Practice Quiz
... Previous material – H atom, laser, blackbody radiation New material – QM wavefunction Physics 274 ...
... Previous material – H atom, laser, blackbody radiation New material – QM wavefunction Physics 274 ...
From Classical to Quantum Mechanics Chapter 12
... the center, with a negatively charged electron cloud around it (Rutherford) – The nuclear atom. The electrical attraction between the proton and the electron (centrifugal force) keeps the nucleus and the electrons in the atom ‘together’. However classical physics predicts, because the moving/ orbiti ...
... the center, with a negatively charged electron cloud around it (Rutherford) – The nuclear atom. The electrical attraction between the proton and the electron (centrifugal force) keeps the nucleus and the electrons in the atom ‘together’. However classical physics predicts, because the moving/ orbiti ...
o Atomic Number = Protons = Electrons o Mass – Atomic Number
... o The overall charge of a stable atom is zero because the number of protons and electrons are equal (Always assume the number of protons and electrons are equal unless you are told differently!). o The charge of an atom’s nucleus is always positive due to the protons it contains (Carbon’s nucleus ha ...
... o The overall charge of a stable atom is zero because the number of protons and electrons are equal (Always assume the number of protons and electrons are equal unless you are told differently!). o The charge of an atom’s nucleus is always positive due to the protons it contains (Carbon’s nucleus ha ...
chapter40
... Multiple waves are superimposed so that one of its crests is at x = 0 The result is that all the waves add constructively at x=0 There is destructive interference at every point except x = 0 The small region of constructive interference is called a wave packet ...
... Multiple waves are superimposed so that one of its crests is at x = 0 The result is that all the waves add constructively at x=0 There is destructive interference at every point except x = 0 The small region of constructive interference is called a wave packet ...
Chapter 4 Powerpoint
... energy, those further out are higher in energy. 3.) When energy is absorbed by the atom, the electron moves into a higher energy orbit. This energy is released when the electron falls back to a lower energy orbit. A photon of light is emitted. ...
... energy, those further out are higher in energy. 3.) When energy is absorbed by the atom, the electron moves into a higher energy orbit. This energy is released when the electron falls back to a lower energy orbit. A photon of light is emitted. ...
Chemical and Molecular Formulas PPT
... A: Letters of the alphabet can be combined in many different ways to form words, the atoms of 2 or more elements can also be combined in different ways to form more than one type of compound • consider elements A&B: AB, A2B2, AB2 … • what does the subscript 2 represent in the chemical formula, H2O? ...
... A: Letters of the alphabet can be combined in many different ways to form words, the atoms of 2 or more elements can also be combined in different ways to form more than one type of compound • consider elements A&B: AB, A2B2, AB2 … • what does the subscript 2 represent in the chemical formula, H2O? ...
ppt - UCSC Bayesian Data Analysis Workshop
... – run the forward simulation a very large number of times, keeping those runs which triggered the same detectors that were triggered in the event we are analysing – compute the mean, variance etc of the photon direction and energy from the runs that are retained – clearly this is computationally inf ...
... – run the forward simulation a very large number of times, keeping those runs which triggered the same detectors that were triggered in the event we are analysing – compute the mean, variance etc of the photon direction and energy from the runs that are retained – clearly this is computationally inf ...
Chapter 3
... thus experience a lower Zeff. (2%) (b) False. The 2p-electrons experience a lower Zeff, because they do not penetrate to the nucleus as the 2s-electrons do. (2%) (c) Because the electrons are in the same orbital, they must have opposite spin quantum number ms (The Pauli exclusion principle). (2%) (d ...
... thus experience a lower Zeff. (2%) (b) False. The 2p-electrons experience a lower Zeff, because they do not penetrate to the nucleus as the 2s-electrons do. (2%) (c) Because the electrons are in the same orbital, they must have opposite spin quantum number ms (The Pauli exclusion principle). (2%) (d ...
N - MPS
... N is the number of collisions between Sun and Earth orbit. • Since in fast wind N < 1, Coulomb collisions require kinetic treatment! • Yet, only a few collisions (N 1) remove extreme anisotropies! • Slow wind: N > 5 about 10%, N > 1 about 30-40% of the time. ...
... N is the number of collisions between Sun and Earth orbit. • Since in fast wind N < 1, Coulomb collisions require kinetic treatment! • Yet, only a few collisions (N 1) remove extreme anisotropies! • Slow wind: N > 5 about 10%, N > 1 about 30-40% of the time. ...
Modern Model of the Atom Student Notes and Assignment
... 2. PAULI EXCLUSION PRINCIPLE - an atomic orbital may hold at most two electrons. Each must have an opposite spin. 3. HUND’S RULE - when electrons occupy orbitals of equal energy one electron enters each orbital until all the orbitals contain one electron with parallel spins before filling the orbita ...
... 2. PAULI EXCLUSION PRINCIPLE - an atomic orbital may hold at most two electrons. Each must have an opposite spin. 3. HUND’S RULE - when electrons occupy orbitals of equal energy one electron enters each orbital until all the orbitals contain one electron with parallel spins before filling the orbita ...
Chem 2 AP Ch 7 MC Review Key
... B) No, fluorescent materials only emit purple and green visible light. C) Yes, fluorescent materials emit a broad spectrum of light. D) Yes, after storing enough visible light energy, the fluorescent material can emit ultraviolet light. ...
... B) No, fluorescent materials only emit purple and green visible light. C) Yes, fluorescent materials emit a broad spectrum of light. D) Yes, after storing enough visible light energy, the fluorescent material can emit ultraviolet light. ...
ppt - SLAC
... the cold electrons associated with the bulk motion of the jet • If Gjet = 10, the ~10 eV H Lya photons should appear bulk-upscattered to 102 x 10 eV ~ E > 1 keV (E is higher for “hotter” internal electrons) • X-ray flare should precede the g-ray flare (form a “precursor”) • X-ray monitoring concurre ...
... the cold electrons associated with the bulk motion of the jet • If Gjet = 10, the ~10 eV H Lya photons should appear bulk-upscattered to 102 x 10 eV ~ E > 1 keV (E is higher for “hotter” internal electrons) • X-ray flare should precede the g-ray flare (form a “precursor”) • X-ray monitoring concurre ...
Types of radiation
... detectors, TV’s and computers) Even the potassium in bananas is radioactive. ...
... detectors, TV’s and computers) Even the potassium in bananas is radioactive. ...
N 2
... with another atom or absorption of high-energy radiation). It then decays to E3, then to E2, and finally to the ground state E1. Let us assume that the time it takes to decay from E4 to E3 is much longer than the time it takes to decay from E2 to E1. In a large population of such atoms, at equilibri ...
... with another atom or absorption of high-energy radiation). It then decays to E3, then to E2, and finally to the ground state E1. Let us assume that the time it takes to decay from E4 to E3 is much longer than the time it takes to decay from E2 to E1. In a large population of such atoms, at equilibri ...
Calculating Empirical and Molecular Formulas
... • What if a percent composition is given. How do we find the empirical formula? • Example: Chemical analysis of a liquid shows that it is 60.00% C, 13.40% H, and 26.60% O by mass. Calculate the empirical formula of this substance. – Step 1: Convert to grams • Assume you have a 100.00 g sample, and c ...
... • What if a percent composition is given. How do we find the empirical formula? • Example: Chemical analysis of a liquid shows that it is 60.00% C, 13.40% H, and 26.60% O by mass. Calculate the empirical formula of this substance. – Step 1: Convert to grams • Assume you have a 100.00 g sample, and c ...
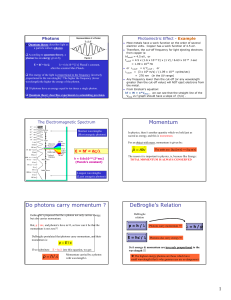
Momentum Do photons carry momentum ? DeBroglie`s Relation
... or cutoff = c/ fcutoff , or cutoff = (3 x 108 m/s) / (1.09 x 1015 cycles/sec) = 276 nm (in the UV range) Any frequency lower than the cut-off (or any wavelength greater than the cut-off value) will NOT eject electrons from the metal. From Einstein’s equation: hf = W + e*Vstop , we can see that ...
... or cutoff = c/ fcutoff , or cutoff = (3 x 108 m/s) / (1.09 x 1015 cycles/sec) = 276 nm (in the UV range) Any frequency lower than the cut-off (or any wavelength greater than the cut-off value) will NOT eject electrons from the metal. From Einstein’s equation: hf = W + e*Vstop , we can see that ...
The Exam 2 Solutions are also available now.
... Show, using “spin arrows” (↑ and/or ↓), the valence electron configuration of Co in this ion. 3d 4s ...
... Show, using “spin arrows” (↑ and/or ↓), the valence electron configuration of Co in this ion. 3d 4s ...
Chemistry Fall Final Review 2012-2013 Alchemy Unit
... 1. Using the periodic table, where are the metals and nonmetals? What is hydrogen? Metals are in the left side of the periodic table. Nonmetals are on the right side of the periodic table. Hydrogen is an nonmetal. 2. Where are the alkali, alkaline earth, transition metals, halogens, and noble gases? ...
... 1. Using the periodic table, where are the metals and nonmetals? What is hydrogen? Metals are in the left side of the periodic table. Nonmetals are on the right side of the periodic table. Hydrogen is an nonmetal. 2. Where are the alkali, alkaline earth, transition metals, halogens, and noble gases? ...
Atomic Structure Guided Notes- Key 1. The simplest form of matter is
... b. Atoms have a nucleus that consists of protons and neutrons i. Protons- positively charged atomic particles ii. Neutrons- uncharged, “neutral” atomic particles 3. Atomic Number a. The atomic number is equal to the number of protons in the nucleus of an element b. The atomic number identifies the e ...
... b. Atoms have a nucleus that consists of protons and neutrons i. Protons- positively charged atomic particles ii. Neutrons- uncharged, “neutral” atomic particles 3. Atomic Number a. The atomic number is equal to the number of protons in the nucleus of an element b. The atomic number identifies the e ...
Problem Set 1
... be the spin up and down wave function for a single electron .(SZ is diagonal) Write down all the possible spin wave functions of the system in terms of the single particle wave function such that the wave funstions are eigenstates of the total spin and its z-component in terms of α and β. 7. The rel ...
... be the spin up and down wave function for a single electron .(SZ is diagonal) Write down all the possible spin wave functions of the system in terms of the single particle wave function such that the wave funstions are eigenstates of the total spin and its z-component in terms of α and β. 7. The rel ...
Bremsstrahlung
Bremsstrahlung (German pronunciation: [ˈbʁɛmsˌʃtʁaːlʊŋ], from bremsen ""to brake"" and Strahlung ""radiation"", i.e. ""braking radiation"" or ""deceleration radiation"") is electromagnetic radiation produced by the deceleration of a charged particle when deflected by another charged particle, typically an electron by an atomic nucleus. The moving particle loses kinetic energy, which is converted into a photon, thus satisfying the law of conservation of energy. The term is also used to refer to the process of producing the radiation. Bremsstrahlung has a continuous spectrum, which becomes more intense and whose peak intensity shifts toward higher frequencies as the change of the energy of the accelerated particles increases.Strictly speaking, braking radiation is any radiation due to the acceleration of a charged particle, which includes synchrotron radiation, cyclotron radiation, and the emission of electrons and positrons during beta decay. However, the term is frequently used in the more narrow sense of radiation from electrons (from whatever source) slowing in matter.Bremsstrahlung emitted from plasma is sometimes referred to as free/free radiation. This refers to the fact that the radiation in this case is created by charged particles that are free both before and after the deflection (acceleration) that caused the emission.