Chapter 14 - Illinois State University
... measurement that represents how far from the axis of rotation all of the object’s mass must be concentrated to create the same resistance to change in the angular motion as the object had in its original shape. ...
... measurement that represents how far from the axis of rotation all of the object’s mass must be concentrated to create the same resistance to change in the angular motion as the object had in its original shape. ...
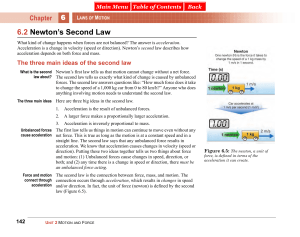
6.2 Newton`s Second Law
... What kind of change happens when forces are not balanced? The answer is acceleration. Acceleration is a change in velocity (speed or direction). Newton’s second law describes how acceleration depends on both force and mass. ...
... What kind of change happens when forces are not balanced? The answer is acceleration. Acceleration is a change in velocity (speed or direction). Newton’s second law describes how acceleration depends on both force and mass. ...
Lesson 8
... So why didn't we treat projectile motion using the concepts of centripetal and tangential acceleration? Because it makes the math harder to perform!! In Cartesian coordinates, the acceleration has only one component (vertical) and it is constant in magnitude. Thus, we can use the kinematic equations ...
... So why didn't we treat projectile motion using the concepts of centripetal and tangential acceleration? Because it makes the math harder to perform!! In Cartesian coordinates, the acceleration has only one component (vertical) and it is constant in magnitude. Thus, we can use the kinematic equations ...
Centripetal force keeps an object in circular motion.
... fictitious force, unlike gravitational, electromagnetic, and nuclear forces. Nevertheless, to observers who are in a rotating system, centrifugal force is very real. Just as gravity is ever present at Earth’s surface, centrifugal force is ever present within a rotating system. ...
... fictitious force, unlike gravitational, electromagnetic, and nuclear forces. Nevertheless, to observers who are in a rotating system, centrifugal force is very real. Just as gravity is ever present at Earth’s surface, centrifugal force is ever present within a rotating system. ...
ME 230 Kinematics and Dynamics
... to assist in lifting heavy objects. The total lifting force required from the truck depends on the acceleration of the cabinet ...
... to assist in lifting heavy objects. The total lifting force required from the truck depends on the acceleration of the cabinet ...
Honors Physics I - Neshaminy School District
... of energy appear very different, each can be measured in a way that makes it possible to keep track of how much of one form is converted into another. Whenever the amount of energy in one place diminishes, the amount in other places or forms increases by the same amount. If no energy is transferred ...
... of energy appear very different, each can be measured in a way that makes it possible to keep track of how much of one form is converted into another. Whenever the amount of energy in one place diminishes, the amount in other places or forms increases by the same amount. If no energy is transferred ...
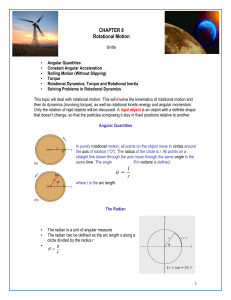
Rotational Motion - Physics In Motion
... An object traveling in a circle, even though it moves with a constant speed, will have an acceleration The centripetal acceleration is due to the change in the direction of the velocity Centripetal refers to “center-seeking” The direction of the velocity changes The acceleration is directed toward t ...
... An object traveling in a circle, even though it moves with a constant speed, will have an acceleration The centripetal acceleration is due to the change in the direction of the velocity Centripetal refers to “center-seeking” The direction of the velocity changes The acceleration is directed toward t ...
Chapter 11
... Both the magnitude and direction of the angular momentum depend on the choice of origin The magnitude is L = mvr sin f f is the angle between p and r The direction of L is perpendicular to the plane formed by r and p ...
... Both the magnitude and direction of the angular momentum depend on the choice of origin The magnitude is L = mvr sin f f is the angle between p and r The direction of L is perpendicular to the plane formed by r and p ...
Version B
... A small mass m attached to the end of a string revolves in a circle on a frictionless tabletop. The other end of the string passes through a hole in the table. Initially, the mass revolves with a speed v1 = 2.4 m/s in a circle of radius R1 = 0.80 m. The string is then pulled slowly through the hole ...
... A small mass m attached to the end of a string revolves in a circle on a frictionless tabletop. The other end of the string passes through a hole in the table. Initially, the mass revolves with a speed v1 = 2.4 m/s in a circle of radius R1 = 0.80 m. The string is then pulled slowly through the hole ...
BLACKBOARD COURSE PHYSICS 1.2. PHYS 1433
... supposed that object eventually comes to rest, so the rest is the natural state of each object. Galileo revised this concept. He introduced the concept of the frictional force and stated that when there is no this force, the motion with the constant velocity will be also natural state for each objec ...
... supposed that object eventually comes to rest, so the rest is the natural state of each object. Galileo revised this concept. He introduced the concept of the frictional force and stated that when there is no this force, the motion with the constant velocity will be also natural state for each objec ...