Files - ittip
... 14. For each case, draw the Total Force arrow. Write which direction you think the object is moving and whether it will speed up or slow down. ...
... 14. For each case, draw the Total Force arrow. Write which direction you think the object is moving and whether it will speed up or slow down. ...
doc
... cases our mind associates an axis through the body of the object. When we say “rotate” or “spin”, we must THINK change in orientation – change in angular position. We must also be cautioned to guard against our mind’s selection of axis. Consider the following question: Is a ball rolling along on a f ...
... cases our mind associates an axis through the body of the object. When we say “rotate” or “spin”, we must THINK change in orientation – change in angular position. We must also be cautioned to guard against our mind’s selection of axis. Consider the following question: Is a ball rolling along on a f ...
Mechanics II - Thierry Karsenti
... resposible factor for this impression is not the lack of information or theoretical concepts but rather the absence of clear and correct ideas about the relations between the concepts of physics. Learners often cannot say what forms the basis of a definition, what is the result of an experiment, and ...
... resposible factor for this impression is not the lack of information or theoretical concepts but rather the absence of clear and correct ideas about the relations between the concepts of physics. Learners often cannot say what forms the basis of a definition, what is the result of an experiment, and ...
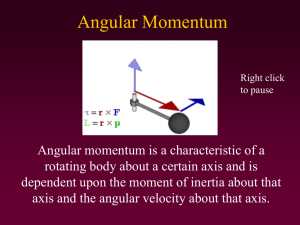
Angular Momentum
... angular momentum can be put into a system that has a high moment of inertia. • This is partly due to the force-velocity properties of human muscle. • An example would be spinning a person on a turn table with the arms outstretched as opposed to tucked in. ...
... angular momentum can be put into a system that has a high moment of inertia. • This is partly due to the force-velocity properties of human muscle. • An example would be spinning a person on a turn table with the arms outstretched as opposed to tucked in. ...
Physics 106P: Lecture 6 Notes
... line that breaks when the tension reaches 180 N. The string snaps when the acceleration of the fish is observed to be is 12.2 m/s2. What is the mass of the fish? ...
... line that breaks when the tension reaches 180 N. The string snaps when the acceleration of the fish is observed to be is 12.2 m/s2. What is the mass of the fish? ...
12.2 Newton`s First and Second Laws of Motion
... careful observation and logical reasoning. Aristotle incorrectly proposed that force is required to keep an object moving at constant speed. ...
... careful observation and logical reasoning. Aristotle incorrectly proposed that force is required to keep an object moving at constant speed. ...
Work-Kinetic Energy Theorem for Rotational Motion
... the spinning object are moving in different directions, but the object itself may be stationary. We need a new analysis system to cover items that are spinning about an axis. Rotation is the motion of an object about a fixed axis. Rotation covers everything from spinning wheels and planets, to the u ...
... the spinning object are moving in different directions, but the object itself may be stationary. We need a new analysis system to cover items that are spinning about an axis. Rotation is the motion of an object about a fixed axis. Rotation covers everything from spinning wheels and planets, to the u ...
How to enhance effectiveness of Direct Attack
... 2. The second notation is about the shifting velocity of Couple of Athletes system, normally in high competitions the shifting velocity of Couple is very low and more often Tori applies the attack with very high speed, when Uke (Defender) is stationary or proceeds slowly in right line (horizontal or ...
... 2. The second notation is about the shifting velocity of Couple of Athletes system, normally in high competitions the shifting velocity of Couple is very low and more often Tori applies the attack with very high speed, when Uke (Defender) is stationary or proceeds slowly in right line (horizontal or ...
MAE 241 –Statics Fall 2006 Jacky C. Prucz
... The motion of a particle is governed by Newton’s three laws of motion. First Law: A particle originally at rest, or moving in a straight line at constant velocity, will remain in this state if the resultant force acting on the particle is zero. Second Law: If the resultant force on the particle ...
... The motion of a particle is governed by Newton’s three laws of motion. First Law: A particle originally at rest, or moving in a straight line at constant velocity, will remain in this state if the resultant force acting on the particle is zero. Second Law: If the resultant force on the particle ...
The Genesis of the Theory of Relativity
... constancy of the velocity of light; Einstein only had to combine these two principles to derive relativity theory. As a counterpoise to this myth, there is a third, idealist account in which Einstein is supposed to have reached his theory by a philosophical criticism of fundamental concepts in the s ...
... constancy of the velocity of light; Einstein only had to combine these two principles to derive relativity theory. As a counterpoise to this myth, there is a third, idealist account in which Einstein is supposed to have reached his theory by a philosophical criticism of fundamental concepts in the s ...
KEY - Wadness
... 1. Motion and Forces Central Concept: Newton’s laws of motion and gravitation describe and predict the motion of most objects. 1.1 Compare and contrast vector quantities (e.g., displacement, velocity, acceleration force, linear momentum) and scalar quantities (e.g., distance, speed, energy, mass, wo ...
... 1. Motion and Forces Central Concept: Newton’s laws of motion and gravitation describe and predict the motion of most objects. 1.1 Compare and contrast vector quantities (e.g., displacement, velocity, acceleration force, linear momentum) and scalar quantities (e.g., distance, speed, energy, mass, wo ...
problems on mechanics 1 introduction 2 first laws — theoretical basis
... is the net torque acting on the system; here Fi stands for the The application point of contact forces is obviously the contact net force acting on the i-th point mass. In particular, the net point; in the case of body forces, the torque can be calculated by dividing the entire body (system of bodie ...
... is the net torque acting on the system; here Fi stands for the The application point of contact forces is obviously the contact net force acting on the i-th point mass. In particular, the net point; in the case of body forces, the torque can be calculated by dividing the entire body (system of bodie ...