever, malaise, headache, cough, shortness of breath, and chest pain Fever and shock may occur later ...
... Begins with fever, malaise, headache, cough, shortness of breath, and chest pain Fever and shock may occur later ...
Volume VIII, Number 1 - Sabin Vaccine Institute
... To protect them, we put them in child safety seats and install childproof door latches. One of the most important ways we protect our children is to follow the childhood immunization schedule and get them vaccinated against serious but preventable diseases. Vaccines are one of medicine’s greatest tr ...
... To protect them, we put them in child safety seats and install childproof door latches. One of the most important ways we protect our children is to follow the childhood immunization schedule and get them vaccinated against serious but preventable diseases. Vaccines are one of medicine’s greatest tr ...
Infanrix
... Diphtheria and Tetanus Toxoids and Acellular Pertussis (DTaP) vaccines from different manufacturers for successive doses of the DTaP vaccination series. Because the pertussis antigen components of INFANRIX and PEDIARIX® [Diphtheria and Tetanus Toxoids and Acellular Pertussis Adsorbed, Hepatitis B (R ...
... Diphtheria and Tetanus Toxoids and Acellular Pertussis (DTaP) vaccines from different manufacturers for successive doses of the DTaP vaccination series. Because the pertussis antigen components of INFANRIX and PEDIARIX® [Diphtheria and Tetanus Toxoids and Acellular Pertussis Adsorbed, Hepatitis B (R ...
Typhoid fever

Typhoid fever, also known simply as typhoid, is a symptomatic bacterial infection due to Salmonella typhi. Symptoms may vary from mild to severe and usually begin six to thirty days after exposure. Often there is a gradual onset of a high fever over several days. Weakness, abdominal pain, constipation, and headaches also commonly occur. Diarrhea and vomiting are uncommon. Some people develop a skin rash with rose colored spots. In severe cases there may be confusion. Without treatment symptoms may last weeks or months. Other people may carry the bacterium without being affected; however, they are still able to spread the disease to others. Typhoid fever is a type of enteric fever along with paratyphoid fever.The cause is the bacterium Salmonella typhi, also known as Salmonella enterica serotype typhi, growing in the intestines and blood. Typhoid is spread by eating or drinking food or water contaminated with the feces of an infected person. Risk factors include poor sanitation and poor hygiene. Those who travel to the developing world are also at risk. Humans are the only animal infected. Diagnosis is by either culturing the bacteria or detecting the bacterium's DNA in the blood, stool, or bone marrow. Culturing the bacterium can be difficult. Bone marrow testing is the most accurate. Symptoms are similar to that of many other infectious diseases. Typhus is a different disease.A typhoid vaccine can prevent about 50% to 70% of cases. The vaccine may be effective for up to seven years. It is recommended for those at high risk or people traveling to areas where the disease is common. Other efforts to prevent the disease include providing clean drinking water, better sanitation, and better handwashing. Until it has been confirmed that an individual's infection is cleared, the individual should not prepare food for others. Treatment of disease is with antibiotics such as azithromycin, fluoroquinolones or third generation cephalosporins. Resistance to these antibiotics has been developing, which has made treatment of the disease more difficult.In 2010 there were 27 million cases reported. The disease is most common in India, and children are most commonly affected. Rates of disease decreased in the developed world in the 1940s as a result of improved sanitation and use of antibiotics to treat the disease. About 400 cases are reported and the disease is estimated to occur in about 6,000 people per year in the United States. In 2013 it resulted in about 161,000 deaths – down from 181,000 in 1990 (about 0.3% of the global total). The risk of death may be as high as 25% without treatment, while with treatment it is between 1 and 4%. The name typhoid means ""resembling typhus"" due to the similarity in symptoms.